Related Research Articles

A composite or composite material is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Composite materials with more than one distinct layer are called composite laminates.
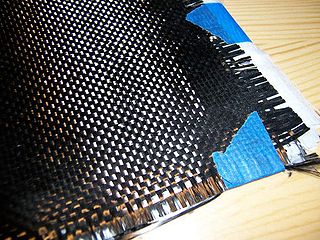
Carbon fibers or carbon fibres are fibers about 5 to 10 micrometers (0.00020–0.00039 in) in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. Carbon fibers have several advantages: high stiffness, high tensile strength, high strength to weight ratio, high chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low thermal expansion. These properties have made carbon fiber very popular in aerospace, civil engineering, military, motorsports, and other competition sports. However, they are relatively expensive compared to similar fibers, such as glass fiber, basalt fibers, or plastic fibers.

Polymer degradation is the reduction in the physical properties of a polymer, such as strength, caused by changes in its chemical composition. Polymers and particularly plastics are subject to degradation at all stages of their product life cycle, including during their initial processing, use, disposal into the environment and recycling. The rate of this degradation varies significantly; biodegradation can take decades, whereas some industrial processes can completely decompose a polymer in hours.
Polyimide is a polymer containing imide groups belonging to the class of high-performance plastics. With their high heat-resistance, polyimides enjoy diverse applications in roles demanding rugged organic materials, such as high temperature fuel cells, displays, and various military roles. A classic polyimide is Kapton, which is produced by condensation of pyromellitic dianhydride and 4,4'-oxydianiline.

Pre-preg is a composite material made from "pre-impregnated" fibers and a partially cured polymer matrix, such as epoxy or phenolic resin, or even thermoplastic mixed with liquid rubbers or resins. The fibers often take the form of a weave and the matrix is used to bond them together and to other components during manufacture. The thermoset matrix is only partially cured to allow easy handling; this B-Stage material requires cold storage to prevent complete curing. B-Stage pre-preg is always stored in cooled areas since heat accelerates complete polymerization. Hence, composite structures built of pre-pregs will mostly require an oven or autoclave to cure. The main idea behind a pre-preg material is the use of anisotropic mechanical properties along the fibers, while the polymer matrix provides filling properties, keeping the fibers in a single system.

Electrospinning is a fiber production method that uses electrical force to draw charged threads of polymer solutions for producing nanofibers with diameters ranging from nanometers to micrometers. Electrospinning shares characteristics of both electrospraying and conventional solution dry spinning of fibers. The process does not require the use of coagulation chemistry or high temperatures to produce solid threads from solution. This makes the process particularly suited to the production of fibers using large and complex molecules. Electrospinning from molten precursors is also practiced; this method ensures that no solvent can be carried over into the final product.

Delamination is a mode of failure where a material fractures into layers. A variety of materials, including laminate composites and concrete, can fail by delamination. Processing can create layers in materials, such as steel formed by rolling and plastics and metals from 3D printing which can fail from layer separation. Also, surface coatings, such as paints and films, can delaminate from the coated substrate.

Ceramic engineering is the science and technology of creating objects from inorganic, non-metallic materials. This is done either by the action of heat, or at lower temperatures using precipitation reactions from high-purity chemical solutions. The term includes the purification of raw materials, the study and production of the chemical compounds concerned, their formation into components and the study of their structure, composition and properties.

Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are cylinders of one or more layers of graphene (lattice). Diameters of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) are typically 0.8 to 2 nm and 5 to 20 nm, respectively, although MWNT diameters can exceed 100 nm. CNT lengths range from less than 100 nm to 0.5 m.

