Isomers
Including the stereoisomers, six further isomers could be added: D-leucine, D-isoleucine, L-alloisoleucine, D-alloisoleucine, D-tert-leucine and D-norleucine.
| Leucines | ||||
| Name | L-Leucine | L-Isoleucine | L-tert-Leucine (terleucine, pseudoleucine) | L-Norleucine |
| Other names | 2-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid, Isobutylglycine | 2-Amino-3-methylpentanoic acid, sec-Butylglycine | 2-Amino-3,3-dimethylbutanoic acid, tert-Butylglycine | 2-Amino-hexanoic acid, n-Butylglycine |
| Structure | 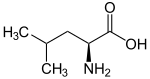 |  |  |  |
| CAS-number | 61-90-5 | 73-32-5 | 20859-02-3 | 327-57-1 |
| PubChem | CID 6106 from PubChem | CID 791 from PubChem | CID 164608 from PubChem | CID 21236 from PubChem |
| Molecular formula | C6H13NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 131.18 g/mol | |||
