
LDS-1 (Line Drawing System-1) was a calligraphic (vector, rather than raster) display processor and display device created by Evans & Sutherland in 1969. [1] This model was known as the first graphics device with a graphics processing unit. [2]

LDS-1 (Line Drawing System-1) was a calligraphic (vector, rather than raster) display processor and display device created by Evans & Sutherland in 1969. [1] This model was known as the first graphics device with a graphics processing unit. [2]

It was controlled by a variety of host computers. Straight lines were smoothly rendered in real-time animation. General principles of operation were similar to the systems used today: 4x4 transformation matrices, 1x4 vertices. Possible uses included flight simulation (in the product brochure there are screenshots of landing on a carrier), scientific imaging and GIS systems.
The first LDS-1 was shipped to the customer (BBN) in August 1969. [3] Only a few of these systems were ever built. One was used by the Los Angeles Times as their first typesetting/layout computer. One went to NASA Ames Research Center for Human Factors Research. Another was bought by the Port Authority of New York to develop a tugboat pilot trainer for navigation in the harbor. The MIT Dynamic Modeling had one, and there was a program for viewing an ongoing game of Maze War . [4] [5]

Rendering or image synthesis is the process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model by means of a computer program. The resulting image is referred to as a rendering. Multiple models can be defined in a scene file containing objects in a strictly defined language or data structure. The scene file contains geometry, viewpoint, textures, lighting, and shading information describing the virtual scene. The data contained in the scene file is then passed to a rendering program to be processed and output to a digital image or raster graphics image file. The term "rendering" is analogous to the concept of an artist's impression of a scene. The term "rendering" is also used to describe the process of calculating effects in a video editing program to produce the final video output.
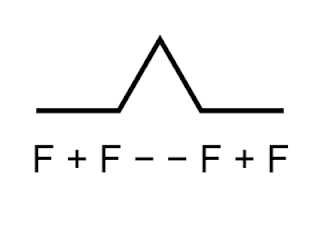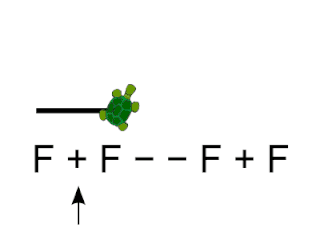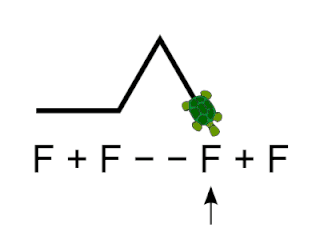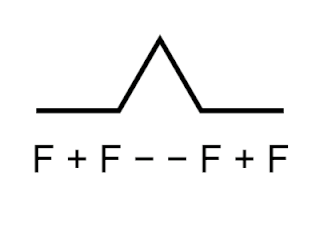
Logo is an educational programming language, designed in 1967 by Wally Feurzeig, Seymour Papert, and Cynthia Solomon. Logo is not an acronym: the name was coined by Feurzeig while he was at Bolt, Beranek and Newman, and derives from the Greek logos, meaning 'word' or 'thought'.
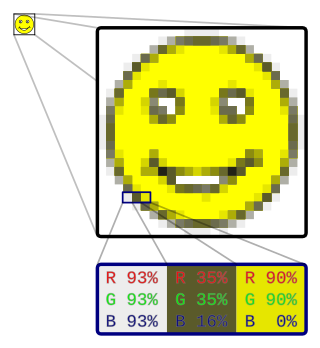
In computer graphics and digital photography, a raster graphic represents a two-dimensional picture as a rectangular matrix or grid of pixels, viewable via a computer display, paper, or other display medium. A raster image is technically characterized by the width and height of the image in pixels and by the number of bits per pixel. Raster images are stored in image files with varying dissemination, production, generation, and acquisition formats.

Vector graphics are a form of computer graphics in which visual images are created directly from geometric shapes defined on a Cartesian plane, such as points, lines, curves and polygons. The associated mechanisms may include vector display and printing hardware, vector data models and file formats, as well as the software based on these data models. Vector graphics are an alternative to raster or bitmap graphics, with each having advantages and disadvantages in specific situations.

Ivan Edward Sutherland is an American computer scientist and Internet pioneer, widely regarded as a pioneer of computer graphics. His early work in computer graphics as well as his teaching with David C. Evans in that subject at the University of Utah in the 1970s was pioneering in the field. Sutherland, Evans, and their students from that era developed several foundations of modern computer graphics. He received the Turing Award from the Association for Computing Machinery in 1988 for the invention of the Sketchpad, an early predecessor to the sort of graphical user interface that has become ubiquitous in personal computers. He is a member of the National Academy of Engineering, as well as the National Academy of Sciences among many other major awards. In 2012, he was awarded the Kyoto Prize in Advanced Technology for "pioneering achievements in the development of computer graphics and interactive interfaces".

