
A tepal is one of the outer parts of a flower. The term is used when these parts cannot easily be classified as either sepals or petals. This may be because the parts of the perianth are undifferentiated, as in Magnolia, or because, although it is possible to distinguish an outer whorl of sepals from an inner whorl of petals, the sepals and petals have similar appearance to one another. The term was first proposed by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1827 and was constructed by analogy with the terms "petal" and "sepal".

In botany, a bract is a modified or specialized leaf, especially one associated with a reproductive structure such as a flower, inflorescence axis or cone scale. Bracts are often different from foliage leaves. They may be smaller, larger, or of a different color, shape, or texture. Typically, they also look different from the parts of the flower, such as the petals or sepals. The state of having bracts is referred to as bracteate or bracteolate, and conversely the state of lacking them is referred to as ebracteate and ebracteolate, without bracts.
In anatomy, an apex is part of the shell of a mollusk. The apex is the pointed tip of the shell of a gastropod, scaphopod, or cephalopod.

Busycotypus canaliculatus, commonly known as the channeled whelk, is a very large predatory sea snail, a marine prosobranch gastropod, a busycon whelk, belonging to the family Busyconidae.

Helicoprion is an extinct genus of shark-like eugeneodont fish. Almost all fossil specimens are of spirally arranged clusters of the individuals' teeth, called "tooth whorls", which in life were embedded in the lower jaw. As with most extinct cartilaginous fish, the skeleton is mostly unknown. Fossils of Helicoprion are known from a 20 million year timespan during the Permian period from the Artinskian stage of the Cisuralian to the Roadian stage of the Guadalupian. The closest living relatives of Helicoprion are the chimaeras, though their relationship is very distant. The unusual tooth arrangement is thought to have been an adaption for feeding on soft bodied prey, and may have functioned as a deshelling mechanism for hard bodied cephalopods such as nautiloids and ammonoids. In 2013, systematic revision of Helicoprion via morphometric analysis of the tooth whorls found only H. davisii, H. bessonowi and H. ergassaminon to be valid, with some of the larger tooth whorls being outliers.

The body whorl is part of the morphology of the shell in those gastropod mollusks that possess a coiled shell. The term is also sometimes used in a similar way to describe the shell of a cephalopod mollusk.

A whorl is a single, complete 360° revolution or turn in the spiral growth of a mollusc shell. A spiral configuration of the shell is found in numerous gastropods, but it is also found in shelled cephalopods including Nautilus, Spirula and the large extinct subclass of cephalopods known as the ammonites.

A spire is a part of the coiled shell of molluscs. The spire consists of all of the whorls except for the body whorl. Each spire whorl represents a rotation of 360°. A spire is part of the shell of a snail, a gastropod mollusc, a gastropod shell, and also the whorls of the shell in ammonites, which are fossil shelled cephalopods.

A spindle is a straight spike usually made from wood used for spinning, twisting fibers such as wool, flax, hemp, cotton into yarn. It is often weighted at either the bottom, middle, or top, commonly by a disc or spherical object called a whorl; many spindles, however, are weighted simply by thickening their shape towards the bottom, e.g. Orenburg and French spindles. The spindle may also have a hook, groove, or notch at the top to guide the yarn. Spindles come in many different sizes and weights depending on the thickness of the yarn one desires to spin.

Erica tetralix, the cross-leaved heath, is a species of flowering plant in the family Ericaceae, native to western Europe, from southern Portugal to central Norway, as well as a number of boggy regions further from the coast in Central Europe such as Austria and Switzerland. In bogs, wet heaths and damp coniferous woodland, E. tetralix can become a dominant part of the flora. It has also been introduced to parts of North America.

A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants. The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate outcrossing resulting from cross pollination or allow selfing when self pollination occurs.

A protoconch is an embryonic or larval shell which occurs in some classes of molluscs, e.g., the initial chamber of an ammonite or the larval shell of a gastropod. In older texts it is also called "nucleus". The protoconch may sometimes consist of several whorls, but when this is the case, the whorls show no growth lines.

The Buckquoy spindle-whorl is an Ogham-inscribed spindle-whorl dating from the Early Middle Ages, probably the 8th century, which was found in 1970 in Buckquoy, Birsay, Orkney, Scotland. Made of sandy limestone, it is about 36 mm in diameter and 10 mm thick. It is the only known spindle-whorl with an Ogham inscription.
Merosity refers to the number of component parts in a distinct whorl of a plant structure. It is most commonly used in the context of flowers where it refers to the number of sepals in a whorl of the calyx, the number of petals in a whorl of the corolla, the number of stamens in a whorl of the androecium, or the number of carpels in a whorl of the gynoecium. The term may also be used to refer to the number of leaves in a leaf whorl.

The umbilicus of a shell is the axially aligned, hollow cone-shaped space within the whorls of a coiled mollusc shell. The term umbilicus is often used in descriptions of gastropod shells, i.e. it is a feature present on the ventral side of many snail shells, including some species of sea snails, land snails, and freshwater snails.

The gastropod shell is part of the body of a gastropod or snail, a kind of mollusc. The shell is an exoskeleton, which protects from predators, mechanical damage, and dehydration, but also serves for muscle attachment and calcium storage. Some gastropods appear shell-less (slugs) but may have a remnant within the mantle, or the shell is reduced such that the body cannot be retracted within (semi-slug). Some snails also possess an operculum that seals the opening of the shell, known as the aperture, which provides further protection. The study of mollusc shells is known as conchology. The biological study of gastropods, and other molluscs in general, is malacology. Shell morphology terms vary by species group. An excellent source for terminology of the gastropod shell is "How to Know the Eastern Land Snails" by John B. Burch now freely available at the Hathi Trust Digital Library.

Ammonitina comprises a diverse suborder of ammonite cephalopods that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods of the Mesozoic Era. They are excellent index fossils, and it is often possible to link the rock layer in which they are found to specific geological time periods.
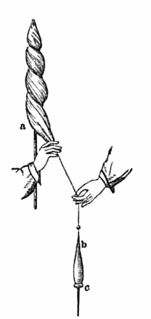
A spindle whorl is a disc or spherical object fitted onto the spindle to increase and maintain the speed of the spin. For ages the whorls have been made of many different materials: amber, antler, bone, ceramic, coral, glass, metal, and wood (oak). Some types of local materials have been also used, such as chalk, limestone, mudstone, sandstone, slate, and soapstone. One of the most famous spindle whorl artists is Susan Point.

Placenticeras is a genus of ammonites from the Late Cretaceous. Its fossils have been found in Asia, Europe, North and South America.

In botany, a whorl or verticil is an arrangement of leaves, sepals, petals, stamens, or carpels that radiate from a single point and surround or wrap around the stem or stalk. A leaf whorl consists of at least three elements; a pair of opposite leaves is not called a whorl.

















