
The taxonomy of Nepenthes has been revised several times during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries.

The taxonomy of Nepenthes has been revised several times during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries.
The first subgeneric division of the Nepenthes was made by Joseph Dalton Hooker in his 1873 monograph, "Nepenthaceae". Hooker distinguished N. pervillei from all other taxa based on its seeds, which lack the appendages typical of most Nepenthes. He placed it in the monotypic section Anourosperma. All other species were subsumed in the second section, Eunepenthes.
A second attempt to establish a natural subdivision within the genus was made in 1895 by Günther Beck von Mannagetta und Lerchenau in "Die Gattung Nepenthes". Beck kept the two sections created by Hooker, but divided Eunepenthes into three subgroups: Apruinosae, Pruinosae, and Retiferae.
Nepenthes taxonomy was once again revised in 1908 by John Muirhead Macfarlane in his own monograph. Oddly, Macfarlane did not name the groups he distinguished. His revision is generally not considered to be a natural division of the genus.
In 1928, B. H. Danser published his seminal monograph, "The Nepenthaceae of the Netherlands Indies", in which he divided Nepenthes into six clades, based on observations of herbarium material. The clades were: the Vulgatae, Montanae, Nobiles, Regiae, Insignes and Urceolatae. Regiae appears to reflect the relationships of its members quite well, although the same cannot be said for the other clades. Despite this, Danser's classification was undoubtedly a great improvement on previous attempts.
Danser classified Nepenthes as follows:
Vulgatae
Montanae
Nobiles
Regiae
Insignes
Urceolatae
The taxonomic work of Danser (1928) was revised by Hermann Harms in 1936. Harms divided Nepenthes into three subgenera: Anourosperma Hook.f. (1873), Eunepenthes Hook.f. (1873) and Mesonepenthes Harms (1936) (Latin: meso: middle; "middle" Nepenthes). The Nepenthes species found in the subgenera Anourosperma and Mesonepenthes differ from those in the Vulgatae, where Danser had placed them. Harms placed the great majority of Nepenthes species in the Eunepenthes; Anourosperma was a monotypic subgenus, while Mesonepenthes contained only three species. He also created an additional clade, the Distillatoriae (after N. distillatoria ).

Nepenthes rajah is a carnivorous pitcher plant species of the family Nepenthaceae. It is endemic to Mount Kinabalu and neighbouring Mount Tambuyukon in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. Nepenthes rajah grows exclusively on serpentine substrates, particularly in areas of seeping ground water where the soil is loose and permanently moist. The species has an altitudinal range of 1,500–2,650 metres (4,920–8,690 ft) a.s.l. and is thus considered a highland or sub-alpine plant. Due to its localised distribution, N. rajah is classified as an endangered species by the IUCN and listed on CITES Appendix I.

Nepenthes villosa, or the villose pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Mount Kinabalu and neighbouring Mount Tambuyukon in northeastern Borneo. It grows at higher elevations than any other Bornean Nepenthes species, occurring at elevations of over 3,200 m (10,500 ft). Nepenthes villosa is characterised by its highly developed and intricate peristome, which distinguishes it from the closely related N. edwardsiana and N. macrophylla.

Nepenthes tentaculata, or the fringed pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant with a wide distribution across Borneo and Sulawesi. It grows at altitudes of 400–2550 m.

Nepenthes hirsuta, the hairy pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo. It is characterised by an indumentum of thick brown hairs, which is even present on the inflorescence. Pitchers are mostly green throughout with some having red blotches on the inside surfaces.

Nepenthes lowii, or Low's pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo. It is named after Hugh Low, who discovered it on Mount Kinabalu. This species is perhaps the most unusual in the genus, being characterised by its strongly constricted upper pitchers, which bear a greatly reduced peristome and a reflexed lid with numerous bristles on its lower surface.

Nepenthes edwardsiana, or the splendid pitcher-plant, is a carnivorous tropical pitcher plant endemic to Mount Kinabalu and neighbouring Mount Tambuyukon in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. It is considered one of the most spectacular of all Nepenthes, producing some of the largest pitchers and the most highly developed peristome ribs of any species in the genus.

