Related Research Articles

Ovintiv Inc., formerly Encana Corporation, is a hydrocarbon exploration and production company organized in Delaware and headquartered in Denver, United States. It was founded and headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, and was the largest energy company and largest natural gas producer in Canada. The company was rebranded as Ovintiv and relocated to Denver in 2019–20.
Hydraulic fracturing in the United States began in 1949. According to the Department of Energy (DOE), by 2013 at least two million oil and gas wells in the US had been hydraulically fractured, and that of new wells being drilled, up to 95% are hydraulically fractured. The output from these wells makes up 43% of the oil production and 67% of the natural gas production in the United States. Environmental safety and health concerns about hydraulic fracturing emerged in the 1980s, and are still being debated at the state and federal levels.
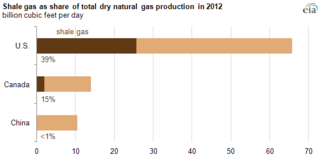
Shale gas is natural gas that is found trapped within shale formations. Shale gas has become an increasingly important source of natural gas in the United States since the start of this century, and interest has spread to potential gas shales in the rest of the world. In 2000 shale gas provided only 1% of U.S. natural gas production; by 2010 it was over 20% and the U.S. government's Energy Information Administration predicts that by 2035, 46% of the United States' natural gas supply will come from shale gas.

The Bakken Formation is a rock unit from the Late Devonian to Early Mississippian age occupying about 200,000 square miles (520,000 km2) of the subsurface of the Williston Basin, underlying parts of Montana, North Dakota, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. The formation was initially described by geologist J.W. Nordquist in 1953. The formation is entirely in the subsurface, and has no surface outcrop. It is named after Henry O. Bakken (1901-1982), a farmer in Tioga, North Dakota, who owned the land where the formation was initially discovered while drilling for oil.

The Monterey Formation is an extensive Miocene oil-rich geological sedimentary formation in California, with outcrops of the formation in parts of the California Coast Ranges, Peninsular Ranges, and on some of California's off-shore islands. The type locality is near the city of Monterey, California. The Monterey Formation is the major source-rock for 37 to 38 billion barrels of oil in conventional traps such as sandstones. This is most of California's known oil resources. The Monterey has been extensively investigated and mapped for petroleum potential, and is of major importance for understanding the complex geological history of California. Its rocks are mostly highly siliceous strata that vary greatly in composition, stratigraphy, and tectono-stratigraphic history.
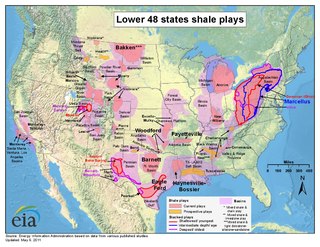
Shale gas in the United States is an available source of natural gas. Led by new applications of hydraulic fracturing technology and horizontal drilling, development of new sources of shale gas has offset declines in production from conventional gas reservoirs, and has led to major increases in reserves of U.S. natural gas. Largely due to shale gas discoveries, estimated reserves of natural gas in the United States in 2008 were 35% higher than in 2006.

The Utica Shale is a stratigraphical unit of Upper Ordovician age in the Appalachian Basin. It underlies much of the northeastern United States and adjacent parts of Canada.

The inclusion of shale gas with conventional gas reserves has caused a sharp increase in estimated recoverable natural gas in Canada. Until the 1990s success of hydraulic fracturing in the Barnett Shales of north Texas, shale gas was classed as "unconventional reserves" and was considered too expensive to recover. There are a number of prospective shale gas deposits in various stages of exploration and exploitation across the country, from British Columbia to Nova Scotia.

Tight oil is light crude oil contained in petroleum-bearing formations of low permeability, often shale or tight sandstone. Economic production from tight oil formations requires the same hydraulic fracturing and often uses the same horizontal well technology used in the production of shale gas. While sometimes called "shale oil", tight oil should not be confused with oil shale or shale oil. Therefore, the International Energy Agency recommends using the term "light tight oil" for oil produced from shales or other very low permeability formations, while the World Energy Resources 2013 report by the World Energy Council uses the terms "tight oil" and "shale-hosted oil".

