East Berlin was the partially recognised capital of East Germany (GDR) from 1949 to 1990. From 1945, it was the Soviet occupation sector of Berlin. The American, British, and French sectors were known as West Berlin. From 13 August 1961 until 9 November 1989, East Berlin was separated from West Berlin by the Berlin Wall. The Western Allied powers did not recognize East Berlin as the GDR's capital, nor the GDR's authority to govern East Berlin. For most of its administrative existence, East Berlin was officially known as Berlin, capital of the GDR by the GDR government. On 3 October 1990, the day Germany was officially reunified, East and West Berlin formally reunited as the city of Berlin.

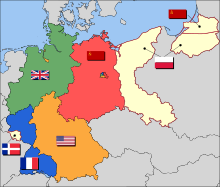
The Potsdam Agreement was the agreement among three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union after the war ended in Europe that was signed on 1 August 1945 and it was published the next day. A product of the Potsdam Conference, it concerned the military occupation and reconstruction of Germany, its border, and the entire European Theatre of War territory. It also addressed Germany's demilitarisation, reparations, the prosecution of war criminals and the mass expulsion of ethnic Germans from various parts of Europe. France was not invited to the conference but formally remained one of the powers occupying Germany.

West Germany is the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany from its formation on 23 May 1949 until its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republic after its capital city of Bonn. During the Cold War, the western portion of Germany and the associated territory of West Berlin were parts of the Western Bloc. West Germany was formed as a political entity during the Allied occupation of Germany after World War II, established from 12 states formed in the three Allied zones of occupation held by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France.
High commissioner is the title of various high-ranking, special executive positions held by a commission of appointment.

The history of Germany from 1945 to 1990 comprises the period following World War II. The period began with the Berlin Declaration, marking the abolition of the German Reich and Allied-occupied period in Germany on 5 June 1945, and ended with the German reunification on 3 October 1990.

The final battles of the European theatre of World War II continued after the definitive surrender of Nazi Germany to the Allies, signed by Field marshal Wilhelm Keitel on 8 May 1945 in Karlshorst, Berlin. After German leader Adolf Hitler's suicide and handing over of power to grand admiral Karl Dönitz on the last day of April 1945, Soviet troops conquered Berlin and accepted surrender of the Dönitz-led government. The last battles were fought on the Eastern Front which ended in the total surrender of all of Nazi Germany’s remaining armed forces such as in the Courland Pocket in western Latvia from Army Group Courland in the Baltics surrendering on 10 May 1945 and in Czechoslovakia during the Prague offensive on 11 May 1945.
The Soviet Military Administration in Germany was the Soviet military government, headquartered in Berlin-Karlshorst, that directly ruled the Soviet occupation zone in Germany from the German surrender in May 1945 until after the establishment of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) in October 1949.

The Bizone or Bizonia was the combination of the American and the British occupation zones on 1 January 1947 during the occupation of Germany after World War II. With the addition of the French occupation zone on 1 August 1948 the entity became the Trizone. Later, on 23 May 1949, the Trizone became the Federal Republic of Germany, commonly known as West Germany.
Following the termination of hostilities in World War II, the Allies were in control of the defeated Axis countries. Anticipating the defeat of Germany, Italy and Japan, they had already set up the European Advisory Commission and a proposed Far Eastern Advisory Commission to make recommendations for the post-war period. Accordingly, they managed their control of the defeated countries through Allied Commissions, often referred to as Allied Control Commissions (ACC), consisting of representatives of the major Allies.

The Soviet occupation zone in Germany was an area of Germany that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a communist area, established as a result of the Potsdam Agreement on 2 August 1945. On 7 October 1949 the German Democratic Republic (GDR), commonly referred to in English as East Germany, was established in the Soviet occupation zone.

The German Instrument of Surrender was a legal document effecting the unconditional surrender of the remaining German armed forces to the Allies, ending World War II in Europe. It was signed at 22:43 CET on 8 May 1945 and took effect at 23:01 CET on the same day.

The entirety of Germany was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II, from the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945 to the establishment of West Germany on 23 May 1949. Unlike occupied Japan, Nazi Germany was stripped of its sovereignty and former state: after Germany formally surrendered on 8 May 1945, the four countries representing the Allies asserted joint authority and sovereignty through the Allied Control Council (ACC).

The Office of Military Government, United States was the United States military-established government created shortly after the end of hostilities in occupied Germany in World War II. Under General Lucius D. Clay, it administered the area of Germany and sector of Berlin controlled by the United States Army. The Allied Control Council comprised military authorities from the United States, the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union and France. Though created on January 1, 1946, OMGUS previously reported to the U.S. Group Control Council, Germany (USGCC), which existed from May 8, 1945, until October 1, 1945. OMGUS was eliminated on December 5, 1949, and the U.S. High Commissioner for Germany assumed control of its functions.

The Allied leaders of World War II listed below comprise the important political and military figures who fought for or supported the Allies during World War II. Engaged in total war, they had to adapt to new types of modern warfare, on the military, psychological and economic fronts.
The legal status of Germany concerns the question of the extinction, or otherwise continuation, of the German nation-state following the rise and downfall of Nazi Germany, and constitutional hiatus of the military occupation of Germany by the four Allied powers from 1945 to 1949. It became current once again when the German Democratic Republic joined the Federal Republic of Germany in 1990.

The Berlin Declaration of 5 June 1945 or the Declaration regarding the defeat of Germany, had the governments of the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and France, acting on behalf of the Allies of World War II, jointly assume de jure "supreme authority" over Germany after its military defeat and asserted the legitimacy of their joint determination of issues regarding its administration and boundaries prior to the forthcoming Potsdam Conference.

The Allied Control Council (ACC) or Allied Control Authority, and also referred to as the Four Powers, was the governing body of the Allied occupation zones in Germany (1945–1949/1991) and Austria (1945–1955) after the end of World War II in Europe. After the defeat of the Nazis, Germany and Austria were occupied as two different areas, both by the same four Allies. Both were later divided into four zones by the 1 August 1945 Potsdam Agreement. Its members were the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, the United States, and France. The organisation was based in Schöneberg, Berlin.

The American occupation zone in Germany, also known as the US-Zone, and the Southwest zone, was one of the four occupation zones established by the Allies of World War II in Germany west of the Oder–Neisse line in July 1945, around two months after the German surrender and the end of World War II in Europe. It was controlled by the Office of Military Government, United States (OMGUS) and ceased to exist after the establishment of the Federal Republic of Germany on 21 September 1949, but the United States maintains military presence across Germany.