
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in a brachial artery, where it is most commonly measured. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure over diastolic pressure in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in kilopascals (kPa). The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is known as pulse pressure, while the average pressure during a cardiac cycle is known as mean arterial pressure.
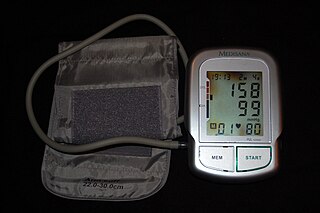
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. It is, however, a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide.

The renin–angiotensin system (RAS), or renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure, fluid and electrolyte balance, and systemic vascular resistance.

Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex to promote sodium retention by the kidneys.
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke, heart failure, kidney failure and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34% and of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and can reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used medications are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.

Ramipril, sold under the brand name Altace among others, is an ACE inhibitor type medication used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease. It can also be used as a preventative medication in patients over 55 years old to reduce the risk of having a heart attack, stroke or cardiovascular death in patients shown to be at high risk, such as some diabetics and patients with vascular disease. It is a reasonable initial treatment for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth.

Potassium-sparing diuretics refers to drugs that cause diuresis without causing potassium loss in the urine. They are typically used as an adjunct in management of hypertension, cirrhosis, and congestive heart failure. The steroidal aldosterone antagonists can also be used for treatment of primary hyperaldosteronism. Spironolactone, a steroidal aldosterone antagonist, is also used in management of female hirsutism and acne from PCOS or other causes.
Secondary hypertension is a type of hypertension which by definition is caused by an identifiable underlying primary cause. It is much less common than the other type, called essential hypertension, affecting only 5-10% of hypertensive patients. It has many different causes including endocrine diseases, kidney diseases, and tumors. It also can be a side effect of many medications.

Hypertensive heart disease includes a number of complications of high blood pressure that affect the heart. While there are several definitions of hypertensive heart disease in the medical literature, the term is most widely used in the context of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) coding categories. The definition includes heart failure and other cardiac complications of hypertension when a causal relationship between the heart disease and hypertension is stated or implied on the death certificate. In 2013 hypertensive heart disease resulted in 1.07 million deaths as compared with 630,000 deaths in 1990.

Eplerenone, sold under the brand name Inspra, is an aldosterone antagonist type of potassium-sparing diuretic that is used to treat chronic heart failure and high blood pressure, particularly for patients with resistant hypertension due to elevated aldosterone. It is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group and a selective aldosterone receptor antagonist (SARA). Eplerenone is more selective than spironolactone at the mineralocorticoid receptor relative to binding at androgen, progestogen, glucocorticoid, or estrogen receptors.

Aldosterone synthase, also called steroid 18-hydroxylase, corticosterone 18-monooxygenase or P450C18, is a steroid hydroxylase cytochrome P450 enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone and other steroids. The enzyme catalyzes sequential hydroxylations of the steroid angular methyl group at C18 after initial 11β-hydroxylation. It is encoded by the CYP11B2 gene in humans.

Aliskiren is the first in a class of drugs called direct renin inhibitors. It is used for essential (primary) hypertension. While used for high blood pressure, other better studied medications are typically recommended due to concerns of higher side effects and less evidence of benefit.

Renin inhibitors are pharmaceutical drugs inhibiting the activity of renin that is responsible for hydrolyzing angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which in turn reduces the formation of angiotensin II that facilitates blood pressure.
Naproxcinod (nitronaproxen) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) developed by the French pharmaceutical company NicOx. It is a derivative of naproxen with a nitroxybutyl ester to allow it to also act as a nitric oxide (NO) donor. This second mechanism of action makes naproxcinod the first in a new class of drugs, the cyclooxygenase inhibiting nitric oxide donators (CINODs), that are hoped to produce similar analgesic efficacy to traditional NSAIDs, but with less gastrointestinal and cardiovascular side effects.
CYT006-AngQb was an investigational vaccine against angiotensin II, designed to lower blood pressure. It was somewhat effective in clinical trials, but less so than conventional drugs against hypertension.

Evacetrapib was a drug under development by Eli Lilly & Company that inhibits cholesterylester transfer protein. CETP collects triglycerides from very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) or low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and exchanges them for cholesteryl esters from high-density lipoproteins (HDL), and vice versa, but primarily increasing high-density lipoprotein and lowering low-density lipoprotein. It is thought that modifying lipoprotein levels modifies the risk of cardiovascular disease. The first CETP inhibitor, torcetrapib, was unsuccessful because it increased levels of the hormone aldosterone and increased blood pressure, which led to excess cardiac events when it was studied. Evacetrapib does not have the same effect. When studied in a small clinical trial in people with elevated LDL and low HDL, significant improvements were noted in their lipid profile.
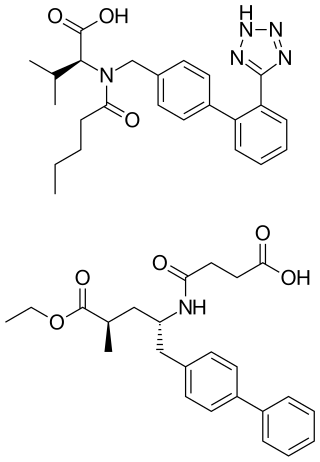
Sacubitril/valsartan, sold under the brand name Entresto, is a fixed-dose combination medication for use in heart failure. It consists of the neprilysin inhibitor sacubitril and the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan. The combination is sometimes described as an "angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor" (ARNi). In 2016, the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force recommended it as a replacement for an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker in people with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
Renal sympathetic denervation (RSDN) is a minimally invasive, endovascular catheter based procedure using radiofrequency ablation or ultrasound ablation aimed at treating resistant hypertension. Nerves in the wall of the renal artery are ablated by applying radiofrequency pulses or ultrasound to the renal arteries. This causes reduction of sympathetic afferent and efferent activity to the kidney and blood pressure can be decreased. Early data from international clinical trials without sham controls was promising - demonstrating large blood pressure reductions in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension. However, in 2014 a prospective, single-blind, randomized, sham-controlled clinical trial failed to confirm a beneficial effect on blood pressure. A 2014 consensus statement from The Joint UK Societies did not recommend the use of renal denervation for treatment of resistant hypertension on current evidence. More recent sham-controlled trials suggest renal denervation can lead to lower systolic blood pressure.
Refractory Hypertension, also known as a refractory hypertensive state, RfHTN, or status angiotensus, is a hypertensive condition which can occur, for no apparent reason, in patients with previously well-managed hypertension. Refractory hypertension is characterized by a blood pressure that remains uncontrolled on maximal or near-maximal therapy, which is the use of ≥5 antihypertensive agents of different classes, including a long-acting thiazide-like diuretic and spironolactone. Patients with refractory hypertension typically exhibit increased sympathetic nervous system activity. The phenotype of refractory hypertension was first proposed in a retrospective analysis of patients referred to the University of Alabama at Birmingham Hypertension Clinic whose blood pressure could not be controlled on any antihypertensive regimen.

Baxdrostat is an investigational drug that is being evaluated for the treatment of hypertension. It is an aldosterone synthase inhibitor.