Nepenthes northiana, or Miss North's pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo, where it grows at elevations ranging from 0 to 500 m above sea level. The specific epithet northiana honours Marianne North, who first illustrated the species. Nepenthes northiana is one of the most famous Nepenthes, and its discovery in the latter half of the 19th century contributed to Sarawak's reputation as a land of spectacular exotic plants.

Nepenthes pervillei is the only pitcher plant found in the Seychelles, where it is endemic to the islands of Mahé and Silhouette. It grows in rocky areas near granitic mountain summits, its roots reaching deep into rock fissures. The species has an altitudinal range of 350–750 m above sea level. Like all members of the genus, N. pervillei is dioecious, having separate male and female plants.

Nepenthes distillatoria is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Sri Lanka. It was the second Nepenthes species to be described in print and the first to be formally named under the Linnaean system of taxonomy. It is therefore the type species of the genus.

Nepenthes boschiana, or Bosch's pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo. It is most closely allied to N. faizaliana. Nepenthes borneensis is considered a synonym of this species. Nepenthes boschiana has no known natural hybrids. No valid forms or varieties have been described. Nepenthes boschiana belongs to the loosely defined "N. maxima complex", which also includes, among other species, N. chaniana, N. epiphytica, N. eymae, N. faizaliana, N. fusca, N. klossii, N. maxima, N. platychila, N. stenophylla, and N. vogelii.

Nepenthes hispida is a tropical pitcher plant species native to Borneo. It grows at elevations of 100 to 800 m in kerangas forest. It is known with certainty only from Lambir Hills National Park and surrounding areas.

Nepenthes sumatrana is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to the Indonesian island of Sumatra, after which it is named.

Nepenthes neoguineensis is a tropical pitcher plant native to the island of New Guinea, after which it is named.

Nepenthes beccariana is a tropical pitcher plant. The species was described in 1908 by John Muirhead Macfarlane based on a specimen collected from the island of Nias, which lies off the western coast of Sumatra. It appears to be closely related to both N. longifolia and N. sumatrana, and the former is possibly a heterotypic synonym of this taxon.
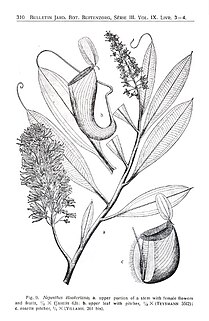
"The Nepenthaceae of the Netherlands Indies" is a seminal monograph by B. H. Danser on the tropical pitcher plants of the Dutch East Indies and surrounding regions. It was originally published in the Bulletin du Jardin Botanique de Buitenzorg in 1928, and reprinted by Natural History Publications (Borneo) in 2006.

"A skeletal revision of Nepenthes (Nepenthaceae)" is a monograph by Matthew Jebb and Martin Cheek on the tropical pitcher plants of the genus Nepenthes. It was published in the May 1997 issue of the botanical journal Blumea. The work represented the first revision of the entire genus since John Muirhead Macfarlane's 1908 monograph. Jebb and Cheek's revision was based on "collaborative work by both authors since 1984, largely on herbarium specimens, but including fieldwork in New Guinea, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore and Madagascar". It was a precursor to their more exhaustive 2001 monograph, "Nepenthaceae".

"Nepenthaceae" is a monograph by John Muirhead Macfarlane on the tropical pitcher plants of the genus Nepenthes. It was published in 1908 in Adolf Engler's Das Pflanzenreich. It was the most exhaustive revision of the genus up to that point, covering all known species, and included detailed accounts of the structure, anatomy, and development of Nepenthes.

"Nepenthaceae" is a monograph by Joseph Dalton Hooker on the tropical pitcher plants of the genus Nepenthes. It was published in 1873 in the seventeenth and final volume of Augustin Pyramus de Candolle's Prodromus Systematis Naturalis Regni Vegetabilis, which was edited by Augustin's son, Alphonse. The monograph focused primarily on new discoveries from northern Borneo. Unlike most major works on Nepenthes, it included no illustrations.

"Die Gattung Nepenthes: Eine monographische Skizze" is a German-language monograph by Günther Beck von Mannagetta und Lerchenau on the tropical pitcher plants of the genus Nepenthes. It was published in 1895 in four parts, spread over the March, April, May and June issues of Wiener Illustrirte Garten-Zeitung.

Nepenthes hemsleyana is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo, where it grows in peat swamp forest and heath forest below 200 m above sea level.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nepenthes . |