Proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase mos is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MOS gene. [5] [6]
Proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase mos is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MOS gene. [5] [6]

MyoD, also known as myoblast determination protein 1, is a protein in animals that plays a major role in regulating muscle differentiation. MyoD, which was discovered in the laboratory of Harold M. Weintraub, belongs to a family of proteins known as myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs). These bHLH transcription factors act sequentially in myogenic differentiation. Vertebrate MRF family members include MyoD1, Myf5, myogenin, and MRF4 (Myf6). In non-vertebrate animals, a single MyoD protein is typically found.

Merlin is a cytoskeletal protein. In humans, it is a tumor suppressor protein involved in neurofibromatosis type II. Sequence data reveal its similarity to the ERM protein family.

Myogenin, is a transcriptional activator encoded by the MYOG gene. Myogenin is a muscle-specific basic-helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor involved in the coordination of skeletal muscle development or myogenesis and repair. Myogenin is a member of the MyoD family of transcription factors, which also includes MyoD, Myf5, and MRF4.

The proto-oncogene c-Rel is a protein that in humans is encoded by the REL gene. The c-Rel protein is a member of the NF-κB family of transcription factors and contains a Rel homology domain (RHD) at its N-terminus and two C-terminal transactivation domains. c-Rel is a myeloid checkpoint protein that can be targeted for treating cancer. c-Rel has an important role in B-cell survival and proliferation. The REL gene is amplified or mutated in several human B-cell lymphomas, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Hodgkin's lymphoma.

DnaJ homolog subfamily A member 3, mitochondrial, also known as Tumorous imaginal disc 1 (TID1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAJA3 gene on chromosome 16. This protein belongs to the DNAJ/Hsp40 protein family, which is known for binding and activating Hsp70 chaperone proteins to perform protein folding, degradation, and complex assembly. As a mitochondrial protein, it is involved in maintaining membrane potential and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) integrity, as well as cellular processes such as cell movement, growth, and death. Furthermore, it is associated with a broad range of diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, inflammatory diseases, and cancers.

Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C , also known as CDKN1C, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CDKN1C imprinted gene.

Heat shock 70 kDa protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HSPA4 gene.

CDC34 is a gene that in humans encodes the protein Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 R1. This protein is a member of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family, which catalyzes the covalent attachment of ubiquitin to other proteins.
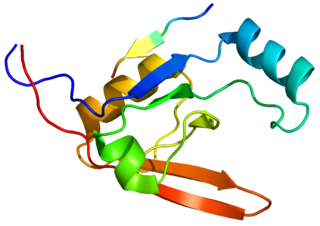
Serine protease HTRA1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HTRA1 gene. The HTRA1 protein is composed of four distinct protein domains. They are from amino-terminus to carboxyl-terminus an Insulin-like growth factor binding domain, a kazal domain, a trypsin-like peptidase domain and a PDZ domain.

MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MKNK1 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase PLK2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PLK2 gene.

Large tumor suppressor kinase 2 (LATS2) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the LATS2 gene.

Fibroblast growth factor 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGF6 gene.
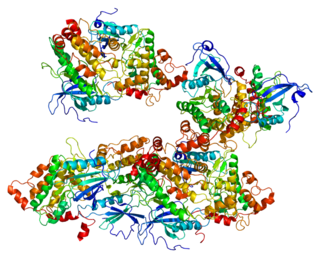
Death-associated protein kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DAPK2 gene.

MyoD family inhibitor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MDFI gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase Nek3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NEK3 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase PCTAIRE-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCTK2 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the WNK2 gene.

Myogenic factor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYF5 gene. It is a protein with a key role in regulating muscle differentiation or myogenesis, specifically the development of skeletal muscle. Myf5 belongs to a family of proteins known as myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs). These basic helix loop helix transcription factors act sequentially in myogenic differentiation. MRF family members include Myf5, MyoD (Myf3), myogenin, and MRF4 (Myf6). This transcription factor is the earliest of all MRFs to be expressed in the embryo, where it is only markedly expressed for a few days. It functions during that time to commit myogenic precursor cells to become skeletal muscle. In fact, its expression in proliferating myoblasts has led to its classification as a determination factor. Furthermore, Myf5 is a master regulator of muscle development, possessing the ability to induce a muscle phenotype upon its forced expression in fibroblastic cells.

Myogenic factor 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYF6 gene. This gene is also known in the biomedical literature as MRF4 and herculin. MYF6 is a myogenic regulatory factor (MRF) involved in the process known as myogenesis.
{{cite book}}: |journal= ignored (help)