Pulakeshi II popularly known as Immaḍi Pulakeśi, was the greatest Chalukyan Emperor who reigned from Vatapi. During his reign, the Chalukya empire expanded to cover most of the Deccan region in peninsular India.
Kirttivarman I was a ruler of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi in India. He ruled parts of present-day Karnataka, Goa, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh.
Pulakeshin was the first sovereign ruler of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi. He ruled parts of the present-day Maharashtra and Karnataka states in the western Deccan region of India. Pulakeshin established the city of Vatapi, and performed the Ashvamedha sacrifice to assert his sovereign status. The dynasty established by him went on to rule a major part of peninsular India in the subsequent years.
Mangalesha was a king of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi in Karnataka, India. He succeeded his brother Kirttivarman I on the throne, and ruled a kingdom that stretched from southern Gujarat in north to Bellary-Kurnool region in the south, in the western part of the Deccan region. It included parts of present-day Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
Vikramaditya I was the third son and followed his father, Pulakeshi II on to the Chalukya throne. He restored order in the fractured empire and made the Pallavas retreat from the capital Vatapi.
Shri Prithvi-vallabha, or Vallabha-rāja, was an imperial title used by several kings that ruled in present-day India, including the Chalukyas of Vatapi and the Rashtrakutas. It is a Kshatriya title that translates as "Lord of the Earth," or alternatively as "Husband of the Earth and Her Fortunes."
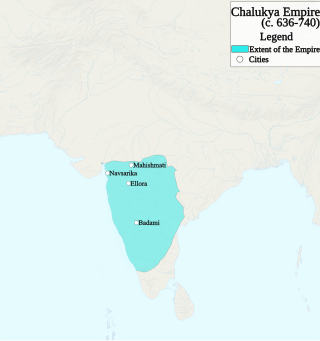
The Chalukya dynasty was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the "Badami Chalukyas", ruled from Vatapi from the middle of the 6th century. The Badami Chalukyas began to assert their independence at the decline of the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi and rapidly rose to prominence during the reign of Pulakeshin II. After the death of Pulakeshin II, the Eastern Chalukyas became an independent kingdom in the eastern Deccan. They ruled from Vengi until about the 11th century. In the western Deccan, the rise of the Rashtrakutas in the middle of the 8th century eclipsed the Chalukyas of Badami before being revived by their descendants, the Western Chalukyas, in the late 10th century. These Western Chalukyas ruled from Kalyani until the end of the 12th century.

Alampuram Navabrahma Temples are a group of nine early Badami Chalukyan Hindu temples dated between the 7th and 9th centuries that are located at Alampuram (Hemalapuram) in Telangana, India, near the meeting point of Tungabhadra River and Krishna River at the border of Andhra Pradesh. They are called Nava-Brahma temples though they are dedicated to Shiva. They exemplify early North Indian Nagara style architecture with cut rock as the building block. The temples of Alampur resemble the style of Pattadakal, Aihole style as they were Karnata Dravida, Vesara style native to Karnataka.
Bhoja dynasty also known as Bhojas of Goa, were a dynasty that ruled Goa, parts of Konkan, and some parts of Karnataka from at least the 3rd century AD to the 6th century. They were feudatories to the Mauryas of Konkana, and possibly to the Chalukyas of Vatapi who expelled the Mauryas. The Bhoja seat of power was located at Chandrapura or Chandraura in Goa.

The Chaulukya dynasty, also Solanki dynasty, was a dynasty that ruled the Kingdom of Gujarat in western India, between c. 940 CE and c. 1244 CE. Their capital was located at Anahilavada. At times, their rule extended to the Malwa region in present-day Madhya Pradesh. The family is also known as the "Solanki dynasty" in the vernacular literature. They belonged to the Solanki clan of Rajputs.
The Chalukyasof Navasarika were an Indian dynasty that ruled parts of present-day Gujarat and Maharashtra during 7th and 8th centuries, as vassals of the Chalukyas of Vatapi. They are also known as the "Early Chalukyas of Gujarat".
Jayasimha was the first ruler of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi in present-day India. He ruled the area around modern Bijapur in the early 6th century, and was the grandfather of the dynasty's first sovereign ruler, Pulakeshin I.
Ranaraga was an early 6th century ruler of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi in present-day India. A vassal ruler, he was the father of the dynasty's first sovereign ruler, Pulakeshin I.
Adityavarman was a king of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi in southern India. He was a son of Pulakeshin II, who was defeated and probably killed when the Pallavas invaded and captured the Chalukya capital Vatapi. The immediate history of the dynasty after Pulakeshin's death is not clear, but inscriptions of Adityavarman and his son suggest that Adityavarman ruled a weakened Chalukya kingdom for a short period, before his younger brother Vikramaditya I defeated the Pallavas and restored the Chalukya power.
Chandraditya was a king of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi that ruled in the Deccan region of peninsular India. His father Pulakeshin II was a powerful emperor, who was defeated and most probably killed during a Pallava invasion.
Vijaya-Bhattarika was a member of the Chalukya royal family of Deccan region in southern India. She is known from her Nerur and Kochre grant inscriptions, which call her Vijaya-Bhattarika and Vijaya-Mahadevi respectively.
Abhinavaditya was a king of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi in southern India. He appears to have succeeded his father Adityavarman on the weakened Chalukya throne, in the period following the death of his grandfather Pulakeshin II. He appears to have died heirless, and was probably succeeded by his uncle Chandraditya.
Revatidvipa or Govapuri was a province under the Chalukya dynasty, encompassing parts of modern-day Goa and Maharashtra, India. Revatidvipa was an important trading port of the dynasties that controlled it, including the Chalukyas. It was conquered by the Rashtrakuta ruler Krishna I in 753 AD.
The Battle of Narmada was fought between king Pulakeshin II of Chalukya dynasty and king Harshavardhana of Pushyabhuti dynasty on the banks of the river Narmada, India. The battle resulted in the great victory of Pulakeshin II and the retreat of Harsha and his forces
The Maurya dynasty ruled the coastal Konkan region in present-day Goa and Maharashtra states of India, between the 4th and the 7th centuries. Their capital was Puri, which is variously identified as Gharapuri (Elephanta), Salsette, or Rajapuri. The dynasty is known only from a few records, and there is very little clarity on its genealogy, chronology, territory, administration and political status.


