This is a list of alternative names for currency. A currency refers to money in any form when in actual use or circulation as a medium of exchange, especially circulating banknotes and coins. [1] [2] A more general definition is that a currency is a system of money (monetary units) in common use, especially in a nation. [3]

Rhyming slang is a form of slang word construction in the English language. It is especially prevalent among Cockneys in England, and was first used in the early 19th century in the East End of London; hence its alternative name, Cockney rhyming slang. In the US, especially the criminal underworld of the West Coast between 1880 and 1920, rhyming slang has sometimes been known as Australian slang.

The denarius was the standard Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War c. 211 BC to the reign of Gordian III, when it was gradually replaced by the antoninianus. It continued to be minted in very small quantities, likely for ceremonial purposes, until and through the Tetrarchy (293–313).

The yen is the official currency of Japan. It is the third-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar (US$) and the euro. It is also widely used as a third reserve currency after the US dollar and the euro.

The Canadian dollar is the currency of Canada. It is abbreviated with the dollar sign $, there is no standard disambiguating form, but the abbreviation Can$ is often suggested by notable style guides for distinction from other dollar-denominated currencies. It is divided into 100 cents (¢).

Federal Reserve Notes, also United States banknotes, are the currently issued banknotes of the United States dollar. The United States Bureau of Engraving and Printing produces the notes under the authority of the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 and issues them to the Federal Reserve Banks at the discretion of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. The Reserve Banks then circulate the notes to their member banks, at which point they become liabilities of the Reserve Banks and obligations of the United States.
Fiver may refer to:

Sterling is the official currency of the United Kingdom and its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and may be referred to by the compound noun pound sterling or the term British pound, although neither of these are official names of the currency itself. One pound is subdivided into 100 pence.
The Venezuelan bolívar[boˈli.β̞aɾ] is the official currency of Venezuela. Named after the hero of Latin American independence Simón Bolívar, it was introduced following the monetary reform in 1879, before which the venezolano was circulating. Due to its decade-long reliance on silver and gold standards, and then on a peg to the United States dollar, it was considered among the most stable currencies and was internationally accepted until 1983, when the government decided to adopt a floating exchange rate instead.
The dinar is the official currency of Libya. The dinar is divided into 1,000 dirhams (درهم). It is issued by the Central Bank of Libya, which also supervises the banking system and regulates credit.
£sd is the popular name for the pre-decimal currencies once common throughout Europe, especially in the British Isles and hence in several countries of the British Empire and subsequently the Commonwealth. The abbreviation originates from the Latin currency denominations librae, solidi, and denarii. In the United Kingdom, these were referred to as pounds, shillings, and pence.
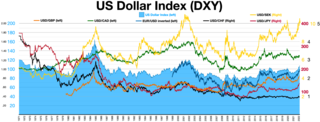
The foreign exchange market is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspects of buying, selling and exchanging currencies at current or determined prices. In terms of trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market.
Australian English is a major variety of the English language spoken throughout Australia. Most of the vocabulary of Australian English is shared with British English, though there are notable differences. The vocabulary of Australia is drawn from many sources, including various dialects of British English as well as Gaelic languages, some Indigenous Australian languages, and Polynesian languages.

Counterfeit money is currency produced without the legal sanction of a state or government, usually in a deliberate attempt to imitate that currency and so as to deceive its recipient. Producing or using counterfeit money is a form of fraud or forgery, and is illegal. The business of counterfeiting money is almost as old as money itself: plated copies have been found of Lydian coins, which are thought to be among the first Western coins. Before the introduction of paper money, the most prevalent method of counterfeiting involved mixing base metals with pure gold or silver. Another form of counterfeiting is the production of documents by legitimate printers in response to fraudulent instructions. During World War II, the Nazis forged British pounds and American dollars. Today some of the finest counterfeit banknotes are called Superdollars because of their high quality and imitation of the real US dollar. There has been significant counterfeiting of Euro banknotes and coins since the launch of the currency in 2002, but considerably less than that of the US dollar.
A currency pair is the dyadic quotation of the relative value of a currency unit against the unit of another currency in the foreign exchange market. The currency that is used as the reference is called the counter currency, quote currency, or currency and the currency that is quoted in relation is called the base currency or transaction currency.
Promotional fake United States currency is faux "currency" that makes no assertion of being legal tender. This money is often created by individuals as a way to promote practical jokes, or social statements. It is legal to print so long as it makes no assertion, whether by appearance or statement, of authenticity. Promotional United States fake currency is not to be confused with counterfeit currency or conflated with legitimate currency that has been demonetized.
In finance, specifically in foreign exchange markets, a percentage in point or price interest point (pip) is a unit of change in an exchange rate of a currency pair.

Hyperinflation in Zimbabwe is an ongoing period of currency instability in Zimbabwe that, using Cagan's definition of hyperinflation, began in February 2007. During the height of inflation from 2008 to 2009, it was difficult to measure Zimbabwe's hyperinflation because the government of Zimbabwe stopped filing official inflation statistics. However, Zimbabwe's peak month of inflation is estimated at 79.6 billion percent month-on-month, 89.7 sextillion percent year-on-year in mid-November 2008.

The United States dollar is the official currency of the United States and several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar, divided it into 100 cents, and authorized the minting of coins denominated in dollars and cents. U.S. banknotes are issued in the form of Federal Reserve Notes, popularly called greenbacks due to their predominantly green color.
A penny bun or a penny loaf was a small bread bun or loaf which cost one old penny at the time when there were 240 pence to the pound. A penny loaf was a common size loaf of bread in England regulated by the Assize of Bread and Ale act of 1266. The size of the loaf could vary depending on the prevailing cost of the flour used in the baking. The nursery rhyme London Bridge Is Falling Down has a version which includes the line "Build it up with penny loaves".
Slang terms for money often derive from the appearance and features of banknotes or coins, their values, historical associations or the units of currency concerned. Within a language community, some of the slang terms vary in social, ethnic, economic, and geographic strata but others have become the dominant way of referring to the currency and are regarded as mainstream, acceptable language.