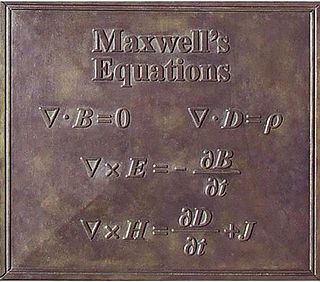This article is about "lines of force", as used in the early history and philosophy of electromagnetism. For the modern use of "lines of force" as a way to depict electromagnetic and other vector fields, see
Field line.
In the history of physics, a line of force in Michael Faraday's extended sense is synonymous with James Clerk Maxwell's line of induction. [1] According to J.J. Thomson, Faraday usually discusses lines of force as chains of polarized particles in a dielectric, yet sometimes Faraday discusses them as having an existence all their own as in stretching across a vacuum. [2] In addition to lines of force, J.J. Thomson—similar to Maxwell—also calls them tubes of electrostatic inductance, or simply Faraday tubes. [2] From the 20th century perspective, lines of force are energy linkages embedded in a 19th-century field theory that led to more mathematically and experimentally sophisticated concepts and theories, including Maxwell's equations and Albert Einstein's theory of relativity.
Lines of force originated with Michael Faraday, whose theory holds that all of reality is made up of force itself. His theory predicts that electricity, light, and gravity have finite propagation delays. The theories and experimental data of later scientific figures such as Maxwell, Heinrich Hertz, Einstein, and others are in agreement with the ramifications of Faraday's theory. Nevertheless, Faraday's theory remains distinct. Unlike Faraday, Maxwell and others (e.g., J.J. Thomson) thought that light and electricity must propagate through an ether. In Einstein's relativity, there is no ether, yet the physical reality of force is much weaker than in the theories of Faraday. [3] [4]
Historian Nancy J. Nersessian in her paper "Faraday's Field Concept" distinguishes between the ideas of Maxwell and Faraday: [5]
The specific features of Faraday's field concept, in its 'favourite' and most complete form, are that force is a substance, that it is the only substance and that all forces are interconvertible through various motions of the lines of force. These features of Faraday's 'favourite notion' were not carried on. Maxwell, in his approach to the problem of finding a mathematical representation for the continuous transmission of electric and magnetic forces, considered these to be states of stress and strain in a mechanical aether. This was part of the quite different network of beliefs and problems with which Maxwell was working.

In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interactions of atoms and molecules. Electromagnetism can be thought of as a combination of electrostatics and magnetism, which are distinct but closely intertwined phenomena. Electromagnetic forces occur between any two charged particles. Electric forces cause an attraction between particles with opposite charges and repulsion between particles with the same charge, while magnetism is an interaction that occurs between charged particles in relative motion. These two forces are described in terms of electromagnetic fields. Macroscopic charged objects are described in terms of Coulomb's law for electricity and Ampère's force law for magnetism; the Lorentz force describes microscopic charged particles.

An electromagnetic field is a physical field, mathematical functions of position and time, representing the influences on and due to electric charges. The field at any point in space and time can be regarded as a combination of an electric field and a magnetic field. Because of the interrelationship between the fields, a disturbance in the electric field can create a disturbance in the magnetic field which in turn affects the electric field, leading to an oscillation that propagates through space, known as an electromagnetic wave.

Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be positive or negative. Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with no net charge is referred to as electrically neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that do not require consideration of quantum effects.
In physics, the fundamental interactions or fundamental forces are interactions in nature that appear not to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four fundamental interactions known to exist:
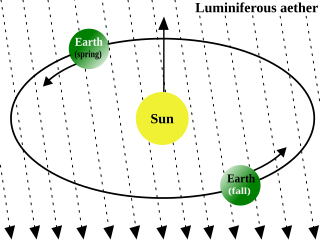
Luminiferous aether or ether was the postulated medium for the propagation of light. It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently wave-based light to propagate through empty space, something that waves should not be able to do. The assumption of a spatial plenum of luminiferous aether, rather than a spatial vacuum, provided the theoretical medium that was required by wave theories of light.
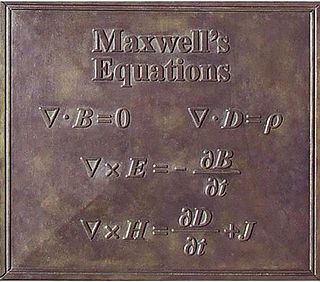
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, electric and magnetic circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar, etc. They describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated by charges, currents, and changes of the fields. The equations are named after the physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell, who, in 1861 and 1862, published an early form of the equations that included the Lorentz force law. Maxwell first used the equations to propose that light is an electromagnetic phenomenon. The modern form of the equations in their most common formulation is credited to Oliver Heaviside.

