Related Research Articles

A tenrec is any species of mammal within the afrotherian family Tenrecidae endemic to Madagascar. Tenrecs are widely diverse; as a result of convergent evolution some resemble hedgehogs, shrews, opossums, rats, or mice. They occupy aquatic, arboreal, terrestrial and fossorial environments. Some of these species, including the greater hedgehog tenrec, can be found in the Madagascar dry deciduous forests. However, the speciation rate in this group has been higher in humid forests.

Ravenala is a genus of monocotyledonous flowering plants. Classically, the genus was considered to include a single species, Ravenala madagascariensis, commonly known as the traveller's tree, traveller's palm or East-West palm, from Madagascar. It is not a true palm but a member of the family Strelitziaceae. The genus is closely related to the southern African genus Strelitzia and the South American genus Phenakospermum. Some older classifications include these genera in the banana family (Musaceae). Although it is usually considered to be a single species, four different forms have been distinguished. Five other species were described in 2021, all from Madagascar: Ravenala agatheae Haev. & Razanats., R. blancii Haev., V.Jeannoda & A.Hladik, R. grandis Haev., Razanats, A.Hladik & P.Blanc, R. hladikorum Haev., Razanats., V. Jeannoda & P.Blanc, R. madagascariensis Sonn., et R. menahirana Haev. & Razanats.

The fossa is a carnivorous mammal that is endemic to Madagascar. It is a member of the Eupleridae, a family of carnivorans closely related to the mongoose family Herpestidae.
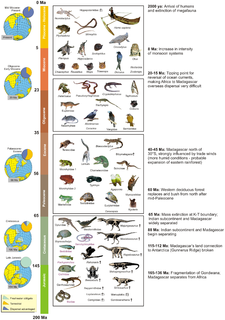
The fauna of Madagascar is a part of the wildlife of Madagascar.

Eupleridae is a family of carnivorans endemic to Madagascar and comprising 10 known living species in seven genera, commonly known as euplerids, Malagasy mongooses or Malagasy carnivorans. The best known species is the fossa, in the subfamily Euplerinae. All species of Euplerinae were formerly classified as viverrids, while all species in the subfamily Galidiinae were classified as herpestids.

The ring-tailed vontsira, locally still known as the ring-tailed mongoose is a euplerid in the subfamily Galidiinae, a carnivoran native to Madagascar.

Galidiinae is a subfamily of carnivorans that is restricted to Madagascar and includes six species classified into four genera. Together with the three other species of indigenous Malagasy carnivorans, including the fossa, they are currently classified in the family Eupleridae within the suborder Feliformia. Galidiinae are the smallest of the Malagasy carnivorans, generally weighing about 600 to 900 g. They are agile, short-legged animals with long, bushy tails.

Cryptoprocta spelea, also known as the giant fossa, is an extinct species of carnivore from Madagascar in the family Eupleridae, which is most closely related to the mongooses and includes all Malagasy carnivorans. It was first described in 1902, and in 1935 was recognized as a separate species from its closest relative, the living fossa. C. spelea was larger than the fossa, about the size of a gray wolf, but otherwise similar. The two have not always been accepted as distinct species. When and how C. spelea became extinct is unknown; there is some anecdotal evidence, including reports of very large fossas, that there is more than one surviving species.

Grandidier's trident bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae endemic to Madagascar. It was formerly assigned to the genus Triaenops, but is now placed in the separate genus Paratriaenops.

Malagasy is an Austronesian language and the national language of Madagascar. Malagasy is the westernmost Malayo-Polynesian language, brought to Madagascar by the settlement of Austronesian peoples from the Sunda islands around the 5th century AD. The Malagasy language is one of the Barito languages and is most closely related to the Ma'anyan language, still spoken on Borneo to this day. Malagasy also includes numerous Malay and Javanese loanwords, from the time of the early Austronesian settlement and trading between Madagascar and the Sunda Islands. After c. 1000 AD, Malagasy incorporated numerous Bantu and Arabic loanwords, brought over by new settlers and traders.
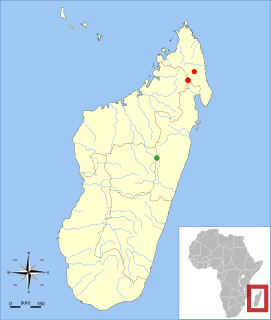
Voalavo is a genus of rodent in the subfamily Nesomyinae, found only in Madagascar. Two species are known, both of which occur in mountain forest above 1250 m (4100 ft) altitude; the northern voalavo lives in northern Madagascar and eastern voalavo is restricted to a small area in the central part of the island. The genus was discovered in 1994 and formally described in 1998. Within Nesomyinae, it is most closely related to the genus Eliurus, and DNA sequence data suggest that the current definitions of these two genera need to be changed.

