
Lunenburg is a port town on the South Shore of Nova Scotia, Canada. Founded in 1753, the town was one of the first British attempts to settle Protestants in Nova Scotia.

Bluenose was a fishing and racing gaff rig schooner built in 1921 in Lunenburg, Nova Scotia, Canada. A celebrated racing ship and fishing vessel, Bluenose under the command of Angus Walters, became a provincial icon for Nova Scotia and an important Canadian symbol in the 1930s, serving as a working vessel until she was wrecked in 1946. Nicknamed the "Queen of the North Atlantic", she was later commemorated by the Bluenose one-design sloop (1946) and a replica, Bluenose II (1963). The name Bluenose originated as a nickname for Nova Scotians from as early as the late 18th century.

Portia May White was a Canadian contralto, known for becoming the first Black Canadian concert singer to achieve international fame. Growing up as part of her father's church choir in Halifax, Nova Scotia, White competed in local singing competitions as a teenager and later trained at the Halifax Conservatory of Music. In 1941 and 1944, she made her national and international debuts as a singer, receiving critical acclaim for her performances of both classical European music and African-American spirituals. White later completed tours throughout Europe, the Caribbean, and Central and South America.

Mary Jane Lamond is a Canadian Celtic folk musician who performs traditional Canadian Gaelic folk songs from Cape Breton Island. Her music combines traditional and contemporary material. Lamond is known as the vocalist on Ashley MacIsaac's 1995 hit single "Sleepy Maggie", and for her solo Top 40 hit "Horo Ghoid thu Nighean", the first single from her 1997 album Suas e!. Her 2012 collaboration with fiddler Wendy MacIsaac, Seinn, was named one of the top 10 folk and americana albums of 2012 by National Public Radio in the United States.

The Halifax and South Western Railway was a historic Canadian railway operating in the province of Nova Scotia.
The Portia White Prize is the largest prize of its type awarded by the Province of Nova Scotia and is named for Portia White, a Nova Scotian artist who rose through adversity to achieve international acclaim as a classical singer on the stages of Europe and North America. Although Portia White began her career teaching in Africville, she eventually turned her energy to developing her enormous musical talent. Portia White became a world-renowned contralto through much hard work and dedication and the financial support of the Nova Scotia Talent Trust, a charitable organization created in 1944 by the Halifax Ladies Music Club, the music community and the Province. Upon retiring from the stage, Ms. White devoted her time to teaching and coaching young singers. Her achievements continue to instill a sense of pride in the African Nova Scotian community and stand as a model to all Nova Scotians.

The Diocese of Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island is a diocese of the Ecclesiastical Province of Canada of the Anglican Church of Canada. It encompasses the provinces of Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island and has two cathedrals: All Saints' in Halifax and St. Peter's in Charlottetown. Its de facto see city is Halifax, and its roughly 24 400 Anglicans distributed in 239 congregations are served by approximately 153 clergy and 330 lay readers according to the last available data. According to the 2001 census, 120,315 Nova Scotians identified themselves as Anglicans, while 6525 Prince Edward Islanders did the same.

Government House of Nova Scotia is the official residence of the lieutenant governor of Nova Scotia, as well as that in Halifax of the Canadian monarch. It stands in the provincial capital at 1451 Barrington Street; unlike other provincial Government Houses in Canada, this gives Nova Scotia's royal residence a prominent urban setting, though it is still surrounded by gardens.

St. Paul's Church is an evangelical Anglican church in downtown Halifax, Nova Scotia, within the Diocese of Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island of the Anglican Church of Canada. It is located at the south end of the Grand Parade, an open square in downtown Halifax with Halifax City Hall at the northern end.
John Greer is a Canadian sculptor who likes to bring cultural and natural history together. One critic calls him one of Canada's most philosophically minded artists. He looks to ancient Celtic stones and Greek sculpture for inspiration. Greer was the catalyst behind "Halifax Sculpture," a 1990s movement, rooted in minimalism and conceptualism.

The Raid on Lunenburg occurred during the French and Indian War when Indigenous forces attacked a British settlement at Lunenburg, Nova Scotia on May 8, 1756. The indigenous forces raided two islands on the northern outskirts of the fortified Township of Lunenburg, Rous Island and Payzant Island. The raiding party killed five settlers and took five prisoners. This raid was the first of nine that the Indigenous and Acadian forces conducted against the Lunenburg peninsula over the next three-years of the war. The Indigenous forces took John Payzant and Lewis Payzant prisoner, both of whom left captivity narratives of their experiences.

The Raid on Lunenburg occurred during the American Revolution when the US privateer, Captain Noah Stoddard of Fairhaven, Massachusetts, and four other privateer vessels attacked the British settlement at Lunenburg, Nova Scotia on July 1, 1782. The raid was the last major privateer attack on a Nova Scotia community during the war.
Sylvia D. Hamilton is a Canadian filmmaker, writer, poet, and artist. Based in Nova Scotia, her work explores the lives and experiences of people of African descent. Her special focus is on African Nova Scotians, and especially women. In particular, her work takes the form of documentary films, writing, public presentations, teaching, mentoring, extensive volunteer work and community involvement. She has uncovered stories of struggles and contributions of African Canadians and introduced them to mainstream audiences. Through her work, she exposes the roots and the presence of systemic racism in Canada. She aims to provide opportunities for Black and Indigenous youth through education and empowerment.

ABCO Industries is located on the waterfront of the UNESCO World Heritage Site-designated port town of Lunenburg, Nova Scotia.

Information Morning is CBC Radio One's local morning show program for mainland Nova Scotia. It is produced out of the studios of CBHA-FM in Halifax and is simulcast on all CBC Radio One transmitters on mainland Nova Scotia.

Suzanne Lohnes-Croft is a Canadian politician, who was elected to the Nova Scotia House of Assembly in the 2013 provincial election and was re-elected in 2017. A member of the Nova Scotia Liberal Party, she represented the electoral district of Lunenburg until her defeat in the 2021 Nova Scotia general election.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Nova Scotia:
Ursula Johnson is a multidisciplinary Mi’kmaq artist based in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. Her work combines the Mi’kmaq tradition of basket weaving with sculpture, installation, and performance art. In all its manifestations her work operates as didactic intervention, seeking to both confront and educate her viewers about issues of identity, colonial history, tradition, and cultural practice. In 2017, she won the Sobey Art Award.
HMCS Lockeport was a Bangor-class minesweeper initially constructed for the Royal Navy during the Second World War. Loaned to the Royal Canadian Navy in 1942, the minesweeper saw service on both coasts of Canada as a patrol vessel and convoy escort. Returned to the Royal Navy in 1945, Lockeport was discarded in 1948.
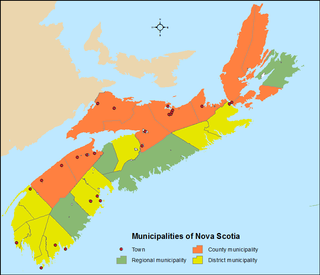
The Canadian province of Nova Scotia is divided into 49 municipalities, of which there are three types: regional (4), town (25), and county or district municipality (20).
















