Related Research Articles

In mathematics, the Klein bottle is an example of a non-orientable surface; that is, informally, a one-sided surface which, if traveled upon, could be followed back to the point of origin while flipping the traveler upside down. More formally, the Klein bottle is a two-dimensional manifold on which one cannot define a normal vector at each point that varies continuously over the whole manifold. Other related non-orientable surfaces include the Möbius strip and the real projective plane. While a Möbius strip is a surface with a boundary, a Klein bottle has no boundary. For comparison, a sphere is an orientable surface with no boundary.
The Möbius function μ(n) is a multiplicative function in number theory introduced by the German mathematician August Ferdinand Möbius (also transliterated Moebius) in 1832. It is ubiquitous in elementary and analytic number theory and most often appears as part of its namesake the Möbius inversion formula. Following work of Gian-Carlo Rota in the 1960s, generalizations of the Möbius function were introduced into combinatorics, and are similarly denoted μ(x).

In mathematics, a Möbius strip, Möbius band, or Möbius loop is a surface that can be formed by attaching the ends of a strip of paper together with a half-twist. As a mathematical object, it was discovered by Johann Benedict Listing and August Ferdinand Möbius in 1858, but it had already appeared in Roman mosaics from the third century CE. The Möbius strip is a non-orientable surface, meaning that within it one cannot consistently distinguish clockwise from counterclockwise turns. Every non-orientable surface contains a Möbius strip.

August Ferdinand Möbius was a German mathematician and theoretical astronomer.

A biocenosis, coined by Karl Möbius in 1877, describes the interacting organisms living together in a habitat (biotope). The use of this term has declined in the 21st сentury.
In geometry and complex analysis, a Möbius transformation of the complex plane is a rational function of the form
Blumberg's sign is a clinical sign in which there is pain upon removal of pressure rather than application of pressure to the abdomen. It is indicative of peritonitis. It was named after German surgeon Jacob Moritz Blumberg.

The universal recycling symbol is a symbol consisting of three chasing arrows folded in a Möbius strip. It is an internationally recognized symbol for recycling. The symbol originated on the first Earth Day in 1970, created by Gary Anderson, then a 23-year-old student for the Container Corporation of America. The symbol is not trademarked and is in the public domain. Many variations on the logo have been created since its creation.
Necroscope is the title of a series of horror novels by British author Brian Lumley.
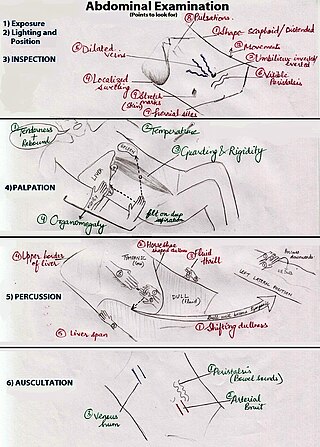
An abdominal examination is a portion of the physical examination which a physician or nurse uses to clinically observe the abdomen of a patient for signs of disease. The abdominal examination is conventionally split into four different stages: first, inspection of the patient and the visible characteristics of their abdomen. Auscultation (listening) of the abdomen with a stethoscope. Palpation of the patient's abdomen. Finally, percussion (tapping) of the patient's abdomen and abdominal organs. Depending on the need to test for specific diseases such as ascites, special tests may be performed as a part of the physical examination. An abdominal examination may be performed because the physician suspects a disease of the organs inside the abdominal cavity (including the liver, spleen, large or small intestines), or simply as a part of a complete physical examination for other conditions. In a complete physical examination, the abdominal exam classically follows the respiratory examination and cardiovascular examination.
In medicine, Homans' sign is considered by some physicians to be a sign of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). It was defined by John Homans in 1941 as discomfort behind the knee upon forced dorsiflexion of the foot. After many examples of false-positive Homans' signs were reported, Homans redefined it in 1944, stating that "discomfort need have no part in the reaction", and that increased resistance, involuntary flexure of the knee or pain in the calf upon forced dorsiflexion should be considered positive responses.

A pulmonary consolidation is a region of normally compressible lung tissue that has filled with liquid instead of air. The condition is marked by induration of a normally aerated lung. It is considered a radiologic sign. Consolidation occurs through accumulation of inflammatory cellular exudate in the alveoli and adjoining ducts. The liquid can be pulmonary edema, inflammatory exudate, pus, inhaled water, or blood. Consolidation must be present to diagnose pneumonia: the signs of lobar pneumonia are characteristic and clinically referred to as consolidation.

Castell's sign is a medical sign assessed to evaluate splenomegaly and typically part of an abdominal examination. It is an alternative physical examination maneuver to percussion over Traube's space.
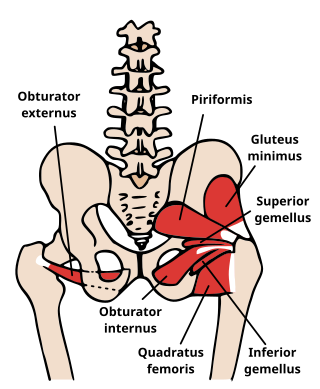
The obturator sign, also called Cope's obturator test, is an indicator of irritation to the obturator internus muscle.

Paul Julius Möbius was a German neurologist born in Leipzig. His grandfather was German mathematician and theoretical astronomer, August Ferdinand Möbius (1790–1868).

In geometry, a uniform star polyhedron is a self-intersecting uniform polyhedron. They are also sometimes called nonconvex polyhedra to imply self-intersecting. Each polyhedron can contain either star polygon faces, star polygon vertex figures, or both.
Lethargy is a state of tiredness, sleepiness, weariness, fatigue, sluggishness or lack of energy. It can be accompanied by depression, decreased motivation, or apathy. Lethargy can be a normal response to inadequate sleep, overexertion, overworking, stress, lack of exercise, improper nutrition, drug abuse, boredom, or a symptom of an underlying illness or a disorder. It may also be a side-effect of medication or caused by an interaction between medications or medication(s) and alcohol. It may also be an altered level of consciousness.
Bancroft's sign, also known as Moses' sign, is a clinical sign found in patients with deep vein thrombosis of the lower leg involving the posterior tibial veins. The sign is positive if pain is elicited when the calf muscle is compressed forwards against the tibia, but not when the calf muscle is compressed from side to side. Like other clinical signs for deep vein thrombosis, such as Homans sign and Lowenberg's sign, this sign is neither sensitive nor specific for the presence of thrombosis.
Lowenberg's sign is a clinical sign found in patients with deep vein thrombosis of the lower leg. The sign is positive when pain is elicited rapidly when a blood pressure cuff is placed around the calf and inflated to 80mmHg. Like other signs of deep vein thrombosis, such as Homans sign and Bancroft's sign, this sign is neither sensitive nor specific for the presence of thrombosis.
In chemistry, the Möbius–Hückel treatment is a methodology used to predict whether a reaction is allowed or forbidden. It is often used along with the Woodward–Hoffmann approach. The description in this article uses the plus-minus sign notation for parity as shorthand while proceeding around a cycle of orbitals in a molecule or system, while the Woodward–Hoffmann methodology uses a large number of rules with the same consequences.
References
- ↑ "Moebius syndrome". Genetics Home Reference. Retrieved 2020-08-17.
- ↑ Möbius sign at TheFreeDictionary.com
- ↑ White, Michele C. (2009-04-15). Physical Signs in Medicine and Surgery: An Atlas of Rare, Lost and Forgotten Physical Signs. Xlibris Corporation. ISBN 9781453502211.
- ↑ Pryse-Phillips, William (2003). Companion to Clinical Neurology. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195159387.