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter along with liquid, gas, and plasma. The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to a force applied to the surface. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. The atoms in a solid are bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice, or irregularly. Solids cannot be compressed with little pressure whereas gases can be compressed with little pressure because the molecules in a gas are loosely packed.
A thermoset polymer matrix is a synthetic polymer reinforcement where polymers act as binder or matrix to secure in place incorporated particulates, fibres or other reinforcements. They were first developed for structural applications, such as glass-reinforced plastic radar domes on aircraft and graphite-epoxy payload bay doors on the Space Shuttle.
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers, carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic, also known as carbon fiber, carbon composite, or just carbon, are extremely strong and light fiber-reinforced plastics that contain carbon fibers. CFRPs can be expensive to produce, but are commonly used wherever high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness (rigidity) are required, such as aerospace, superstructures of ships, automotive, civil engineering, sports equipment, and an increasing number of consumer and technical applications.
A void or a pore is three-dimensional region that remains unfilled with polymer and fibers in a composite material. Voids are typically the result of poor manufacturing of the material and are generally deemed undesirable. Voids can affect the mechanical properties and lifespan of the composite. They degrade mainly the matrix-dominated properties such as interlaminar shear strength, longitudinal compressive strength, and transverse tensile strength. Voids can act as crack initiation sites as well as allow moisture to penetrate the composite and contribute to the anisotropy of the composite. For aerospace applications, a void content of approximately 1% is still acceptable, while for less sensitive applications, the allowance limit is 3-5%. Although a small increase in void content may not seem to cause significant issues, a 1-3% increase in void content of carbon fiber reinforced composite can reduce the mechanical properties by up to 20%
Thermoplastics containing short fiber reinforcements were first introduced commercially in the 1960s. The most common type of fibers used in short fiber thermoplastics are glass fiber and carbon fiber . Adding short fibers to thermoplastic resins improves the composite performance for lightweight applications. In addition, short fiber thermoplastic composites are easier and cheaper to produce than continuous fiber reinforced composites. This compromise between cost and performance allows short fiber reinforced thermoplastics to be used in myriad applications.
Transfer molding is a manufacturing process in which casting material is forced into a mold. Transfer molding is different from compression molding in that the mold is enclosed rather than open to the fill plunger resulting in higher dimensional tolerances and less environmental impact. Compared to injection molding, transfer molding uses higher pressures to uniformly fill the mold cavity. This allows thicker reinforcing fiber matrices to be more completely saturated by resin. Furthermore, unlike injection molding, the transfer mold casting material may start the process as a solid. This can reduce equipment costs and time dependency. The transfer process may have a slower fill rate than an equivalent injection molding process.
In materials science, a polymer matrix composite (PMC) is a composite material composed of a variety of short or continuous fibers bound together by a matrix of organic polymers. PMCs are designed to transfer loads between fibers of a matrix. Some of the advantages with PMCs include their light weight, high resistance to abrasion and corrosion, and high stiffness and strength along the direction of their reinforcements.
Welding of advanced thermoplastic composites is a beneficial method of joining these materials compared to mechanical fastening and adhesive bonding. Mechanical fastening requires intense labor, and creates stress concentrations, while adhesive bonding requires extensive surface preparation, and long curing cycles. Welding these materials is a cost-effective method of joining concerning preparation and execution, and these materials retain their properties upon cooling, so no post processing is necessary. These materials are widely used in the aerospace industry to reduce weight of a part while keeping strength.
Silicon carbide fibers are fibers ranging from 5 to 150 micrometres in diameter and composed primarily of silicon carbide molecules. Depending on manufacturing process, they may have some excess silicon or carbon, or have a small amount of oxygen. Relative to organic fibers and some ceramic fibers, silicon carbide fibers have high stiffness, high tensile strength, low weight, high chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance and low thermal expansion. (refs) These properties have made silicon carbide fiber the choice for hot section components in the next generation of gas turbines, e.g. the LEAP engine from GE.
