Related Research Articles

Stuttgart is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the Stuttgarter Kessel and lies an hour from the Swabian Jura and the Black Forest. Stuttgart has a population of 632,865 as of 2022, making it the sixth largest city in Germany, while over 2.8 million people live in the city's administrative region and nearly 5.5 million people in its metropolitan area, making it the fourth largest metropolitan area in Germany. The city and metropolitan area are consistently ranked among the top 4 European metropolitan areas by GDP; Mercer listed Stuttgart as 21st on its 2015 list of cities by quality of living; innovation agency 2thinknow ranked the city 24th globally out of 442 cities in its Innovation Cities Index; and the Globalization and World Cities Research Network ranked the city as a Beta-status global city in their 2020 survey. Stuttgart was one of the host cities for the official tournaments of the 1974 and 2006 FIFA World Cups.

Ingelheim, officially Ingelheim am Rhein, is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district in the Rhineland-Palatinate state of Germany. The town sprawls along the Rhine's left bank. It has been Mainz-Bingen's district seat since 1996.

Biberach an der Riß, often referred to as simply Biberach, is a town in southern Germany. It is the capital of Biberach district, in the Upper Swabia region of the German state (Land) of Baden-Württemberg. It is called Biberach an der Riß after the small river Riß which flows through the city to distinguish it from the other towns of similar names.
Heidesheim am Rhein is an Ortsbezirk (borough) of the town Ingelheim am Rhein in the Mainz-Bingen district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Before July 2019, it was a separate municipality belonging to the former Verbandsgemeinde Heidesheim am Rhein, of which it was the administrative seat. Heidesheim was one of the biggest municipalities in Rhenish Hesse.
Pompeiopolis was a Roman city in ancient Paphlagonia, identified in the early 19th century with the ruins of Zımbıllı Tepe, located near Taşköprü, Kastamonu Province in the Black Sea Region of Turkey. The exact location is 40 km north-east of Kastamonu and a short distance across the river from modern Taşköprü, in the valley of the Gökırmak or Gök River. The borders of Pompeiopolis reached the Küre mountains to the north, Ilgaz mountains to the south, Halys river to the east and Pınarbaşı valley to the west.

Hohenasperg, located in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg near Stuttgart, Germany, of which it is administratively part, is an ancient fortress and prison overlooking the town of Asperg.
C.H. Boehringer Sohn AG & Co. KG is the parent company of the Boehringer Ingelheim group, which was founded in 1885 by Albert Boehringer (1861–1939) in Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany. As of 2018, Boehringer Ingelheim is one of the world's largest pharmaceutical companies, and the largest private one. Headquartered in Ingelheim, it operates globally with 146 affiliates and more than 47,700 employees. Unlike most large pharmaceutical companies which are listed, the company is private and fully owned by the Boehringer, Liebrecht and von Baumbach families. The company's key areas of interest are: respiratory diseases, metabolism, immunology, oncology and diseases of the central nervous system. Boehringer Ingelheim is a full member of the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA). The corporate logo of Boehringer Ingelheim depicts a stylized rendition of the central section of the imperial palace of Charlemagne.
Buchau Abbey, otherwise the Imperial Abbey of Buchau, was a self-ruling Imperial Estate and its abbess had a seat and vote at the Imperial Diet.

Saint Blaise Abbey was a Benedictine monastery in the village of St. Blasien in the Black Forest in Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
Stadecken-Elsheim is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Mainz-Bingen district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.

Schwabenheim an der Selz is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Mainz-Bingen district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.

The following list of works by German philosopher Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (1770–1831).
Heinrich Karl Walter was a German-Russian botanist and eco-physiologist.

The Ingelheim Imperial Palace was an important imperial palace erected in the second half of the 8th century in Germany. It served kings of Francia and later Holy Roman Emperors and Kings as a residenz and place for governance until the 11th century.
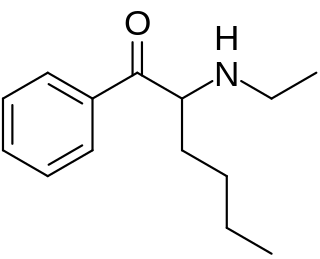
N-Ethylhexedrone (also known as α-ethylaminocaprophenone, N-ethylnorhexedrone, hexen, and NEH) is a stimulant of the cathinone class that acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) with IC50 values of 0.0978 and 0.0467 μM, respectively. N-Ethylhexedrone was first mentioned in a series of patents by Boehringer Ingelheim in the 1960s which led to the development of the better-known drug methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV). Since the mid-2010s, N-ethylhexedrone has been sold online as a designer drug. In 2018, N-ethylhexedrone was the second most common drug of the cathinone class to be identified in Drug Enforcement Administration seizures.

The Imperial Palace at Gelnhausen is located on a former island in the Kinzig river in Gelnhausen, Hesse, Germany.
Volkold of Meissen was the second Bishop of Meissen.

The proclamation of the German Empire, also known as the Deutsche Reichsgründung, took place in January 1871 after the joint victory of the German states in the Franco-Prussian War. As a result of the November Treaties of 1870, the southern German states of Baden, Hesse-Darmstadt, with their territories south of the Main line, Württemberg and Bavaria, joined the Prussian-dominated "North German Confederation" on 1 January 1871. On the same day, the new Constitution of the German Confederation came into force, thereby significantly extending the federal German lands to the newly created German Empire. The Day of the founding of the German Empire, January 18, became a day of celebration, marking when the Prussian King William I was proclaimed German Emperor at the Palace of Versailles, outside Paris, France.

Dora Livia Felicia Maria Duncker was a German writer of novels, short stories, essays, poems and stage works. She was also active as a theatre critic.
References
- ↑ "Burgholzhausen". www.friedrichsdorf.de. 2016. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ↑ Urkunde 19. December 823 (= 822); vgl. Königliches Staatsarchiv Stuttgart (Hrsg.): Wirtembergisches Urkundenbuch. Bd. I, F. H. Köhler, Stuttgart 1849, S. 101; Bd. 3, Nachtrag 1. Text und Übertragung der Urkunde Kaiser Ludwigs des Frommen von 822; Regesta Imperii Online, Nr. 768 (retrieved 15 May 2013).