
The economy of Canada is a highly developed mixed economy,with the world's tenth-largest economy as of 2023,and a nominal GDP of approximately US$2.117 trillion. Canada is one of the world's largest trading nations,with a highly globalized economy. In 2021,Canadian trade in goods and services reached $2.016 trillion. Canada's exports totalled over $637 billion,while its imported goods were worth over $631 billion,of which approximately $391 billion originated from the United States. In 2018,Canada had a trade deficit in goods of $22 billion and a trade deficit in services of $25 billion. The Toronto Stock Exchange is the tenth-largest stock exchange in the world by market capitalization,listing over 1,500 companies with a combined market capitalization of over US$3 trillion.

The economy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo has declined drastically around the 1980s,despite being home to vast potential in natural resources and mineral wealth;their gross domestic product is $69.474 billion as of 2023. During the last five reported years the exports of Democratic Republic of the Congo have changed by $15.2B from $13.3B in 2017 to $28.5B in 2022.

The economy of Eritrea has undergone extreme changes after the War of Independence. It experienced considerable growth in recent years,indicated by an improvement in gross domestic product in 2011 of 8.7 percent and in 2012 of 7.5% over 2011,and has a total of $8.090 billion as of 2020. However,worker remittances from abroad are estimated to account for 32 percent of gross domestic product.

Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic health of a country or region. Definitions of GDP are maintained by several national and international economic organizations,such as the OECD and the International Monetary Fund.

The economy of Senegal is driven by mining,construction,tourism,fishing and agriculture,which are the main sources of employment in rural areas,despite abundant natural resources in iron,zircon,gas,gold,phosphates,and numerous oil discoveries recently. Senegal's economy gains most of its foreign exchange from fish,phosphates,groundnuts,tourism,and services. As one of the dominant parts of the economy,the agricultural sector of Senegal is highly vulnerable to environmental conditions,such as variations in rainfall and climate change,and changes in world commodity prices.

The world economy or global economy is the economy of all humans in the world,referring to the global economic system,which includes all economic activities conducted both within and between nations,including production,consumption,economic management,work in general,financial transactions and trade of goods and services. In some contexts,the two terms are distinct:the "international" or "global economy" is measured separately and distinguished from national economies,while the "world economy" is simply an aggregate of the separate countries' measurements. Beyond the minimum standard concerning value in production,use and exchange,the definitions,representations,models and valuations of the world economy vary widely. It is inseparable from the geography and ecology of planet Earth.

Susan Strange was a British author,journalist,and scholar who was "almost single-handedly responsible for creating international political economy." Notable publications include Sterling and British Policy (1971),Casino Capitalism (1986),States and Markets (1988),The Retreat of the State (1996),and Mad Money (1998).

Dame Diane Coyle is a British economist. Since March 2018,she has been the Bennett Professor of Public Policy at the University of Cambridge,co-directing the Bennett Institute.
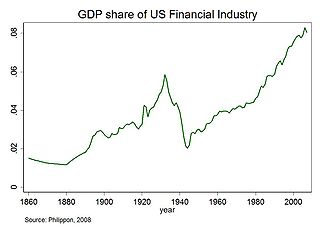
Financialization is a term sometimes used to describe the development of financial capitalism during the period from 1980 to present,in which debt-to-equity ratios increased and financial services accounted for an increasing share of national income relative to other sectors.
Simon Zadek is a writer and advisor focused on business and sustainability. He is the Co-Director of the UNEP Inquiry into the Design of a Sustainable Financial System.

The Five Star Movement is a political party in Italy. Its leader and president is Giuseppe Conte,who served as Prime Minister of Italy from 2018 until 2021. The party was founded on 4 October 2009 by Beppe Grillo,a political activist and comedian,and Gianroberto Casaleggio,a web strategist,and is primarily described as populist of the syncretic kind,due to its members' insistence that it has no place in the left–right political spectrum. The party is a proponent of green politics,direct democracy and,broadly,progressivism.
The Centre for the Study of Governance Innovation (GovInn) is a research centre of the University of Pretoria. It was launched at the International Studies Association annual conference on 6 April 2013 and then in South Africa on 20 May 2013 by the University of Pretoria,with a keynote lecture by political scientist and activist Susan George.
LSE Cities is a research centre at the London School of Economics and Political Science.
Julia Mary Black is the strategic director of innovation and a professor of law at the London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE). She was the interim director of the LSE,a post she held from September 2016 until September 2017,at which time Minouche Shafik took over the directorship. She is the president of the British Academy,the UK's national academy for the humanities and social sciences,and became the academy's second female president in July 2021 for a four-year term.
Science and technology in Botswana examines recent trends and developments in science,technology and innovation policy in this country. The Republic of Botswana was one of the first countries of the Southern African Development Community (SADC) to adopt a science and technology policy in 1998. This was later updated in 2011.
Malawi is one of the least developed countries in the world. But it spends 1% of its gross domestic product (GDP) on research and development (R&D),making it have one of the highest ratios in Africa. The country has 93% of its population still lacking access to electricity,47% of whom have improved sanitation,and one in four adults lacks any form of family planning.
This article examines trends and developments in science and technology in Zimbabwe since 2009.
Science and technology in Tanzania describes developments and trends in higher education,science,technology,innovation policy,and governance in the United Republic of Tanzania since the turn of the century.

The second Conte government was the 66th government of the Italian Republic and the second government led by Giuseppe Conte. The government was sworn in on 5 September 2019 to 13 February 2021.

Mattia Fantinati is an Italian politician. He was the Undersecretary of the State for Pubblic Administration and Member of Italian Parliament in the XVII and XVIII legislatures.














