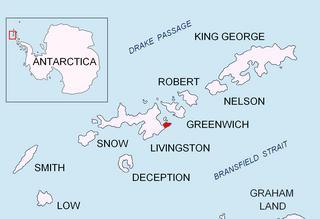
Lyutitsa Nunatak (Nunatak Lyutitsa \'nu-na-tak lyu-'ti-tsa\) is a rocky peak of elevation 430 m projecting from the ice cap in Breznik Heights on Greenwich Island, Antarctica. Overlooking Musala Glacier to the north, east, and south. Bulgarian topographic survey Tangra 2004/05.

Breznik Heights rises to over 600 m in the southeast part of Greenwich Island in Antarctica. They extend 12 km between Santa Cruz Point in the northeast and the base of the moraine spit of Provadiya Hook at the mouth of Yankee Harbour in the southwest. The heights are ice-covered except for limited precipitous areas such as those at Oborishte Ridge, Ephraim Bluff, Viskyar Ridge and Bogdan Ridge.

Greenwich Island is an island 24 km (15 mi) long and from 0.80 to 9.66 km wide, lying between Robert Island and Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands. Surface area 142.7 square kilometres (55.1 sq mi). The name Greenwich Island dates back to at least 1821 and is now established in international usage.

Antarctica is Earth's southernmost continent. It contains the geographic South Pole and is situated in the Antarctic region of the Southern Hemisphere, almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle, and is surrounded by the Southern Ocean. At 14,200,000 square kilometres, it is the fifth-largest continent. For comparison, Antarctica is nearly twice the size of Australia. At 0.00008 people per square kilometre, it is by far the least densely populated continent. About 98% of Antarctica is covered by ice that averages 1.9 km in thickness, which extends to all but the northernmost reaches of the Antarctic Peninsula.
Contents
The feature is named after the medieval fortress of Lyutitsa in the Eastern Rhodope Mountains, Bulgaria.

The Rhodopes are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, with over 83% of its area in southern Bulgaria and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at 2,191 meters (7,188 ft). The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests Biome and the Palearctic ecozone. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge.

Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. The capital and largest city is Sofia; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. With a territory of 110,994 square kilometres (42,855 sq mi), Bulgaria is Europe's 16th-largest country.