
Megophryidae, commonly known as goose frogs, is a large family of frogs native to the warm southeast of Asia, from the Himalayan foothills eastwards, south to Indonesia and the Greater Sunda Islands in Maritime Southeast Asia, and extending to the Philippines. Fossil remains are also known from North America. As of 2014 it encompasses 246 species of frogs divided between five genera. For lack of a better vernacular name, they are commonly called megophryids.

Leptobrachella is a genus of frogs in the family Megophryidae. Members of Leptobrachella are found throughout Asia including on Borneo and the Natuna Islands. They are sometimes referred to as Borneo frogs, slender-armed frogs, or dwarf litter frogs. The genus contains over 82 species with 25 found in China alone.

Lufengosaurus is a genus of massospondylid dinosaur which lived during the Early Jurassic period in what is now southwestern China.
Leptobrachella alpina is a frog species in the family Megophryidae. It is endemic to Jingdong County in Yunnan, China, where it occurs in Wuliangshan National Nature Reserve; there is also a questionable record from Tianling in Guangxi.

Leptobrachella liui, also known as Fujian Asian toad or Fujian metacarpal-tubercled toad, is a frog species in the family Megophryidae. Originally described from Chong'an in Fujian, it is now known to be widely distributed in southern and southeastern China from Zhejiang and Fujian west to Guizhou and Guangxi.
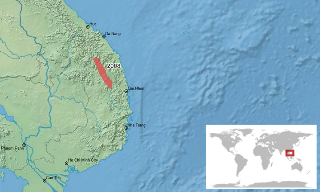
Leptobrachella tuberosa, also known as the granular toad, is a species of frog in the family Megophryidae. As currently known, it is endemic to the Central Highlands of Vietnam in Gia Lai, Quảng Nam, and Thừa Thiên–Huế Provinces. Its true range is probably wider as suitable habitat extends further north and east, reaching northeastern Cambodia and southeastern Laos. The specific name tuberosa is derived from the Latin tuberosus, meaning "full of protuberances".

Oreolalax is a genus of amphibian in the family Megophryidae. They are mostly endemic to southwestern China, with one species in northern Vietnam, and possibly extending into adjacent Laos. There is also a population in Arunachal Pradesh that has not yet been assigned to a species, although it might rather be a Scutiger.

Scutiger is a genus of toads in the family Megophryidae. Common name lazy toads has been coined for them. They occur in China, Burma, Nepal, and northern India in high-altitude habitats. Most are endemic to China.
Scutiger mammatus is a species of frog in the family Megophryidae. It is endemic to Western China and known from eastern Tibet, southeastern Qinghai, western Sichuan, and northwestern Yunnan.
Meleonoma is a genus of moths in the family Autostichidae.

Suiyang County is a county in Guizhou Province, China. It is under the jurisdiction of the prefecture-level city of Zunyi. It has an area of 2,566 square kilometers and a population of 560,000 as of 2017.

Scutiger spinosus is a species of toad in the family Megophryidae. It is found in Medog County, Tibet (China) and in Tawang district, Arunachal Pradesh (India). Prior to its description in 2016, it was confused with Scutiger nyingchiensis. Common name spiny lazy toad has been coined for it.
Leptobrachella lateralis is a species of frog in the family Megophryidae. It was first described by John Anderson (1871), who originally named it Ixalus lateralis. The holotype is lost and its exact origins are uncertain, but it was likely collected "from some portion of the surrounding region [of Bhamò]", Myanmar. It is only known with confidence from the region of its type locality and from Nagaland in Northeast India. Its range might extend into Yunnan, China. It is sometimes called Nagaland Asian toad or Nagaland leaf litter toad.

Diploderma is a genus of lizards in the family Agamidae. Species of Diploderma are native to Myanmar, China, Vietnam, Taiwan, and Japan. Most of the species are found in China, including many endemics.

Leptobrachella suiyangensis, also known as Suiyang leaf-litter toad, is a species of frog in the family Megophryidae. It is endemic to Guizhou province in southern China and so far only known from Huoqiuba Nature Reserve, its type locality in the eponymous Suiyang County.

Parvavis is a genus of enantiornithine bird, known from the upper Cretaceous of China in the Jiangdihe Formation. The type and only species, Parvavis chuxiongensis, was recovered in Luojumei Village, Chuxiong City, Yunnan Province, southern China, and it was the only known Mesozoic bird from south China at the time of its discovery. Based on its bone structure, the holotype was determined to be nearly fully grown at its time of death and would have been smaller than Iberomesornis, the smallest known enantiornithine prior to the description of Parvavis.

The Bijie leaf litter toad is a species of frog from the genus Leptobrachella. It's endemic to China and was scientifically described in 2019. It occurs in an elevation range of 1,670 to 1,750 m in wetlands and forests.

The Chishui leaf litter toad is a species of frog endemic to Eastern Asia in China. The species was described in 2020.
The Fei's leaf litter toad is a species of frog in the Leptobrachella genus. It's found in China. The species was first described in 2020.
The Jinsha leaf litter toad is a toad species that is endemic to Eastern Asia in China. Within the country, it is found in Guizhou and a couple of male specimens measured 29.7 to 31.2 mm.













