Libanon Hill, United States Virgin Islands | |
|---|---|
Village | |
| Country | |
| Island | Saint Croix |
| Time zone | UTC-4 (AST) |
Libanon Hill is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands.
Libanon Hill, United States Virgin Islands | |
|---|---|
Village | |
| Country | |
| Island | Saint Croix |
| Time zone | UTC-4 (AST) |
Libanon Hill is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands.
Libanon Hill is a former sugar cane plantation. In 1856, it was acquired by Andreas Michael Dam for 25,000 dollars. Dam was the first of three brothers from the small Danish island of Christiansø who moved to St. Croix. He landed on the island in 1835 and spent many years managing the plantations Envy, Lower Love and Work and Rest. One of his younger brothers, Chrisitan Ulrik Dam, together with H, Kofoed, purchased Sprat Hall. Andreas Michael Dam died from dysentery in 1762. He had three children by two coloured women. Two of the children moved to Bornholm after the death of their father. [1]

The United States Virgin Islands, officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory of the United States. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands archipelago and are located in the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles to the east of Puerto Rico and west of the British Virgin Islands.

The Danish West Indies or Danish Antilles or Danish Virgin Islands were a Danish colony in the Caribbean, consisting of the islands of Saint Thomas with 32 square miles (83 km2); Saint John with 19 square miles (49 km2); and Saint Croix with 84 square miles (220 km2). The islands have belonged to the United States since they were purchased in 1917. Water Island was part of the Danish West Indies until 1905, when the Danish state sold it to the East Asiatic Company, a private shipping company.

Charlotte Amalie, located on St. Thomas, is the capital and the largest city of the United States Virgin Islands. It was founded in 1666 as Taphus. In 1691, the town was renamed to Charlotte Amalie after Charlotte Amalie of Hesse-Kassel (1650–1714), queen consort to King Christian V of Denmark-Norway. It has a deep-water harbor that was once a haven for pirates and is now one of the busiest ports of call for cruise ships in the Caribbean, with about 1.5 million-plus cruise ship passengers landing there annually. Protected by Hassel Island, the harbor has docking and fueling facilities, machine shops, and shipyards and was a U.S. submarine base until 1966. The Town has been inhabited for centuries. When Christopher Columbus arrived in 1493, the area was inhabited by Caribs, Arawaks, Ciboney and Taíno native peoples. It is on the southern shore at the head of Saint Thomas Harbor. In 2010 the City had a population of 18,481, which makes it the largest city in the Virgin Islands Archipelago. Hundreds of ferries and yachts pass by the Town each week.

Saint Croix is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincorporated territory of the United States.

The United States Virgin Islands, often abbreviated USVI, are a group of islands and cays located in the Lesser Antilles of the Eastern Caribbean, consisting of three main islands and fifty smaller islets and cays. Like many of their Caribbean neighbors, the history of the islands is characterized by native Amerindian settlement, European colonization, and the Atlantic slave trade.
Annaly is a settlement on the island of St. Croix in the United States Virgin Islands. It is located in the northwest of the island, to the northeast of Frederiksted.

The Dutch Virgin Islands is the collective name for the enclaves that the Dutch West India Company had in the Virgin Islands. The area was ruled by a director, whose seat was not permanent. The main reason for starting a colony here was that it lay strategically between the Dutch colonies in the south and New Netherland. The Dutch West India Company was mainly affected by the competition from Denmark, England and Spain. In 1680 the remaining islands became a British colony.
Castle Coakley is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands.
Hogensborg is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands.

La Grange is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands.
La Reine is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands.
Montpellier is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands.
Pearl is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands.
Peters Rest is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands. The settlement originally formed around a sugar plantation.
Sion Hill is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix, in the United States Virgin Islands.
Sprat Hall Beach is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands.

Whim is a settlement on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands.

The Danish slave trade occurred separately in two different periods: the trade in European slaves during the Viking Age, from the 8th to 10th century; and the Danish role in selling African slaves during the Atlantic slave trade, which commenced in 1733 and ended in 1807 when the abolition of slaves was announced. The location of the latter slave trade primarily occurred in the Danish West Indies where slaves were tasked with many different manual labour activities, primarily working on sugar plantations. The slave trade had many impacts that varied in their nature, with some more severe than others. After many years of slavery in the Danish West Indies, Christian VII decided to abolish slave trading.
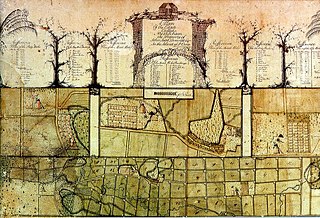
Frederik Christian von Meley was a Danish army officer, administrator, and surveyor who settled on the island of Saint Croix in the Danish West Indies. He is noted for the quality of his maps, which give valuable information on the economy and society of the island in his time.
Slob Historic District, near Christiansted, Virgin Islands, is a historic district which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1987. The listing included nine contributing buildings, three contributing structures, and a contributing site on 9 acres (3.6 ha).