Related Research Articles

The euro is the official currency of 19 of the 27 member states of the European Union. This group of states is known as the eurozone or euro area, and counts about 343 million citizens as of 2019. The euro, which is divided into 100 cents, is the second-largest and second-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market after the United States dollar.

The eurozone, officially called the euro area, is a monetary union of 19 of the 27 European Union (EU) member states which have adopted the euro (€) as their common currency and sole legal tender. The monetary authority of the eurozone is the Eurosystem. The other eight members of the European Union continue to use their own national currencies, although most of them are obliged to adopt the euro in the future.
The euro convergence criteria are the criteria which European Union member states are required to meet to enter the third stage of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) and adopt the euro as their currency. The four main criteria, which actually comprise five criteria as the "fiscal criterion" consists of both a "debt criterion" and a "deficit criterion", are based on Article 140 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union.
Cypriot euro coins feature three separate designs for the three series of coins. Cyprus has been a member of the European Union since 1 May 2004, and is a member of the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union. It has completed the third stage of the EMU and adopted the euro as its official currency on 1 January 2008.
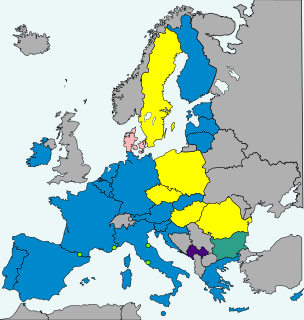
The Czech Republic is bound to adopt the euro in the future and to join the eurozone once it has satisfied the euro convergence criteria by the Treaty of Accession since it joined the European Union (EU) in 2004. The Czech Republic is therefore a candidate for the enlargement of the eurozone and it uses the Czech koruna as its currency, regulated by the Czech National Bank, a member of the European System of Central Banks, and does not participate in European Exchange Rate Mechanism II.

Poland does not use the euro as its currency. However, under the terms of their Treaty of Accession with the European Union, all new Member States "shall participate in the Economic and Monetary Union from the date of accession as a Member State with a derogation", which means that Poland is obliged to eventually replace its currency, the złoty, with the euro.

Bulgaria committed to switching its currency, the lev, to the euro upon its joining the European Union in 2007, as stated in its EU accession treaty.

Sweden does not currently use the euro as its currency and has no plans to replace the krona in the near future. Sweden's Treaty of Accession of 1994 made it subject to the Treaty of Maastricht, which obliges states to join the eurozone once they meet the necessary conditions. Sweden maintains that joining the European Exchange Rate Mechanism II, participation in which for at least two years is a requirement for euro adoption, is voluntary, and has chosen to remain outside pending public approval by a referendum, thereby intentionally avoiding the fulfilment of the adoption requirements.

The euro came into existence on 1 January 1999, although it had been a goal of the European Union (EU) and its predecessors since the 1960s. After tough negotiations, particularly due to opposition from the United Kingdom, the Maastricht Treaty entered into force in 1993 with the goal of creating an economic and monetary union by 1999 for all EU states except the UK and Denmark.

Denmark uses the krone as its currency and does not use the euro, having negotiated the right to opt out from participation under the Maastricht Treaty of 1992. In 2000, the government held a referendum on introducing the euro, which was defeated with 46.8% voting yes and 53.2% voting no. The Danish krone is part of the ERM II mechanism, so its exchange rate is tied to within 2.25% of the euro.

The enlargement of the eurozone is an ongoing process within the European Union (EU). All member states of the European Union, except Denmark which negotiated opt-outs from the provisions, are obliged to adopt the euro as their sole currency once they meet the criteria, which include: complying with the debt and deficit criteria outlined by the Stability and Growth Pact, keeping inflation and long-term governmental interest rates below certain reference values, stabilising their currency's exchange rate versus the euro by participating in the European Exchange Rate Mechanism, and ensuring that their national laws comply with the ECB statute, ESCB statute and articles 130+131 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union. The obligation for EU member states to adopt the euro was first outlined by article 109.1j of the Maastricht Treaty of 1992, which became binding on all new member states by the terms of their treaties of accession.
Eurobonds or stability bonds were proposed government bonds to be issued in euros jointly by the 19 eurozone nations. The idea was first raised by the European Commission in 2011 during the 2009–2012 European sovereign debt crisis. Eurobonds would be debt investments whereby an investor loans a certain amount of money, for a certain amount of time, with a certain interest rate, to the eurozone bloc altogether, which then forwards the money to individual governments.