The northern voalavo, also known as the naked-tailed voalavo or simply the voalavo, is a rodent in the family Nesomyidae found in the highlands of northern Madagascar. Discovered in 1994 and formally described in 1998, it is the type species of the genus Voalavo; its closest relative is the eastern voalavo of the Central Highlands. DNA sequencing suggests that it may be more closely related to Grandidier's tufted-tailed rat than to other species of the closely related genus Eliurus. The northern voalavo is found at 1,250 to 1,950 m above sea level in montane wet and dry forests in the Marojejy and Anjanaharibe-Sud massifs. Nocturnal and solitary, it lives mainly on the ground, but it can climb and probably eats plant matter. Despite having a small range, the species is classified as being of least concern because it lacks obvious threats and much of its range is within protected areas.
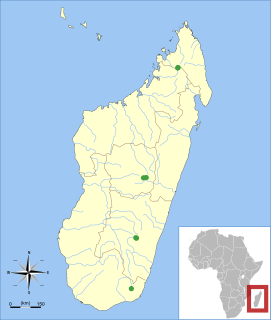
The Malagasy mountain mouse or Koopman's montane voalavo(Monticolomys koopmani) is a rodent within the subfamily Nesomyinae of the family Nesomyidae. It is monotypic within the genus Monticolomys, and is closely related to the big-footed mouse (Macrotarsomys). It is found in the highlands of eastern Madagascar. A small mouse-like rodent, it is dark brown on the upperparts and dark gray below. It has small, rounded, densely haired ears and broad feet with well-developed pads. The long tail lacks a tuft at the tip. The skull is delicate and lacks crests and ridges on its roof.
Petter's tufted-tailed rat is a rodent in the genus Eliurus found in lowland eastern Madagascar. First described in 1994, it is most closely related to the smaller Eliurus grandidieri. Virtually nothing is known of its natural history, except that it occurs in rainforest and is nocturnal and solitary. It is threatened by destruction and fragmentation of its habitat and is listed as "Vulnerable" on the IUCN Red List.

The flora of Madagascar consists of more than 12,000 species of plants, as well as a poorly known number of fungi and algae. Around 83% of Madagascar's vascular plants are found only on the island. These endemics include five plant families, 85% of the over 900 orchid species, around 200 species of palms, and such emblematic species as the traveller's tree, six species of baobab and the Madagascar periwinkle. The high degree of endemism is due to Madagascar's long isolation following its separation from the African and Indian landmasses in the Mesozoic, 150–160 and 84–91 million years ago, respectively. However, few plant lineages remain from the ancient Gondwanan flora; most extant plant groups immigrated via across-ocean dispersal well after continental break-up.

The geology of Madagascar comprises a variety of rocks of Precambrian age which make up the larger part of the east and centre of the island. They are intruded by basalts and rhyolites of Mesozoic to Cenozoic age. In contrast, the western part of the island is formed from sedimentary rocks of Carboniferous to Quaternary age. Archean rocks occur from the northeast portion of the island down to the south in the Ranotsara shear zone. Rocks in the northern portion of Madagascar are greenstone belts, from the Archean or Paleoproterozoic age.
Otto Christian Dahl was a Norwegian missionary in Madagascar, linguist, and government scholar.

The Madagascar succulent woodlands are a xeric shrublands ecoregion in southwestern and central western Madagascar. They are threatened by various human activities.

Sainte Luce Reserve is a nature reserve in south-east Madagascar and part of one of the last remaining intact coastal rainforests in the country. It forms part of the greater Sainte Luce rainforest, which is approximately 15 km long and varies from 100m to 700m wide. The reserve itself is approximately 1 km long and averages 300m across.

Berthe Rakotosamimanana was a primatologist and palaeontologist from Madagascar.
References
- ↑ Blench, Roger & Martin Walsh 2009. Faunal names in Malagasy: their etymologies and implications for the prehistory of the East African coast .
- ↑ Garbutt, N. 1999. Mammals of Madagascar. Sussex: Pica Press.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Beaujard, P. 1998. Dictionnaire Malgache (dialectal) - Français: Dialecte Tañala, sud-est de Madagascar. Paris: L’Harmattan.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Goodman, Steven M. & J. P. Benstead (eds.) 2003. The natural history of Madagascar. Chicago & London: The University of Chicago Press.
- 1 2 Gueunier, N. J. 1987. Lexique du dialecte malgache de Mayotte (Comores). (Études Océan Indien, numéro special 7). Paris: INALCO.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 Richardson, James 1885. A New Malagasy-English Dictionary. Antananarivo: London Missionary Society.
- ↑ Simon, Pierre R. 1988. Ny fiteny fahizany: Reconstitution et périodisation du malgache ancien jusqu'au XIVè siècle. Paris: INALCO.