
Armiński is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, to the northeast of the large walled basin Gagarin. To the northwest of Armiński is the crater Beijerinck, and to the southeast lies Cyrano.

Rost is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southwestern part of the Moon, to the southeast of the elongated formation Schiller. To the southeast of Rost is the larger crater Scheiner. West-southwest of this formation is the smaller Weigel.

Bellinsgauzen is a lunar impact crater that lies in the southern part of Moon, on the far side from the Earth. It is attached to the northern rim of the larger crater Berlage, and within a half crater diameter of Cabannes to the west. North of Bellinsgauzen is the crater Bhabha.

Breislak is a lunar impact crater that lies within one crater diameter north-northwest of the crater Baco, in the southern part of the Moon. To the north-northwest is the crater Barocius, and to the west lies Clairaut. This crater was named in honor of geologist Scipione Breislak.

Bhabha is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southern part of the Moon's far side. It is nearly attached to the southeast rim of the larger crater Bose, and the outer rampart of that crater has produced a slight inward bulge along the northwest face of Bhabha. Other nearby craters of note include Stoney to the east, and Bellinsgauzen to the south.
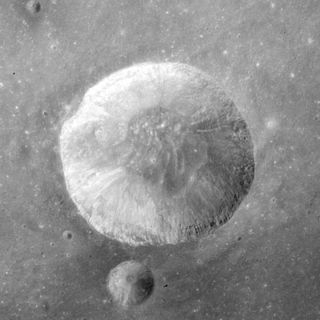
Carmichael is a lunar impact crater that is located along the eastern edge of the Sinus Amoris, in the northeastern quadrant of the Moon's near side. Its diameter is 20 km. It was named after American psychologist Leonard Carmichael. It lies within a couple of crater diameters south-southwest of the smaller crater Hill. Further to the east-northeast is the prominent crater Macrobius. Carmichael was designated Macrobius A before being given its current name by the IAU.

Helmholtz is a lunar impact crater, approximately 110 kilometers in diameter, that is located near the south-southeast limb of the Moon. Attached to the south-southeast rim of Helmholtz is the somewhat smaller crater Neumayer. The larger crater Boussingault is nearly attached to the west-southwestern rim. The crater is named after German physicist and physician Hermann von Helmholtz

Carver is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, due east of the walled plain Van der Waals. To the northeast is the crater Rosseland, and to the south-southeast lies Kozyrev.

Weinek is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the southeastern part of the Moon, to the south of the Mare Nectaris. It was named after Austro-Hungarian astronomer Ladislaus Weinek. It lies about one crater diameter to the east-northeast of the prominent Piccolomini. To the southeast is Neander.

Fraunhofer is a lunar impact crater that is located just to the south-southwest of the walled plain Furnerius, in the southeastern part of the Moon. This crater appears foreshortened when viewed from the Earth, and is actually nearly circular.

Donner is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located just to the northeast of the Mare Australe, behind the southeastern limb of the Moon. During favorable librations this part of the lunar surface can be brought into view of the Earth, but the site is viewed from the edge and so not much detail can be seen.

Dufay is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It lies about one crater diameter to the east of the large walled plain Mandel'shtam. To the northwest is the crater Papaleksi and to the east is Valier.
Eijkman is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon's southern hemisphere. It lies about a half crater diameter to the southeast of the larger crater Lemaître. To the south-southwest is the crater Crommelin, and to the northeast is Fizeau.
Foster is a small lunar impact crater that lies to the southeast of the larger crater Joule, on the far side of the Moon. The rim of Foster is slightly eroded, and the narrow inner walls slope directly down to the relatively dark interior floor. The rim has a small outward bulge along the southwest side. There is a small craterlet on the floor next to the northern rim. A tiny impact in the southeast part of the crater interior is surrounded by a small skirt of high albedo material, producing a bright patch.

Quetelet is a lunar impact crater, approximately 55 kilometers in diameter, that lies in the Moon's northern hemisphere, on the far side from the Earth. It lies to the southeast of the crater Schlesinger, and to the east of Von Zeipel. To the east of Quetelet is Perrine.

Hatanaka is a lunar impact crater that lies on the Moon's far side, just out of sight past the western limb. It lies to the west of the larger crater Leucippus, and to the northwest of the still larger satellite crater Leucippus Q. It recalls the memory of Takeo Hatanaka, a Japanese astronomer.
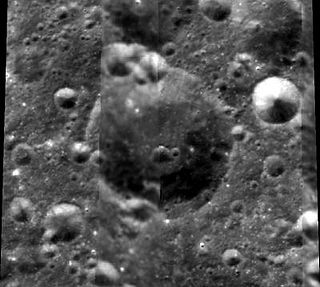
Stoletov is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located in the northern hemisphere, less than one crater diameter to the north of Kulik. To the northwest of Stoletov is Montgolfier.

Kurchatov is a lunar impact crater that is located on the Moon's far side. It is just to the southwest of the crater Wiener, and farther to the southeast of Bridgman. A couple of crater diameters to the south of Kurchatov is the northern edge of the Mare Moscoviense.

Weber is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon, and it cannot be viewed directly from the Earth's surface. This crater is attached to the northwest outer rim of the larger crater Sarton. About two crater diameters to the northwest is the eroded Kramers.

Smoluchowski is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It lies in the part of the lunar surface that is sometimes brought into view of the Earth during periods of favorable libration and illumination from sunlight, but at such times little detail can be seen as the crater is observed from the edge. Smoluchowski lies across the northern rim of the larger walled plain Poczobutt. Nearly attached to the north-northeastern outer rim of Smoluchowski is the smaller crater Paneth.


