Hydraulic fracturing, also called fracking, hydrofracking, and hydrofracturing, is a well stimulation technique involving the fracturing of bedrock formations by a pressurized liquid. The process involves the high-pressure injection of "fracking fluid" into a wellbore to create cracks in the deep-rock formations through which natural gas, petroleum, and brine will flow more freely. When the hydraulic pressure is removed from the well, small grains of hydraulic fracturing proppants hold the fractures open.
Shale gas is natural gas produced from shale, a type of sedimentary rock. Shale gas has become an increasingly important source of natural gas in the United States over the past decade, and interest has spread to potential gas shales in Canada, Europe, Asia, and Australia. One analyst expects shale gas to supply as much as half the natural gas production in North America by 2020.

Southwestern Energy is a natural gas exploration and production company organized in Delaware and headquartered in Spring, Texas. The company is ranked 776th on the Fortune 500.

Range Resources Corporation is a petroleum and natural gas exploration and production company headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas. It is one of the largest exploration companies operating in the Marcellus Formation.

Hydraulic fracturing in the United Kingdom started in the late 1970s with fracturing of the conventional oil and gas fields near the North Sea. It has been used in about 200 British onshore oil and gas wells since the early 1980s. The technique did not attract attention until licences use were awarded for onshore shale gas exploration in 2008.

Hydraulic fracturing has become a contentious environmental and health issue with Tunisia and France banning the practice and a de facto moratorium in place in Quebec (Canada), and some of the states of the US.

The environmental impact of hydraulic fracturing is related to land use and water consumption, air emissions, including methane emissions, brine and fracturing fluid leakage, water contamination, noise pollution, and health. Water and air pollution are the biggest risks to human health from hydraulic fracturing. Research has determined that hydraulic fracturing negatively affects human health and drives climate change.
Shale gas in the United Kingdom has attracted increasing attention since 2007, when onshore shale gas production was proposed. The first shale gas well in England was drilled in 1875. A number of wells have been drilled, and favourable tax treatment has been offered to shale gas producers.

The Marcellus natural gas trend is a large and prolific area of shale gas extraction from the Marcellus Shale or Marcellus Formation of Devonian age in the eastern United States. The shale play encompasses 104,000 square miles and stretches across Pennsylvania and West Virginia, and into eastern Ohio and western New York. In 2012, it was the largest source of natural gas in the United States, and production was still growing rapidly in 2013. The natural gas is trapped in low-permeability shale, and requires the well completion method of hydraulic fracturing to allow the gas to flow to the well bore. The surge in drilling activity in the Marcellus Shale since 2008 has generated both economic benefits and considerable controversy.
The Canol shale play is the name for a region of Canada's Northwest Territories that is being investigated as a potential source of tight oil . The region centers around the known reserves of conventionally exploitable petroleum at Norman Wells.

Hydraulic fracturing in Canada was first used in Alberta in 1953 to extract hydrocarbons from the giant Pembina oil field, the biggest conventional oil field in Alberta, which would have produced very little oil without fracturing. Since then, over 170,000 oil and gas wells have been fractured in Western Canada. Hydraulic fracturing is a process that stimulates natural gas or oil in wellbores to flow more easily by subjecting hydrocarbon reservoirs to pressure through the injection of fluids or gas at depth causing the rock to fracture or to widen existing cracks. New hydrocarbon production areas have been opened as hydraulic fracturing stimulating techniques are coupled with more recent advances in horizontal drilling. Complex wells that are many hundreds or thousands of metres below ground are extended even further through drilling of horizontal or directional sections. Massive fracturing has been widely used in Alberta since the late 1970s to recover gas from low-permeability sandstones such as the Spirit River Formation. The productivity of wells in the Cardium, Duvernay, and Viking formations in Alberta, Bakken formation in Saskatchewan, Montney and Horn River formations in British Columbia would not be possible without hydraulic fracturing technology. Hydraulic fracturing has revitalized legacy oilfields. "Hydraulic fracturing of horizontal wells in unconventional shale, silt and tight sand reservoirs unlocks gas, oil and liquids production that until recently was not considered possible." Conventional oil production in Canada was on a decrease since about 2004 but this changed with the increased production from these formations using hydraulic fracturing. Hydraulic fracturing is one of the primary technologies employed to extract shale gas or tight gas from unconventional reservoirs.
References
- ↑ Jeffrey Jones (2013-10-06). "NWT's shale hopes dimmed by slow approvals, explorer says". The Globe and Mail . Archived from the original on 2014-03-12. Retrieved 2014-08-18.
MGM Energy Corp. chief executive officer Henry Sykes said regulatory hurdles are the main reason he believes that production growth in the Northwest Territories’ Canol shale play in the Central Mackenzie Valley will not mirror the industry’s success in the prolific Bakken oil fields of North Dakota.