
Casablanca is the largest city in Morocco and the country's economic and business centre. Located on the Atlantic coast of the Chaouia plain in the central-western part of Morocco, the city has a population of about 3.71 million in the urban area, and over 4.27 million in Greater Casablanca, making it the most populous city in the Maghreb region, and the eighth-largest in the Arab world.

Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It has a population of approximately 37 million, most of which are ethnically Arab or Berber. Islam is both the official and predominant religion, while Arabic and Berber are the official languages. Additionally, French and the Moroccan dialect of Arabic are widely spoken. The culture of Morocco consists of Arab-Islamist, Berber-Amazigh, and Saharan-Hassanic components with African, Andalusian, Hebraic and Mediterranean influences. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca.

Demographic features of the population of Morocco include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population. The population of Morocco in 2021 is 37.271 million.

Western Sahara is a disputed territory in North-western Africa. It has a surface area of 272,000 square kilometres (105,000 sq mi). Approximately 30% of the territory is controlled by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR); the remaining 70% is occupied and administered by neighboring Morocco. It is the most sparsely populated country in Africa and the second most sparsely populated country in the world, mainly consisting of desert flatlands. The population is estimated at 618,600. Nearly 40% of that population lives in Morocco-controlled Laayoune, the largest city of Western Sahara.

All data about demographic information regarding Western Sahara are extremely error-prone, regardless of source. Most countries take censuses every ten years, and some every five in order to stay abreast of change and miscounts; the last count was conducted in 1970, and even that data by colonial Spain is considered unreliable due to large nomadic populations.

Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also called by their endonym Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arabs in the Arab migrations to the Maghreb. Their main connections are identified by their usage of Berber languages, most of them mutually unintelligible, which are part of the Afroasiatic language family. They are indigenous to the Maghreb region of North Africa, where they live in scattered communities across parts of Morocco, Algeria, Libya, and to a lesser extent Tunisia, Mauritania, northern Mali and northern Niger. Smaller Berber communities are also found in Burkina Faso and Egypt's Siwa Oasis.

Rabat is the capital city of Morocco and the country's seventh-largest city with an urban population of approximately 580,000 (2014) and a metropolitan population of over 1.2 million. It is also the capital city of the Rabat-Salé-Kénitra administrative region. Rabat is located on the Atlantic Ocean at the mouth of the river Bou Regreg, opposite Salé, the city's main commuter town.

Tangier or Tangiers is a city in northwestern Morocco, on the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The city is the capital of the Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima region, as well as the Tangier-Assilah Prefecture of Morocco.

The Maghreb, also known as the Arab Maghreb and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb also includes the disputed territory of Western Sahara. As of 2018, the region had a population of over 100 million people.

Laayoune or El Aaiún is the largest city of the disputed territory named Western Sahara, with a population of 271,344 in 2023. The city is de facto under Moroccan administration as occupied territory. The modern city is thought to have been founded by the Spanish captain Antonio de Oro in 1938. From 1958, it became the administrative capital of the Spanish Sahara, administered by the Governor General of Spanish West Africa.
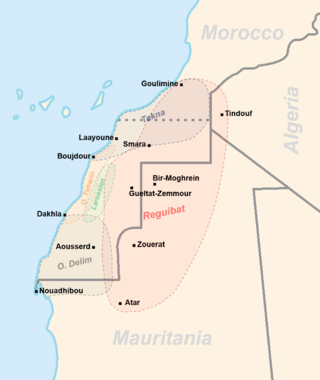
The Sahrawis, or Sahrawi people, are an ethnic group native to the western part of the Sahara desert, which includes the Western Sahara, southern Morocco, much of Mauritania, and along the southwestern border of Algeria. They are of mixed Hassani Arab and Sanhaji Berber descent, as well as West African and other indigenous populations.