An electric field is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles. Charged particles exert attractive forces on each other when their charges are opposite, and repulse each other when their charges are the same. Because these forces are exerted mutually, two charges must be present for the forces to take place. The electric field of a single charge describes their capacity to exert such forces on another charged object. These forces are described by Coulomb's law, which says that the greater the magnitude of the charges, the greater the force, and the greater the distance between them, the weaker the force. Thus, we may informally say that the greater the charge of an object, the stronger its electric field. Similarly, an electric field is stronger nearer charged objects and weaker further away. Electric fields originate from electric charges and time-varying electric currents. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic field, Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions of nature.
Timeline of electromagnetism and classical optics lists, within the history of electromagnetism, the associated theories, technology, and events.

Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
Action at a distance is the concept in physics that an object's motion can be affected by another object without the two being in physical contact; that is, it is the concept of the non-local interaction of objects that are separated in space. Coulomb's law and Newton's law of universal gravitation are based on action at a distance.

A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism is a two-volume treatise on electromagnetism written by James Clerk Maxwell in 1873. Maxwell was revising the Treatise for a second edition when he died in 1879. The revision was completed by William Davidson Niven for publication in 1881. A third edition was prepared by J. J. Thomson for publication in 1892.
"A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field" is a paper by James Clerk Maxwell on electromagnetism, published in 1865. In the paper, Maxwell derives an electromagnetic wave equation with a velocity for light in close agreement with measurements made by experiment, and deduces that light is an electromagnetic wave.
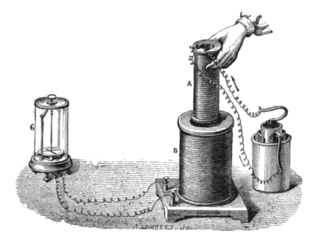
Faraday's law of induction is a law of electromagnetism predicting how a magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit to produce an electromotive force (emf). This phenomenon, known as electromagnetic induction, is the fundamental operating principle of transformers, inductors, and many types of electric motors, generators and solenoids.
In physics, a unified field theory (UFT) is a type of field theory that allows all that is usually thought of as fundamental forces and elementary particles to be written in terms of a pair of physical and virtual fields. According to modern discoveries in physics, forces are not transmitted directly between interacting objects but instead are described and interpreted by intermediary entities called fields.
A classical field theory is a physical theory that predicts how one or more fields in physics interact with matter through field equations, without considering effects of quantization; theories that incorporate quantum mechanics are called quantum field theories. In most contexts, 'classical field theory' is specifically intended to describe electromagnetism and gravitation, two of the fundamental forces of nature.

Relativistic electromagnetism is a physical phenomenon explained in electromagnetic field theory due to Coulomb's law and Lorentz transformations.

The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to understand atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to explain the phenomena. Scientific understanding and research into the nature of electricity grew throughout the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries through the work of researchers such as André-Marie Ampère, Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, Michael Faraday, Carl Friedrich Gauss and James Clerk Maxwell.
"On Physical Lines of Force" is a four-part paper written by James Clerk Maxwell, published in 1861. In it, Maxwell derived the equations of electromagnetism in conjunction with a "sea" of "molecular vortices" which he used to model Faraday's lines of force. Maxwell had studied and commented on the field of electricity and magnetism as early as 1855/56 when "On Faraday's Lines of Force" was read to the Cambridge Philosophical Society. Maxwell made an analogy between the density of this medium and the magnetic permeability, as well as an analogy between the transverse elasticity and the dielectric constant, and using the results of a prior experiment by Wilhelm Eduard Weber and Rudolf Kohlrausch performed in 1856, he established a connection between the speed of light and the speed of propagation of waves in this medium.

By the first half of the 19th century, the understanding of electromagnetics had improved through many experiments and theoretical work. In the 1780s, Charles-Augustin de Coulomb established his law of electrostatics. In 1825, André-Marie Ampère published his force law. In 1831, Michael Faraday discovered electromagnetic induction through his experiments, and proposed lines of forces to describe it. In 1834, Emil Lenz solved the problem of the direction of the induction, and Franz Ernst Neumann wrote down the equation to calculate the induced force by change of magnetic flux. However, these experimental results and rules were not well organized and sometimes confusing to scientists. A comprehensive summary of the electrodynamic principles was needed.
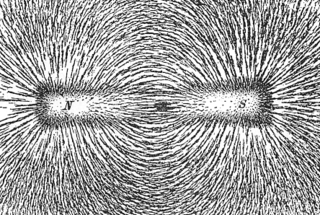
In the history of physics, the concept of fields had its origins in the 18th century in a mathematical formulation of Newton's law of universal gravitation, but it was seen as deficient as it implied action at a distance. In 1852, Michael Faraday treated the magnetic field as a physical object, reasoning about lines of force. James Clerk Maxwell used Faraday's conceptualisation to help formulate his unification of electricity and magnetism in his field theory of electromagnetism.