



Land for cemeteries on mainland or peninsula were made available to the Europeans only.
The cemeteries on Coloane and Taipa were used by the Chinese of Macau. Some cemeteries have a view of sea, something desired by the Chinese.
Coloane
Taipa
For Chinese in Macau, the ashes of the deceased are not interred in cemeteries, but often placed in altars at various Buddhist temples throughout Macau.

Macau is a special administrative region (SAR) of the People's Republic of China. It was leased to Portugal in 1557 as a trading post in exchange for a symbolic annual rent of 500 tael. Despite remaining under Chinese sovereignty and authority, the Portuguese came to consider and administer Macau as a de facto colony. Following the signing of the Treaty of Nanking between China and Britain in 1842, and the signing of treaties between China and foreign powers during the 1860s, establishing the benefit of "the most favoured nation" for them, the Portuguese attempted to conclude a similar treaty in 1862, but the Chinese refused, owing to a misunderstanding over the sovereignty of Macau. In 1887 the Portuguese finally managed to secure an agreement from China that Macau was Portuguese territory. In 1999 it was handed over to China. Macau was the last extant European territory in continental Asia.

Macau is a Special Administrative Region on the southern coast of China. It is located at the south of Guangdong Province, on the tip of the peninsula formed by the Zhujiang estuary on the east and the Xijiang on the west. Macau is situated 60 km (37 mi) west of Hong Kong, and 145 km (90 mi) southwest of Guangzhou, the capital of Guangdong Province. It is situated immediately east and south of Zhuhai.

Transport in Macau includes road, sea, rail and air transport. Road transport is the primary mode of transport within Macau, although a new rail system opened in December 2019 serving the areas of Taipa and Cotai. The main forms of public transport are buses and taxis.

Macau International Airport is an international airport in the special administrative region of Macau, situated at the eastern end of Taipa island and neighbouring waters which opened for commercial operations on 9 November 1995, during Portuguese administration of the region.

Taipa is an area in Macau, connected to Coloane through the area known as Cotai, which is largely built from reclaimed land. Located on the northern half of the island, Taipa’s population is mostly suburban. Administratively, the boundaries of the traditional civil parish Freguesia de Nossa Senhora do Carmo are mostly coterminous with that of the former Taipa Island, except for a portion of the parish that lies on the island of Hengqin (Montanha), housing the campus of the University of Macau.

Coloane is the southernmost area in Macau, connected to Taipa through the area known as Cotai, which is largely built from reclaimed land. Known as “Lou Wan” in Cantonese, Coloane forms the southern part of Macau. Its population consists of several settlements dotted around the parish, such as Vila de Coloane, Hac Sa, Ká-Hó, and Cheoc Van. Administratively, the boundaries of the traditional civil parish of São Francisco Xavier are coterminous with that of Coloane.
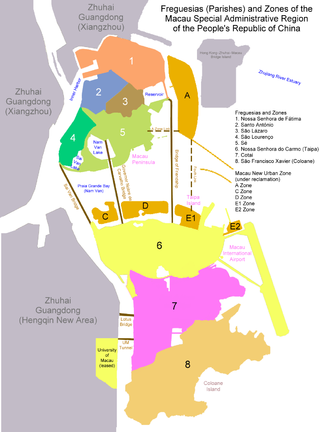
By the end of Portuguese rule, Macau was administratively divided into two municipalities and seven civil parishes. Parishes were administrative subdivisions of the municipalities. After the 1999 handover to China, parishes are still officially recognized divisions but for symbolic reasons only.

Tourism is a major industry in Macau. It is famous for the blend of Portuguese and Chinese cultures and its gambling industry, which includes Casino Lisboa, Macau, Sands Macau, The Venetian Macao, and Wynn Macau.

The Diocese of Macau is a Latin Church exempt ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church, in contrast with the Diocese of Hong Kong, which is, de jure, part of the Ecclesiastical Province of Guangdong.

Religion in Macau is represented predominantly by Buddhism and Chinese folk religions. During the period in which the city was under Portuguese rule (1557–1999) the Catholic Church became one of the dominant faiths, but nowadays it has greatly declined.

Macau Post and Telecommunications is an entity under the Government of Macao responsible for postal services and telecommunications regulation.

Wanzai, Small Hengqin and Great Hengqin are three islands located to the west of the Macau Peninsula and the Macau islands of Taipa and Coloane that were under Portuguese influence. They were inhabited by a very small Chinese population in its early history.

The Taipa Houses–Museum is housed in a set of old houses in Taipa, Macau, China.

Macau was a Portuguese colony from the establishment of the first official Portuguese settlement of Macau in 1557 to its handover to China in 1999. It comprised the Municipality of Macau and the Municipality of Ilhas. Macau was both the first and last European holding in China.

Freguesia de Nossa Senhora do Carmo is a civil parish in Macao Special Administrative Region. The major part of the freguesia is located in Taipa but it runs through to Hengqin Island in mainland China. The freguesia is named after the Igreja de Nossa Senhora do Carmo. It is the largest freguesia in Macau with an area of 7.9 square kilometers.

The Museum of Taipa and Coloane History is a museum in Taipa, Macau, China.

The Macao Public Library is the public library system of Macau. The head office is on the ground floor of the old building of the Sir Robert Ho Tung Library in São Lourenço.