Spanish Sahara, officially the Spanish Possessions in the Sahara from 1884 to 1958, then Province of the Sahara between 1958 and 1976, was the name used for the modern territory of Western Sahara when it was occupied and ruled by Spain between 1884 and 1976. It had been one of the most recent acquisitions as well as one of the last remaining holdings of the Spanish Empire, which had once extended from the Americas to the Spanish East Indies.
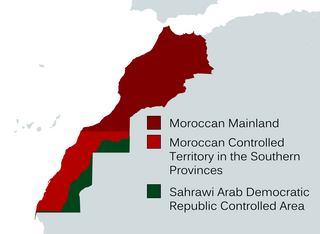
The Southern Provinces or Moroccan Sahara are the terms used by the Moroccan government to refer to the occupied territory of Western Sahara. These designations encompass the entirety of Western Sahara, which spans three of Morocco's 12 top-level administrative regions. The term "Southern Provinces" is frequently used on Moroccan state television.

Moroccans are the citizens and nationals of the Kingdom of Morocco. The country's population is predominantly composed of Arabs and Berbers (Amazigh). The term also applies more broadly to any people who are of Moroccan nationality, sharing a common culture and identity, as well as those who natively speak Moroccan Arabic or other languages of Morocco.

In Morocco, the 75 second-level administrative subdivisions are 13 prefectures and 62 provinces. They are subdivisions of the 12 regions of Morocco. Each prefecture or province is subdivided into arrondissements, municipalities or urban municipalities in other urban areas, and districts in rural areas. The districts are subdivided into rural municipalities. One prefecture (Casablanca) is also subdivided into préfectures d'arrondissements, similar to districts (cercles) except they are grouping a few arrondissements instead of rural municipalities.

Arabic, particularly the Moroccan Arabic dialect, is the most widely spoken language in Morocco, but a number of regional and foreign languages are also spoken. The official languages of Morocco are Modern Standard Arabic and Standard Moroccan Berber. Moroccan Arabic is by far the primary spoken vernacular and lingua franca, whereas Berber languages serve as vernaculars for significant portions of the country. The languages of prestige in Morocco are Arabic in its Classical and Modern Standard Forms and sometimes French, the latter of which serves as a second language for approximately 33% of Moroccans. According to a 2000–2002 survey done by Moha Ennaji, author of Multilingualism, Cultural Identity, and Education in Morocco, "there is a general agreement that Standard Arabic, Moroccan Arabic, and Berber are the national languages." Ennaji also concluded "This survey confirms the idea that multilingualism in Morocco is a vivid sociolinguistic phenomenon, which is favored by many people."

Moroccan Jews are Jews who live in or are from Morocco. Moroccan Jews constitute an ancient community dating to Roman times. Jews began immigrating to the region as early as 70 CE. They were later met by a second wave of migrants from the Iberian peninsula in the period which immediately preceded and followed the issuing of the 1492 Alhambra Decree, when Jews were expelled from Spain, and soon afterward, from Portugal. This second wave of immigrants changed Moroccan Jewry, which largely embraced the Andalusian Sephardic liturgy, to switch to a mostly Sephardic identity.
The main religion in Morocco is Sunni Islam, which is also the state religion of the country. Officially, 99% of the population are Muslim, and virtually all of those are Sunni. The second-largest religion in the country is Christianity, but most Christians in Morocco are foreigners. There is a community of the Baháʼí Faith. Only a fraction of the former number of Maghrebi Jews have remained in the country, many having moved to Israel.

The Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, also known as the Sahrawi Republic and Western Sahara, is a partially recognized state, located in the western Maghreb, which claims the non-self-governing territory of Western Sahara, but controls only the easternmost one-fifth of that territory. It is recognized by 46 UN member states and South Ossetia. Between 1884 and 1975, Western Sahara was known as Spanish Sahara, a Spanish colony. The SADR is one of the two African states in which Spanish is a significant language, the other being Equatorial Guinea.
The COVID-19 vaccination in Morocco is an ongoing immunisation campaign against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), in response to the ongoing pandemic in the country.

















