
The Ykok leader or M-box is a Mg2+-sensing RNA structure that controls the expression of Magnesium ion transport proteins in bacteria. It is a distinct structure to the Magnesium responsive RNA element.

The Actino-ugpB RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Actino-ugpB motifs are found in strains of the species Gardnerella vaginalis, within the phylum Actinomycetota.

The COG2908 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. COG2908 motif RNAs are found in genomic sequences extracted from fresh water environments. They have not, as of 2018, been detected in any classified organism.

The DUF2693-FD RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF2693-FD RNAs are found in Bacteroides, and occur far downstream (FD), i.e., hundreds of DNA base pairs, of genes that encode proteins containing the DUF2693 conserved protein domain. This domain is annotated as being associated with phages. Another motif predicted by bioinformatics is typically located upstream of DUF2693-encoding genes: the DUF2693 RNA motif. However, no case has been observed in which a DUF2693 RNA and a DUF2693-FD RNA flank the same specific gene.
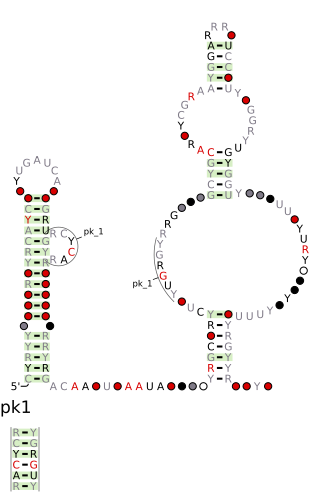
The DUF2800 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF2800 motif RNAs are found in Bacillota. DUF2800 RNAs are also predicted in the phyla Actinomycetota and Synergistota, although these RNAs are likely the result of recent horizontal gene transfer or conceivably sequence contamination.

The DUF3577 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF3577 motifs are found in the organism Cardiobacterium valvarum and metagenomic sequences from unknown organisms.

The DUF805 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The motif is subdivided into the DUF805 motif and the DUF805b motif, which have similar, but distinct secondary structures. Together, these motifs are found in Bacteroidota, Chlorobiota, and Pseudomonadota.
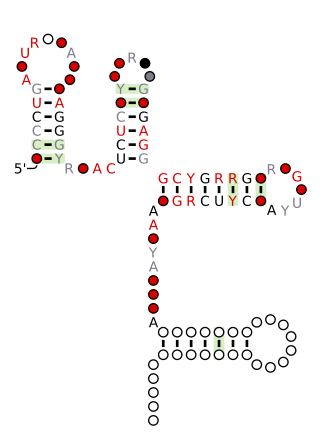
The engA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. engA motifs are found in bacteria within the genus Prevotella.

The GA-cis RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. GA-cis motif RNAs are found in one species classified within the phylum Bacillota: specifically, there are 9 predicted copies in Coprocuccus eutactus ATCC 27759.

The hya RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. hya motif RNAs are found in Actinomycetota.
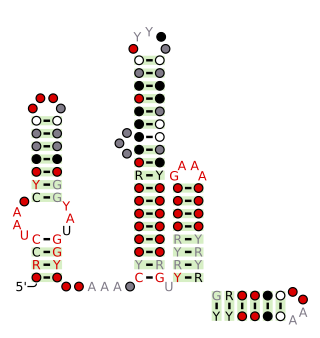
The Latescibacteria, OD1, OP11, TM7 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. LOOT motif RNAs are found in multiple bacterial phyla that have only recently been discovered, and are currently not well understood: Latescibacteria, OD1/Parcubacteria, OP11 AND TM7. In some cases, no specific organism has been isolated in the relevant phylum, but the existence of the bacterial phylum is known only through analysis of metagenomic sequences. Curiously, the LOOT motif is not known in any phylum that has been studied for a long time.
malK RNA motifs are conserved RNA structures that were discovered by bioinformatics. They are defined by being consistently located upstream of malK genes, which encode an ATPase that is used by transporters whose ligand is likely a kind of sugar. Most of these genes are annotated either as transporting maltose or glycerol-3-phosphate, however the substrate of the transporters associated with malK motif RNAs has not been experimentally determined. All known types of malK RNA motif are generally located nearby to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence of the downstream gene.

The MDR-NUDIX RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The MDR-NUDIX motif is found in the poorly studied phylum TM7.

The NLPC-P60 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. NLPC-P60 motif RNAs are found in Streptomyces.
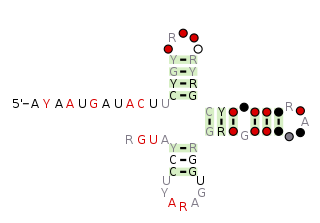
The pemK RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. pemK motif RNAs are found in organisms within the phylum Bacillota, and is very widespread in this phylum.

The PGK RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. PGK motif RNAs are found in metagenomic sequences isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of mammals. PGK RNAs have not yet been detected in a classified organism.
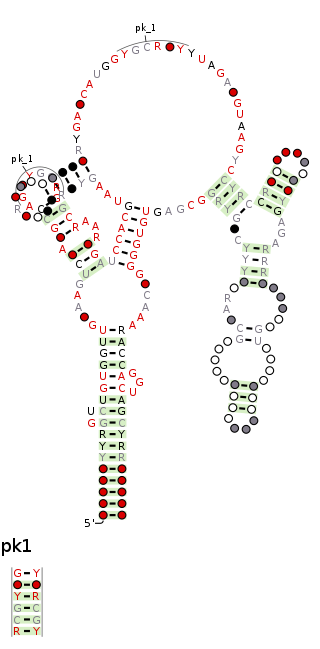
The raiA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. raiA motif RNAs are found in Actinomycetota and Bacillota, and have many conserved features—including conserved nucleotide positions, conserved secondary structures and associated protein-coding genes—in both of these phyla. Some conserved features of the raiA RNA motif suggest that they function as cis-regulatory elements, but other aspects of the motif suggest otherwise.

The sul1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Energetically stable tetraloops often occur in this motif. sul1 motif RNAs are found in Alphaproteobacteria.

The terC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. terC motif RNAs are found in Pseudomonadota, within the sub-lineages Alphaproteobacteria and Pseudomonadales.

The uup RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. uup motif RNAs are found in Bacillota and Gammaproteobacteria.





