The Eurogroup is the recognised collective term for informal meetings of the finance ministers of the eurozone—those member states of the European Union (EU) which have adopted the euro as their official currency. The group has 19 members. It exercises political control over the currency and related aspects of the EU's monetary union such as the Stability and Growth Pact. The current President of the Eurogroup is Mário Centeno, the Minister of Finance of Portugal.

The international status and usage of the euro has grown since its launch in 1999. When the euro formally replaced 12 currencies on 1 January 2002, it inherited their use in territories such as Montenegro and replaced minor currencies tied to the pre-euro currencies, such as in Monaco. Four small states have been given a formal right to use the euro, and to mint their own coins, but all other usage has been unofficial outside the eurozone. With or without an agreement these countries, unlike those in the eurozone, do not participate in the European Central Bank or the Eurogroup.
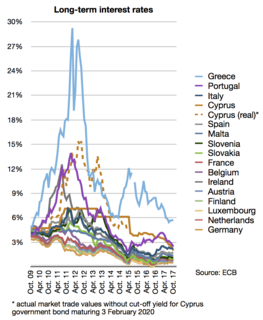
The European debt crisis is a multi-year debt crisis that has been taking place in the European Union since the end of 2009. Several eurozone member states were unable to repay or refinance their government debt or to bail out over-indebted banks under their national supervision without the assistance of third parties like other eurozone countries, the European Central Bank (ECB), or the International Monetary Fund (IMF).

The European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) is a special purpose vehicle financed by members of the eurozone to address the European sovereign-debt crisis. It was agreed by the Council of the European Union on 9 May 2010, with the objective of preserving financial stability in Europe by providing financial assistance to eurozone states in economic difficulty. The Facility's headquarters are in Luxembourg City, as are those of the European Stability Mechanism. Treasury management services and administrative support are provided to the Facility by the European Investment Bank through a service level contract. Since the establishment of the European Stability Mechanism, the activities of the EFSF are carried out by the ESM.

The EU economic governance, Sixpack describes a set of European legislative measures to reform the Stability and Growth Pact and introduces greater macroeconomic surveillance, in response to the European debt crisis of 2009. These measures were bundled into a "six pack" of regulations, tabled in September 2010 as two versions respectively by the European Commission and a European Council task force. In March 2011, the ECOFIN council reached a preliminary agreement for the content of the Sixpack with the Commission, and negotiations for endorsement by the European Parliament then started. Ultimately it entered into force 13 December 2011, after one year of preceding negotiations. The six regulations aim at strengthening the procedures to reduce public deficits and address macroeconomic imbalances.
A Greek withdrawal from the eurozone was a hypothetical scenario under which Greece would withdraw from the Eurozone to deal with the now expired Greek government-debt crisis. This conjecture has been referred to as "Grexit", a portmanteau combining the English words "Greek" and "exit", and which has been expressed in Greek as ελλέξοδος,. The term "Graccident" was coined for the case that Greece exited the EU and the euro unintentionally. These terms first came into use in 2012 and have been revitalised at each of the bailouts made available to Greece since then.

The European debt crisis is an ongoing financial crisis that has made it difficult or impossible for some countries in the euro area to repay or re-finance their government debt without the assistance of third parties.

Withdrawal from the Eurozone denotes the process whereby a Eurozone member-state, whether voluntarily or forcibly, stops using the euro as its national currency and leaves the Eurozone. As of February 2020, no country has withdrawn from the Eurozone.
References
- ↑ "Eurozone". Eurocoins. Retrieved May 20, 2012.
- ↑ Garner, Bryan A. (2001). A Dictionary of Modern Legal Usage . Oxford University Press. p. 526. ISBN 9780195142365 . Retrieved July 2, 2015.
Lex monetae.
- ↑ "Multinationals sweep euros from accounts on daily basis". Telegraph. Retrieved May 20, 2012.
- ↑ "Lex Monetae". Morgan Stanley. Archived from the original on October 23, 2017. Retrieved May 20, 2012.
| This finance-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |