Related Research Articles
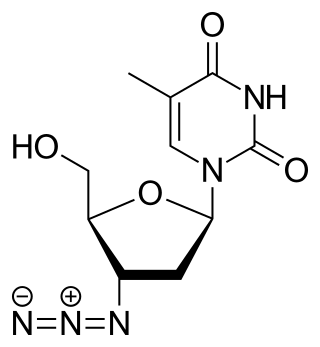
Zidovudine (ZDV), also known as azidothymidine (AZT), was the first antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use in combination with other antiretrovirals. It may be used to prevent mother-to-child spread during birth or after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. It is sold both by itself and together as lamivudine/zidovudine and abacavir/lamivudine/zidovudine. It can be used by mouth or by slow injection into a vein.
The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs as a strategy to control HIV infection. There are several classes of antiretroviral agents that act on different stages of the HIV life-cycle. The use of multiple drugs that act on different viral targets is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). HAART decreases the patient's total burden of HIV, maintains function of the immune system, and prevents opportunistic infections that often lead to death. HAART also prevents the transmission of HIV between serodiscordant same-sex and opposite-sex partners so long as the HIV-positive partner maintains an undetectable viral load.
The spread of HIV/AIDS has affected millions of people worldwide; AIDS is considered a pandemic. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that in 2016 there were 36.7 million people worldwide living with HIV/AIDS, with 1.8 million new HIV infections per year and 1 million deaths due to AIDS. Misconceptions about HIV and AIDS arise from several different sources, from simple ignorance and misunderstandings about scientific knowledge regarding HIV infections and the cause of AIDS to misinformation propagated by individuals and groups with ideological stances that deny a causative relationship between HIV infection and the development of AIDS. Below is a list and explanations of some common misconceptions and their rebuttals.

Lamivudine/zidovudine, sold under the brand name Combivir among others, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication used to treat HIV/AIDS. It contains two antiretroviral medications, lamivudine and zidovudine. It is used together with other antiretrovirals. It is taken by mouth twice a day.
The Centennial Biomedical Campus is 250 acres (1.0 km2) of property owned and operated by North Carolina State University in Raleigh, North Carolina, United States. It is located five minutes west of the NC State's main campus and is considered part of Centennial Campus, the university's research and educational campus.
North Carolina State University College of Veterinary Medicine is an American educational institution located in Raleigh, North Carolina that offers master's and doctorate-level degree programs; interdisciplinary research in a range of veterinary and comparative medicine topics through centers, institutes, programs and laboratories; and external engagement through public service programs and activities.

Janice Ellen Clements is vice dean for faculty at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and the Mary Wallace Stanton Professor of Faculty Affairs. She is a professor in the departments of Molecular and Comparative Pathobiology, Neurology, and Pathology, and has a joint appointment in molecular biology and genetics. Her molecular biology and virology research examines lentiviruses and how they cause neurological diseases.
Opendra "Bill" Narayan was an HIV/AIDS researcher at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and the University of Kansas Medical Center. A veterinarian, Narayan researched animal models of HIV. His focus on finding a vaccine for retroviral infection had some success against a monkey retrovirus, SIV, and he is best known for engineering a type of HIV that could cause AIDS-like disease in monkeys.
Robert F. Siliciano is a professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and an investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Siliciano (sill-ih-CAH-noh) has a joint appointment in the Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics at Johns Hopkins. Siliciano researches the mechanisms by which the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) remains latent in the human body.
Joel N. Blankson is a professor at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in the Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases. Blankson is an expert on HIV infection, particularly HIV latency and long-term control of HIV infection. He is a lead investigator in studies on these topics and is frequently interviewed in the scientific and popular press. Blankson also practices internal and infectious diseases medicine in Lutherville, Maryland.

Steffanie A. Strathdee is a Harold Simon Distinguished Professor at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Co-Director at the Center for Innovative Phage Applications and Therapeutics. She is known for her work on HIV research and prevention programmes in Tijuana.
Stuart C. Ray is an American physician. He is Vice Chair of Medicine for Data Integrity and Analytics, Associate Director of the Infectious Diseases Fellowship Training Program at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and a Professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases. Ray also holds appointments in Viral Oncology and the Division of Health Sciences Informatics. He is affiliated with the Institute for Computational Medicine at Johns Hopkins and is licensed to practice medicine in Maryland.
Julio S. G. Montaner is an Argentine-born Canadian physician, professor and researcher. He is the director of the British Columbia Centre for Excellence in HIV/AIDS, the chair in AIDS Research and head of the Division of AIDS in the Faculty of Medicine at the University of British Columbia and the past-president of the International AIDS Society. He is also the director of the John Ruedy Immunodeficiency Clinic, and the Physician Program Director for HIV/AIDS PHC. He is known for his work on HAART, a role in the discovery of triple therapy as an effective treatment for HIV in the late 1990s, and a role in advocating the "Treatment as Prevention" Strategy in the mid-2000s, led by Myron Cohen of the HPTN 052 trial.
Deborah Persaud is a Guyanese-born American virologist who primarily works on HIV/AIDS at Johns Hopkins Children's Center.

