This article is about the demographic features of the population of Nicaragua, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

Indigenous peoples, also known as first peoples, aboriginal peoples or native peoples, are ethnic groups who are the original settlers of a given region, in contrast to groups that have settled, occupied or colonized the area more recently. Groups are usually described as indigenous when they maintain traditions or other aspects of an early culture that is associated with a given region. Not all indigenous peoples share this characteristic, as many have adopted substantial elements of a colonizing culture, such as dress, religion or language. Indigenous peoples may be settled in a given region (sedentary) or exhibit a nomadic lifestyle across a large territory, but they are generally historically associated with a specific territory on which they depend. Indigenous societies are found in every inhabited climate zone and continent of the world.

Mestizo is a term traditionally used in Spain, Latin America and the Philippines that originally referred to a person of combined European and Indigenous American descent, regardless of where the person was born. The term was used as an ethnic/racial category in the casta system that was in use during the Spanish Empire's control of its American and Asian colonies. Nowadays though, particularly in Spanish America, mestizo has become more of a cultural term, with culturally mainstream Latin Americans regarded or termed as mestizos regardless of their actual ancestry and with the term Indian being reserved exclusively for people who have maintained a separate indigenous ethnic identity, language, tribal affiliation, etc. Consequently, today, the vast majority of Spanish-speaking Latin Americans are regarded as mestizos.

Zambo and cafuzo are racial terms used in the Casta caste class system of the Spanish and Portuguese empires and occasionally today to identify individuals in the Americas who are of mixed African and Amerindian ancestry. Historically, the racial cross between enslaved African and Amerindians was referred to as a zambayga, then zambo, then sambo. In the United States, the word sambo is thought to refer to the racial cross between an enslaved African and a white person.

The Lotud people are an indigenous ethnic group residing in Sabah, eastern Malaysia on the island of Borneo. They reside mainly in the Tuaran District to as far as Kampung Sukoli, Telipok in the West Coast Division of Sabah. Their population was estimated at 5,000 in the year 1985 but now believed to be more than 20,000. They are a sub-ethnic group of the Dusunic group, now also known as Kadazan-Dusun.

Indigenous peoples of Colombia, or Native Colombians, are the ethnic groups who have been in Colombia prior to the Europeans in the early 16th century. Known as pueblos indígenas in Spanish, they comprise 3.4% of the country's population and belong to 87 different tribes.

The Kwere are a matrilineal ethnic and linguistic group based in the Bagamoyo District, Pwani Region of coastal Tanzania. The primary language spoken is Ngh'wele, called Kikwere in Swahili.
Russia is a multi-national state with over 186 ethnic groups designated as nationalities; the populations of these groups vary enormously, from millions to under 10,000.

The Rama are an indigenous people living on the eastern coast of Nicaragua. Since the start of European colonization, the Rama population has declined as a result of disease, conflict, and loss of territory. In recent years, however, the Rama population has increased to around 2,000 individuals. A majority of the population lives on the island of Rama Cay, which is located in the Bluefields Lagoon. Additional small Rama communities are dispersed on the mainland from Bluefields to Greytown. The Rama are one of three main indigenous groups on Nicaragua’s Caribbean coast.
The official language of Nicaragua is Spanish; however, Nicaraguans on the Caribbean coast speak indigenous languages and also English. The communities located on the Caribbean coast also have access to education in their native languages. Additionally, Nicaragua has four extinct indigenous languages.

Indigenous peoples in Ecuador, also Native Ecuadorians or Native Americans, are the groups of people who were present in what became Ecuador before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term also includes their descendants from the time of the Spanish conquest to the present. Their history, which encompasses the last 11,000 years, reaches into the present; 25 percent of Ecuador's population is of indigenous heritage, while another 70 percent is of mixed indigenous and European heritage.
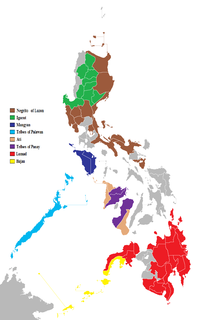
The Philippines consist of a large number of upland and lowland ethnolinguistic groups living in the country. The highland ethnic nations have co-existed with the lowland Austronesian ethnic groups for thousands of years in the Philippine archipelago. The primary difference is that they were not absorbed by centuries of Spanish and United States colonization of the Philippines, and in the process have retained their customs and traditions. This is mainly due to the rugged inaccessibility of the mountains, which discouraged Spanish and American colonizers from coming into contact with the highlanders. The indigenous peoples of northern Philippines are collectively called as Igorot, while the non-Muslim indigenous groups of mainland Mindanao are collectively called as Lumad. Numerous indigenous groups also live outside these two indigenous corridors.
Benga people are an African ethnic group, members of the Bantu group, who are indigenous to Equatorial Guinea and Gabon. Their indigenous language is Benga. Today Bengas inhabit a small coastal portion of Rio Muni, the Cape of San Juan, suburban enclaves of Rio Benito and Bata, the islands of Corisco, and both Small Elobey and Great Elobey. They are referred to as Ndowe or "Playeros", one of several peoples on the Rio Muni coast.
The Bujeba or Kwasio people are an African ethnic group, members of the Bantu group, who are indigenous to Equatorial Guinea. Their indigenous language is Bujeba. Today Bujebas inhabit Northern and Southern Bata, and South of Rio Benito. The ethnic group has decreased in number, as most have assimilated into the Fang ethnic group due to their strong influence in recent decades. They are referred to as Ndowe or "Playeros", one of several peoples on the Rio Muni coast.

Kayeli people is an ethnic group mainly living on the southern coast of the Kayeli Gulf of Indonesian island Buru, mainly from the Kaiely Gulf. From an ethnographic point of view, Kayeli are close to other indigenous people of Buru, such as Lisela and Buru.

Afro-Nicaraguans are Nicaraguans of African descent in Nicaragua. They make up 9% of the population and they're the largest group of African descent in in Central America. Numbering almost 600,000, according to the CIA factbook (2011), they primarily live on the southeastern coast, the Mosquito Coast, Bluefields and Managua. The 1990 Nicaraguan national census recorded 25,000 or 1% of the population. Creoles are from the Anglo-Caribbean and speak a dialect of Jamaican patois known as Miskito Coast Creole. Nicaragua also has a Garifuna population.
The Adjoukrou people, also known as the Adyukru, Adioukrou, Adyoukrou, Ajukru, Ajukru and the Bubari are an ethnic group and tribe of the Ivory Coast indigenous to the Dabou area of the Grands-Ponts region of the country's Lagunes District.













