
Göttingen is a district in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Northeim and Goslar, and by the states of Thuringia and Hesse.

Osterode was a district in Lower Saxony, Germany. It was bounded by the districts of Göttingen, Northeim and Goslar, and by the state of Thuringia.

Osterode am Harz, often simply called Osterode, is a town in south-eastern Niedersachsen on the south-western edge of the Harz mountains. It was the seat of government of the district of Osterode. Osterode is located on the German Timber-Frame Road.
The placename Osterode can refer to:

Hattorf am Harz is a municipality in the district of Göttingen, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated in the southern Harz, approx. 10 km south of Osterode am Harz.

Wulften am Harz is a municipality in Lower Saxony, Germany, near the towns of Northeim and Osterode am Harz.

Söse is a river of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is a right tributary of the river Rhume and 38 kilometres (24 mi) long.

Auf dem Acker is a mountain ridge up to 865.1 metres high, which is located in the southwestern part of the Harz mountains in Lower Saxony (Germany).

The Harz Witches' Trail is a footpath, just under 100 km long, in Germany that runs from Osterode through the Harz mountains and over its highest peak, the Brocken, to Thale. It is a project by the Harz Transport Association and Harz Club and is part of the system of trails known as the Harzer Wandernadel.

The Herzberg–Seesen railway, also known as the West Harz Line, is a 32 km long railway line, that runs along the western edge of the Harz mountains and serves the town and the district of Osterode am Harz. It is the shortest link from Brunswick to Erfurt and is worked today by Lint multiples from Brunswick via Salzgitter, Seesen and Osterode to Herzberg mainly at hourly intervals. In Herzberg there are connexions to Göttingen and Nordhausen.

The B 243 runs from Hildesheim over Seesen and Herzberg am Harz to Nordhausen.

Lerbach is a small river of Lower Saxony, Germany. It flows into the Söse in Osterode am Harz.

The Alte Burg is a ruined spur castle that only comprises half a bergfried and is located in the Lower Saxon district of Osterode in the Harz Mountains of central Germany. The name means "Old Castle".

The Kloppstert is a hill, roughly 553 metres high, in the southwestern Harz in Lower Saxony, Germany. In the topographical map printed in 1978 it can only be made out with difficulty that the third letter is an o and the penultimate one an r. Unfortunately a contour line runs over the letter r so that it looks like a p. In the digitalised 1:25,000 topographic map, the hill is wrongly named as the Klappstept.
Wilhelm Kolle was a German bacteriologist and hygienist. He served as the second director of the Royal Institute for Experimental Therapy, succeeding its founder, the Nobel laureate Paul Ehrlich. He was also the original author, with Heinrich Hetsch, of the famous book Experimental Bacteriology, one of the most authoritative works in microbiology in the first half of the 20th century.
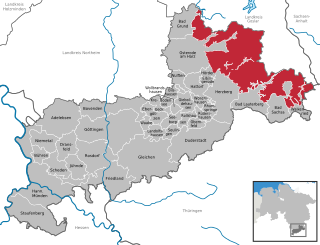
The administrative district (Verwaltungsbezirk) of Harz is an unincorporated area in the German county of Göttingen. Until the merger of the old counties of Osterode am Harz and Göttingen, it was known as "Harz ".

The Kalte Birke is a cross tracks in the Harz Mountains of Germany where there is a refuge hut and former settlement. It is located west of the Innerste Reservoir at about 540 metres above sea level. It lies in the unparished area of Harz in the county of Goslar. Historically it is closely linked to the municipality of Hahausen and village of Neuekrug, four kilometres northwest.

The Lichtenstein is a hill, 260.9 m above sea level (NHN), in the southwestern Harz Foreland. It rises near Osterode am Harz in the Lower Saxon county of Göttingen.
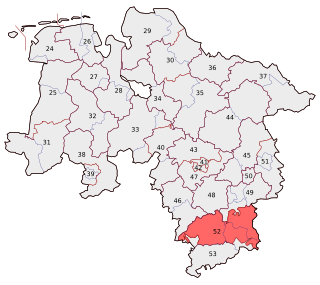
Goslar – Northeim – Osterode is an electoral constituency represented in the Bundestag. It elects one member via first-past-the-post voting. Under the current constituency numbering system, it is designated as constituency 52. It is located in southern Lower Saxony, comprising most of the districts of Goslar, Northeim, and the former Osterode.





















