
The Bahamas are a group of about 700 islands and cays in the western Atlantic Ocean, of which only between 30 and 40 are inhabited. The largest of the islands is Andros Island, located north of Cuba and 200 kilometres southeast of Florida. The Bimini islands are to its northwest. To the North is the island of Grand Bahama, home to the second-largest city in the country, Freeport. The island of Great Abaco is to its east. In the far south is the island of Great Inagua, the second-largest island in the country. Other notable islands include Eleuthera, Cat Island, San Salvador Island, Acklins, Crooked Island, and Mayaguana. Nassau is the capital and largest city, located on New Providence. The islands have a tropical savannah climate, moderated by the Gulf Stream. The total size is 13,878 km2 (5,358 sq mi). Due to the many widespread islands it has the 41st largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 654,715 km2 (252,787 sq mi).
This article talks about transportation in the Bahamas, a North American archipelagic state in the Atlantic Ocean.

The Berry Islands are a chain of islands and a district of the Bahamas, covering about thirty square miles (78 km2) of the northwestern part of the Out Islands.

Andros Island is an archipelago within the Bahamas, the largest of the Bahamian Islands. Politically considered a single island, Andros in total has an area greater than all the other 700 Bahamian islands combined. The land area of Andros consists of hundreds of small islets and cays connected by mangrove estuaries and tidal swamplands, together with three major islands: North Andros, Mangrove Cay, and South Andros. The three main islands are separated by "bights", estuaries that trifurcate the island, connecting the island's east and west coasts. It is 167 kilometres (104 mi) long by 64 km (40 mi) wide at the widest point.

San Salvador Island is an island and district of the Bahamas. It is widely believed that during Christopher Columbus's first expedition to the New World, this island was the first land he sighted and visited on 12 October 1492. He named it San Salvador after Christ the Saviour. Columbus's records indicate that the native Lucayan inhabitants of the territory, who called their island Guanahani, were "sweet and gentle".

The Abaco Islands lie in the northern Bahamas, 180 miles off the South Florida coast. They comprise the main islands of Great Abaco and Little Abaco, along with smaller barrier cays. The northernmost are Walker's Cay, and its sister island Grand Cay. To the south, the next inhabited islands are Spanish Cay and Green Turtle Cay, with its settlement of New Plymouth, Great Guana Cay, private Scotland Cay, Man-O-War Cay, and Elbow Cay, with its settlement of Hope Town. Southernmost are Tilloo Cay and Lubbers Quarters. Another of note off Abaco's western shore is onetime Gorda Cay, now a Disney Island and cruise ship stop and renamed Castaway Cay. Also in the vicinity is Moore's Island. On the Big Island of Abaco is Marsh Harbour, the Abacos' commercial hub and the Bahamas' third largest city, plus the resort area of Treasure Cay. Both have airports. A few mainland settlements of significance are Coopers Town and Fox Town in the north and Cherokee and Sandy Point in the south. Administratively, the Abaco Islands constitute seven of the 31 Local Government Districts of the Bahamas: Grand Cay, North Abaco, Green Turtle Cay, Central Abaco, South Abaco, Moore's Island, and Hope Town.

A private island is a disconnected body of land wholly owned by a private citizen or corporation. Although this exclusivity gives the owner substantial control over the property, private islands remain under the jurisdiction of national and sometimes local governments.
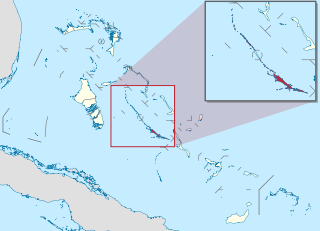
Exuma is a district of The Bahamas, consisting of over 365 islands, also called cays.

Castaway Cay is a private island in the Bahamas which serves as an exclusive port for the Disney Cruise Line ships. It is located near Great Abaco Island and was formerly known as Gorda Cay. In 1997, The Walt Disney Company purchased a 99-year land lease for the cay from the Bahamian government, giving the company substantial control over the island.

Ragged Island is a small island 23 km2 (8.9 sq mi) and district in the southern Bahamas. Ragged Island is part of the Jumentos Cays and Ragged Island Chain. The crescent-shaped chain measures over 180 km (110 mi) in length and includes cays known as Raccoon Cay, Hog Cay and Double-Breasted Cay. On 8 September 2017, Duncan Town took a direct hit from Hurricane Irma.

Rum Cay is an island and district of the Bahamas. It measures 30 square miles (78 km2) in area, it is located at Lat.: N23 42' 30" - Long.: W 74 50' 00". It has many rolling hills that rise to about 120 feet.

CocoCay or Little Stirrup Cay, Bahamas, is one of the Berry Islands, a collection of cays and small islands, and is located approximately 55 miles north of Nassau. It is used for tourism by Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd exclusively. Little Stirrup Cay is adjacent to Great Stirrup Cay, Norwegian Cruises' private island since 1977.

Great Stirrup Cay is a 268-acre (108 ha) island that is part of the Berry Islands in the Bahamas. Norwegian Cruise Line purchased the island from the Belcher Oil Company in 1977 and developed it into a private island for their cruise ship passengers. The northern part of the island has a sandy beach surrounded by rocks with snorkeling areas. The southern part features a helicopter airfield, a large area without vegetation, and numerous concrete blocks. These are all remnants of a previous U.S. military installation and satellite tracking station. The island's lighthouse was originally constructed in 1863 by the Imperial Lighthouse Service. Great Stirrup Cay is adjacent to Little Stirrup Cay, Royal Caribbean Cruises' private island.

The Cat Cays are two islands in the Bahamas, North Cat Cay and South Cat Cay, approximately 10 miles (16 km) south of Bimini. North Cat Cay is a privately owned island and is run as a private members club by the Cat Cay Yacht Club. South Cat Cay is currently under development.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to The Bahamas:

Princess Cays is a tourist resort at the southern end of the island of Eleuthera, Bahamas. It is owned by Carnival Corporation, which owns Princess Cruises, among others. Carnival Corporation also owns nearby Half Moon Cay. Contrary to the implication of its name, it is located on Eleuthera, rather than on separate islands.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the Commonwealth of The Bahamas.

Little Whale Cay is a small private island. Little Whale Cay is located 140 miles (230 km) southeast of Fort Lauderdale, Florida, in the Berry Islands chain of the Bahamas.

Hurricane Joaquin was a powerful tropical cyclone that devastated several districts of The Bahamas and caused damage in the Turks and Caicos Islands, parts of the Greater Antilles, and Bermuda. It was also the strongest Atlantic hurricane of non-tropical origin recorded in the satellite era. The tenth named storm, third hurricane, and second major hurricane of the 2015 Atlantic hurricane season, Joaquin evolved from a non-tropical low to become a tropical depression on September 28, well southwest of Bermuda. Tempered by unfavorable wind shear, the depression drifted southwestward. After becoming a tropical storm the next day, Joaquin underwent rapid intensification, reaching hurricane status on September 30 and Category 4 major hurricane strength on October 1. Meandering over the southern Bahamas, Joaquin's eye passed near or over several islands. On October 3, the hurricane weakened somewhat and accelerated to the northeast. Abrupt re-intensification ensued later that day, and Joaquin acquired sustained winds of 155 mph (250 km/h), just short of Category 5 strength.



