Elaine Ann Ostrander is an American geneticist at the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in Bethesda, Maryland. She holds a number of professional academic appointments, currently serving as Distinguished and Senior Investigator and head of the NHGRI Section of Comparative Genomics; and Chief of the Cancer Genetics and Comparative Genomics Branch. She is known for her research on prostate cancer susceptibility in humans and for conducting genetic investigations with the Canis familiaris —the domestic dog— model, which she has used to study disease susceptibility and frequency and other aspects of natural variation across mammals. In 2007, her laboratory showed that much of the variation in body size of domestic dogs is due to sequence changes in a single gene encoding a growth-promoting protein.

Kenneth W. Witwer is an associate professor of molecular and comparative pathobiology and neurology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. He is President of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV) and previously served as Secretary General and Executive Chair of Science and Meetings of the society. His laboratory studies extracellular vesicles (EVs), noncoding and extracellular RNA (exRNA), and enveloped viruses, including HIV and SARS-CoV-2. Witwer is the managing editor of the journal Cytotherapy and a member of the Richman Family Precision Medicine Center of Excellence in Alzheimer's Disease. He has advised the US Environmental Protection Agency and the US National Institutes of Health and is an associate editor of the Journal of Extracellular Vesicles.
Janet K. Yamamoto is an American immunologist. Yanamoto is a professor of veterinary medicine at the University of Florida where she studies the spread of HIV/AIDS. In 1988, she co-developed a vaccine for the feline version of HIV with Niels C. Pederson and was subsequently elected to the National Academy of Inventors.

Charles Williams Flexner is an American physician, clinical pharmaceutical scientist, academic, author and researcher. He is a Professor of Medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
John Gill Bartlett was an American physician and medical researcher, specializing in infectious diseases. He is known as a pioneer in HIV/AIDS research and for his work on vancomycin as a treatment for Clostridioides difficile infection.
Jean Nachega is a Congolese American physician who is an Associate Professor of Medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. He is an infectious diseases doctor with a focus on improving the public health outcomes of people infected with HIV/AIDS. He is a Fellow of the African Academy of Sciences.
References
- ↑ Dinoso, J.; Rabi, S.; Blankson, J.; Gama, L.; Mankowski, J.; Siliciano, R.; Zink, M.; Clements, J. (2009). "A Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Macaque Model To Study Viral Reservoirs That Persist during Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy". Journal of Virology. 83 (18): 9247–9257. doi:10.1128/JVI.00840-09. PMC 2738256 . PMID 19570871.
- ↑ Zink MC, Uhrlaub J, DeWitt J, Voelker T, Bullock B, Mankowski J, Tarwater P, Clements J, Barber S (April 2005). "Neuroprotective and anti-human immunodeficiency virus activity of minocycline". JAMA. 293 (16): 2003–11. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.16.2003 . PMID 15855434.
- ↑ Johns Hopkins faculty profile Archived 2010-06-19 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Common Antibiotic May Fight HIV Brain Disease" Miranda Hitti, WebMD, April 26, 2005 on: foxnews.com
- 1 2 Canine Sports Archived 2009-02-27 at the Wayback Machine
- 1 2 "One dog's stem-cell venture" The Toronto Star, Barbara Turnbull, July 18, 2009
- ↑ "On the Move: Vet of the Year, M. Christine Zink of Johns Hopkins in Maryland," The Daily Record, Baltimore, Maryland, July 24, 2009.
- ↑ Chris Zink's Photography Website Archived 2011-07-08 at the Wayback Machine
- 1 2 3 4 JHU NIMH researchers profile Archived 2010-04-17 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "The Department of Molecular & Comparative Pathobiology". www.hopkinsmedicine.org. Archived from the original on 2010-04-14. Retrieved 2009-08-28.