
The Viceroyalty of Peru, officially known as the Kingdom of Peru, was a Spanish imperial provincial administrative district, created in 1542, that originally contained modern-day Peru and most of the Spanish Empire in South America, governed from the capital of Lima. Peru was one of the two Spanish viceroyalties in the Americas from the sixteenth to the eighteenth centuries.

The governor of the State of Yucatan is the head of the executive branch of the Mexican state of Yucatán, elected to a six-year-term and not eligible for reelection. The figure of the governor is established on the Constitution of the State of Yucatan on its Title Fifth. The term of the Governor begins on October 1 of the year of the election and finishes September 30, six years later.

The governor of Chiapas is the chief executive of the Mexican state of Chiapas. The state constitution stipulates a term of 6 years, to which governors can only be elected once. It also specifies the qualifications for becoming governor: a Mexican citizen by birth, aged at least 30 years old, and having not less than 5 years residency in Chiapas. The current governor is Rutilio Escandón from the MRN, who assumed the position in 2018.

List of Commanders-in-Chief of the Peruvian Army since the creation of that post on March 12, 1953.

Melchor Liñán y Cisneros was a Roman Catholic prelate who served as Archbishop of Lima (1677–1708), Archbishop of La Plata o Charcas (1672–1675), Bishop of Popayán (1667–1672), and Bishop of Santa Marta (1664–1668). He also served as Viceroy of Peru from July 7, 1678, to November 20, 1681.

Bernardino Fernández de Velasco, 6th Duke of Frias, Grandee of Spain,, was a Spanish nobleman and diplomat.

The Real Audiencia of Quito was an administrative unit in the Spanish Empire which had political, military, and religious jurisdiction over territories that today include Ecuador, parts of northern Peru, parts of southern Colombia and parts of northern Brazil. It was created by Royal Decree on 29 August 1563 by Philip II of Spain in the city of Guadalajara. It ended in 1822 with the incorporation of the area into the Republic of Gran Colombia.

Juan de Espinosa Medrano, known in history as Lunarejo, was an Indigenous cleric, sacred preacher, writer, playwright, theologian, archdeacon and polymath from the Viceroyalty of Peru. He is the most prominent figure of the Literary Baroque of Peru and one of the most important intellectuals from Colonial Spanish America.
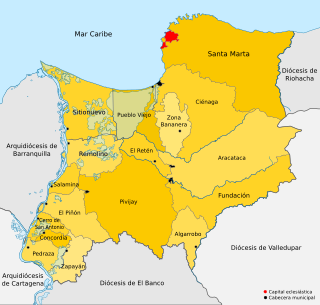
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Santa Marta is a diocese located in the city of Santa Marta in the ecclesiastical province of Barranquilla in Colombia.
The Cuzco Rebellion of 1814 was an episode of the Peruvian War of Independence led by the Angulo brothers and Mateo Pumacahua that took place in much of the province of Cuzco, including Huamanga, Arequipa and Puno, as well as part of the province of Charcas. The uprising involved the proclamation of the autonomy and self-government of Cuzco from the Viceroyalty of Peru, governed by Viceroy José Fernando de Abascal y Sousa. The junta was modelled and intended to follow the steps of the Junta of Buenos Aires.