
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of being launched from submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), each of which carries a nuclear warhead and allows a single launched missile to strike several targets. Submarine-launched ballistic missiles operate in a different way from submarine-launched cruise missiles.

A ballistic missile submarine is a submarine capable of deploying submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) with nuclear warheads. The United States Navy's hull classification symbols for ballistic missile submarines are SSB and SSBN – the SS denotes submarine, the B denotes ballistic missile, and the N denotes that the submarine is nuclear powered. These submarines became a major weapon system in the Cold War because of their nuclear deterrence capability. They can fire missiles thousands of kilometers from their targets, and acoustic quieting makes them difficult to detect, thus making them a survivable deterrent in the event of a first strike and a key element of the mutual assured destruction policy of nuclear deterrence.

The R-39 Rif was a submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) that served with the Soviet Navy from its introduction in 1983 until 1991, after which it served with the Russian Navy until 2004. The missile had GRAU indices of 3M65, 3M20, and 3R65. It was carried on board Typhoon-class submarines.

The Typhoon class, Soviet designation Project 941 Akula, is a class of nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines designed and built by the Soviet Union for the Soviet Navy. With a submerged displacement of 48,000 tonnes, the Typhoons are the largest submarines ever built, able to accommodate comfortable living facilities for the crew of 160 when submerged for months on end. The source of the NATO reporting name remains unclear, although it is often claimed to be related to the use of the word "typhoon" ("тайфун") by General Secretary Leonid Brezhnev of the Communist Party in a 1974 speech while describing a new type of nuclear ballistic missile submarine, as a reaction to the United States Navy's new Ohio-class submarine.
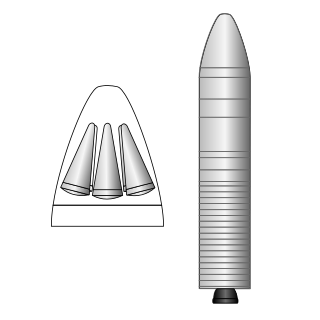
The M45 SLBM was a French Navy submarine-launched ballistic missile Forty-eight M45 were in commission in the Force océanique stratégique, the submarine nuclear deterrent component of the French Navy. The missiles, derived from the M4, were produced by Aérospatiale. Initially, an ICBM land-based version was considered, but these plans were discarded in 1996 to favour an all-naval deployment.

L'Inflexible is the sixth and final of the Redoutable-class SNLE of the Force océanique stratégique (FOST), the submarine nuclear deterrent component of the French Navy.

Project 629, also known by the NATO reporting name Golf, was a class of diesel-electric ballistic missile submarines that served in the Soviet Navy. All boats of this class had left Soviet service by 1990, and have since been disposed of. According to some sources, at least one Golf-class submarine was operated by China, to test new submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs).

The Le Redoutable-class submarine was a ballistic missile submarine class of the French Navy. In French, the type is called Sous-marin Nucléaire Lanceur d'Engins (SNLE), literally "Missile-launching nuclear submarine". When commissioned, they constituted the strategic part of the naval component of the French nuclear triad, then called Force de frappe.

The M51 SLBM is a French submarine-launched ballistic missile, built by ArianeGroup, and deployed with the French Navy. Designed to replace the M45 SLBM, it was first deployed in 2010.

The Strategic Ocean Force has been the synonym of the French Submarine Forces since 1999, which the commandant commands the ensemble related to, along with the squadron of nuclear attack submarine.

A nuclear triad is a three-pronged military force structure that consists of land-launched nuclear missiles, nuclear-missile-armed submarines, and strategic aircraft with nuclear bombs and missiles. Specifically, these components are land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs), and strategic bombers. The purpose of having this three-branched nuclear capability is to significantly reduce the possibility that an enemy could destroy all of a nation's nuclear forces in a first-strike attack. This, in turn, ensures a credible threat of a second strike, and thus increases a nation's nuclear deterrence.

The Triomphant class of ballistic missile submarines of the French Navy is the active lead boat class of four boats that entered service in 1997, 1999, 2004, and 2010. These four superseded the older Redoutable class, and they provide the ocean-based component of France's nuclear deterrent strike force, the Force de dissuasion. Their home port is Île Longue, Roadstead of Brest, Western Brittany.
The TN 71 is a French-built thermonuclear warhead which was used on submarine-launched ballistic missiles in Redoutable class ballistic missile submarines.
The TN 70 is a French-built thermonuclear warhead which was used on submarine-launched ballistic missiles in Redoutable class ballistic missile submarines.
The TN 61 was a French nuclear warhead.

The M20 was a French submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) deployed on the nuclear Redoutable-class submarines from 1977. It was withdrawn from service by 1991.

The Submarine Forces of France are one of the four main components of the French Navy. The force oversees all French submarines regardless of role.

Gymnote (S655) was an experimental submarine of the French Navy. She was a trials submarine for submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBM) and powered by diesel electric engines. She is named in honour of Gymnote, the world's first all-electric submarine built in France in the late 19th century.
The R-29RMU2.1 Layner is a Russian liquid-fuelled submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) and the newest member of the R-29 missile family, developed by the Makeyev Rocket Design Bureau and produced by the Krasnoyarsk Machine-Building Plant. Derived from the R-29RMU2 Sineva SLBM, the Layner can carry twelve nuclear warheads, three times as many as Sineva. It was expected to enter service with the Russian Navy's Delta IV-class submarines after a successful test programme that spanned from May to September 2011. The Russian Navy confirmed in 2014 that the system was now in use.













