The clade Afrosoricida contains the golden moles of Southern Africa, the otter shrews of equatorial Africa and the tenrecs of Madagascar. These three groups of small mammals were for most of the 19th and 20th centuries regarded as a part of the Insectivora or Lipotyphla, but both of those groups, as traditionally used, are polyphyletic.

A tenrec is a mammal belonging to any species within the afrotherian family Tenrecidae, which is endemic to Madagascar. Tenrecs are a very diverse group; as a result of convergent evolution, some resemble hedgehogs, shrews, opossums, rats, and mice. They occupy aquatic, arboreal, terrestrial, and fossorial environments. Some of these species, including the greater hedgehog tenrec, can be found in the Madagascar dry deciduous forests. However, the speciation rate in this group has been higher in humid forests.

The red owl is an owl in the barn owl family Tytonidae. It is also known as the Madagascar red owl, Madagascar grass-owl and Soumagne's owl. It is a rare resident of Madagascar that was virtually unknown from its discovery in 1876 to its rediscovery by researchers from the World Wide Fund for Nature in 1993. It is currently listed as vulnerable because of habitat loss, but recent studies have determined it may have a wider range than first believed, though further research in distribution and ecology is required. It has possibly been overlooked because of its close resemblance to the closely related barn owl.

The fossa is a slender, long-tailed, cat-like mammal that is endemic to Madagascar. It is a member of the carnivoran family Eupleridae.

India is the world's 8th most biodiverse region with a 0.46 BioD score on diversity index, 102,718 species of fauna and 23.39% of the nation's geographical area under forest and tree cover in 2020. India encompasses a wide range of biomes: desert, high mountains, highlands, tropical and temperate forests, swamplands, plains, grasslands, areas surrounding rivers, as well as island archipelago. Officially, three out of the 36 Biodiversity Hotspots in the world are present in India: the Himalayas, the Western Ghats, and the Indo-Burma region. To these may be added the Sundarbans and the Terrai-Duar Savannah grasslands for their unique foliage and animal species. These hotspots have numerous endemic species. Nearly 5% of India's total area is formally classified under protected areas.
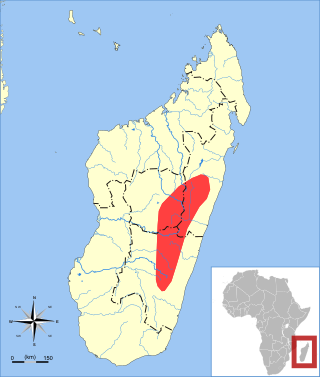
The web-footed tenrec, Malagasy otter shrew, or aquatic tenrec is the only known semiaquatic tenrec, and is found in eastern Madagascar, especially in and around Ranomafana National Park. It grows to between 25 and 39 cm, and was once thought to be extinct. It feeds on crabs, aquatic insects, and crayfish. The population is considered vulnerable. It was formerly placed in the monotypic genus Limnogale, but has been moved to Microgale based on molecular data showing it to be deeply nested within the latter.

The Malagasy or striped civet, also known as the fanaloka or jabady, is an euplerid endemic to Madagascar. It is the only species in genus Fossa.

The fauna of Madagascar is a part of the wildlife of Madagascar.

The tailless tenrec, also known as the common tenrec, is a species of mammal in the family Tenrecidae. It is the only member of the genus Tenrec. Native to Madagascar, it is also found on the Comoros, Mauritius, Réunion, and Seychelles island groups, where it has been purposely introduced. Its natural habitat is the understory of subtropical-tropical forest, open forest, arid shrub-land, savanna, arable land, pastures, crop plantations, private gardens, and some landscaped, urban areas.

The lesser hedgehog tenrec is a species of mammal in the family Tenrecidae. It is the only species in the genus Echinops and is named in honour of Charles Telfair. It is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests, shrubland, and shrubland and dry savanna.

The large-eared tenrec is a species of mammal in the family Tenrecidae. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Geogale, and the only member of the subfamily Geogalinae. It is endemic to Madagascar where its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and shrubland. It is threatened by habitat loss, but to a lesser extent than was previously thought and is listed by the IUCN as being of "Least Concern".

Jenkins's shrew tenrec is a species of mammal in the family Tenrecidae. It is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and shrubland. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The pygmy shrew tenrec is a species of placental mammal in the family Tenrecidae. It is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist forests. While it is not endangered, its population is slowly declining as it is threatened by habitat loss. This is of concern, though does not yet merit a higher protection level.

The greater long-tailed shrew tenrec is a species of mammal in the family Tenrecidae. It is endemic to Madagascar, where its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist forests.

The mole-like rice tenrec, also known as the fossorial tenrec or hova rice tenrec, is a species of mammal in the tenrec family. Like all other tenrecs, it is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist forests, swamps, freshwater lakes, and irrigated or seasonally flooded agricultural land.

The Madagascan flying fox, Madagascar flying-fox, or Madagascar fruit bat is a species of megabat in the genus Pteropus. It is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitats are diverse, and include moist lowland forests, dry forests, succulent woodlands, and spiny thickets, and mangroves. It eats figs and other fruits, flowers, and leaves. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Tenrecinae is a tenrec subfamily endemic to the island of Madagascar. It contains the largest species in the family, Tenrec ecaudatus. All members of the genus possess spines, analogous to those of hedgehogs, for defense against predators.

The Madagascar succulent woodlands are a xeric shrublands ecoregion in southwestern and central western Madagascar. Native plants survive in the arid climate and long dry season with adaptations like succulent leaves, water storing trunks, photosynthetic stems, and dropping leaves during the dry season. The ecoregion is threatened by various human activities.