A framebuffer is a portion of random-access memory (RAM) containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing data representing all the pixels in a complete video frame. Modern video cards contain framebuffer circuitry in their cores. This circuitry converts an in-memory bitmap into a video signal that can be displayed on a computer monitor.
Evans & Sutherland is an American computer graphics firm founded in 1968 by David Evans and Ivan Sutherland. Its current products are used in digital projection environments like planetariums. Its simulation business, which it sold to Rockwell Collins, sold products that were used primarily by the military and large industrial firms for training and simulation.

Digital painting is the creation of imagery on a computer, using pixels which are assigned a color. The process uses raster graphics rather than vector graphics, and can render graduated or blended colors in imagery which mimics traditional drawing and painting media.

The IBM 2250 Graphics Display Unit was a vector graphics display system by IBM for the System/360; the Model IV attached to the IBM 1130.

Maze, also known as Maze War, is a 3D multiplayer first-person shooter maze game originally developed in 1973 and expanded in 1974. The first version was developed by high school students Steve Colley, Greg Thompson, and Howard Palmer for the Imlac PDS-1 minicomputer during a school work/study program at the NASA Ames Research Center. By the end of 1973 the game featured shooting elements and could be played on two computers connected together. After Thompson began school at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), he brought the game to the school's computer science laboratory in February 1974, where he and Dave Lebling expanded it into an eight-player game using the school's Digital Equipment Corporation PDP-10 mainframe computer and PDS-1 terminals along with adding scoring, top-down map views, and a level editor. Other programmers at MIT improved this version of the game, which was also playable between people at different universities over the nascent ARPANET. Due to the popularity of the game, laboratory managers at MIT both played it while also trying to restrict its use due to the large amount of time students were spending on it. There are reports that the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) at one point banned the game from the ARPANET due to its popularity.

IMLAC Corporation was an American electronics company in Needham, Massachusetts, that manufactured graphical display systems, mainly the PDS-1 and PDS-4, in the late 1960s and 1970s.
Digistar is the first computer graphics-based planetarium projection and content system. It was designed by Evans & Sutherland and released in 1983. The technology originally focused on accurate and high quality display of stars, including for the first time showing stars from points of view other than Earth's surface, travelling through the stars, and accurately showing celestial bodies from different times in the past and future. Beginning with the Digistar 3 the system now projects full-dome video.

A vector monitor, vector display, or calligraphic display is a display device used for computer graphics up through the 1970s. It is a type of CRT, similar to that of an early oscilloscope. In a vector display, the image is composed of drawn lines rather than a grid of glowing pixels as in raster graphics. The electron beam follows an arbitrary path, tracing the connected sloped lines rather than following the same horizontal raster path for all images. The beam skips over dark areas of the image without visiting their points.

Pen computing refers to any computer user-interface using a pen or stylus and tablet, over input devices such as a keyboard or a mouse.

Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great deal of specialized hardware and software has been developed, with the displays of most devices being driven by computer graphics hardware. It is a vast and recently developed area of computer science. The phrase was coined in 1960 by computer graphics researchers Verne Hudson and William Fetter of Boeing. It is often abbreviated as CG, or typically in the context of film as computer generated imagery (CGI). The non-artistic aspects of computer graphics are the subject of computer science research.
The history of video games spans a period of time between the invention of the first electronic games and today, covering many inventions and developments. Video gaming reached mainstream popularity in the 1970s and 1980s, when arcade video games, gaming consoles and home computer games were introduced to the general public. Since then, video gaming has become a popular form of entertainment and a part of modern culture in most parts of the world. The early history of video games, therefore, covers the period of time between the first interactive electronic game with an electronic display in 1947, the first true video games in the early 1950s, and the rise of early arcade video games in the 1970s. During this time there was a wide range of devices and inventions corresponding with large advances in computing technology, and the actual first video game is dependent on the definition of "video game" used.

The Advanced Remote Display Station was a desktop storage-tube-based vector graphics and text terminal produced by Computer Displays, Inc. starting in 1968. It was announced at the 1968 Spring Joint Computer Conference and available by August 1968 for $12,750.
The Harvard Laboratory for Computer Graphics and Spatial Analysis pioneered early cartographic and architectural computer applications that led to integrated geographic information systems (GIS). Some of the Laboratory's influential programs included SYMAP, SYMVU, GRID, CALFORM, and POLYVRT. The Laboratory's Odyssey project created a geographic information system that served as a milestone in the development of integrated mapping systems. The Laboratory influenced numerous computer graphic, mapping and architectural systems such as Intergraph, Computervision, and Esri.

The Kahlert School of Computing is a school within the College of Engineering at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, Utah.
Computer-aided design is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. Designers have used computers for calculations since their invention. CAD software was popularized and innovated in the 1960s, although various developments were made between the mid-1940s and 1950s. Digital computers were used in power system analysis or optimization as early as proto-"Whirlwind" in 1949. Circuit design theory or power network methodology was algebraic, symbolic, and often vector-based.