Structural composite supercapacitors are multifunctional materials that can both bear mechanical load and store electrical energy. That when combined with structural batteries, could potentially enable an overall weight reduction of electric vehicles.
Gregory M. Odegard is a materials researcher and academic. He is the John O. Hallquist Endowed Chair in Computational Mechanics in the Department of Mechanical Engineering – Engineering Mechanics at Michigan Technological University and the director of the NASA Institute for Ultra-Strong Composites by Computational Design.
References
- 1 2 "Maciej Kumosa | Engineering & Computer Science". ritchieschool.du.edu.
- 1 2 "Maciej S. Kumosa". T&D World. February 25, 2020.
- ↑ "Editorial board - Composites Science and Technology | ScienceDirect.com by Elsevier". www.sciencedirect.com.
- ↑ "Tech Science Press - Publisher of Open Access Journals". www.techscience.com.
- ↑ "Fibers". www.mdpi.com.
- ↑ "Zmarł Stefan Kumosa". 2 October 2012.
- ↑ http://loslupca.pl/
- 1 2 "Maciej Kumosa".
- ↑ "Center for Novel High Voltage/Temperature Materials and Structures (HVT)". iucrc.nsf.gov.
- ↑ Kumosa, Maciej (January 1986). "Crack and slip phenomena at the tip of a terminated twin". Materials Science and Engineering. 77: 37–44. doi:10.1016/0025-5416(86)90352-6.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Kumosa, M (14 October 1991). "Strain energy of a mechanical twin in alpha -iron". Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics. 24 (10): 1816–1821. Bibcode:1991JPhD...24.1816K. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/24/10/016. S2CID 250839352.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ "Rozwój badań i powstanie Instytutu | Katedra Mechaniki, Inżynierii Materiałowej i Biomedycznej".
- 1 2 Golaski, L.; Hull, D.; Kumosa, M. (1984). "Acoustic Emission from Filament Wound Pipes Under Long Term Loading Conditions". Mechanical Behaviour of Materials. pp. 557–563. doi:10.1016/B978-1-4832-8372-2.50068-3. ISBN 978-1-4832-8372-2.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Kumosa, M.; Hull, D. (January 1988). "Finite element analysis of a circumferentially cracked cylindrical shell under uniform tensile loading". Engineering Fracture Mechanics. 31 (5): 817–826. doi:10.1016/0013-7944(88)90237-8.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Kumosa, M (14 January 1987). "Acoustic emission monitoring of stress corrosion cracks in aligned GRP". Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics. 20 (1): 69–74. Bibcode:1987JPhD...20...69K. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/20/1/011. S2CID 250748421.[ non-primary source needed ]
- 1 2 Kumosa, M.; Hull, D. (October 1987). "Mixed-mode fracture of composites using Iosipescu shear test". International Journal of Fracture. 35 (2): 83–102. doi:10.1007/BF00019793. S2CID 135739599.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Barnes, J.A.; Kumosa, M.; Hull, D. (January 1987). "Theoretical and experimental evaluation of the Iosipescu shear test". Composites Science and Technology. 28 (4): 251–268. doi:10.1016/0266-3538(87)90024-8.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Broughton, W.R.; Kumosa, M.; Hull, D. (January 1990). "Analysis of the Iosipescu shear test as applied to unidirectional carbon-fibre reinforced composites". Composites Science and Technology. 38 (4): 299–325. doi:10.1016/0266-3538(90)90018-Z.[ non-primary source needed ]
- 1 2 Sigalas, I.; Kumosa, M.; Hull, D. (January 1991). "Trigger mechanisms in energy-absorbing glass cloth/epoxy tubes". Composites Science and Technology. 40 (3): 265–287. doi:10.1016/0266-3538(91)90085-4.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Hull, D.; Kumosa, M.; Price, J. N. (March 1985). "Stress corrosion of aligned glass fibre-polyester composite material". Materials Science and Technology. 1 (3): 177–182. Bibcode:1985MatST...1..177H. doi:10.1179/mst.1985.1.3.177.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Kumosa, Maciej S.; Searles, Kevin H.; Odegard, Greg; Thirumalai, V. (15 November 1996). Biaxial Failure Analysis of Graphite Reinforced Polyimide Composites (Report). doi:10.21236/ADA329883. DTIC ADA329883.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Searles, K.; Odegard, G.; Kumosa, M.; Castelli, M. (November 1999). "Failure Investigation of Graphite/Polyimide Fabric Composites at Room and Elevated Temperatures Using the Biaxial Iosipescu Test". Journal of Composite Materials. 33 (22): 2038–2079. Bibcode:1999JCoMa..33.2038S. doi:10.1177/002199839903302201. S2CID 136023520.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Qiu, Q.; Kumosa, M. (1997). "Corrosion of E-glass fibers in acidic environments". Composites Science and Technology. 57 (5): 497–507. doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(96)00158-3.
- ↑ Searles, K.; Odegard, G.; Kumosa, M. (2001). "Micro- and Mesomechanics of 8 Harness Satin Woven Fabric Composites: I Evaluation of Elastic Behavior". Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing. 32 (11): 1627–1655. doi:10.1016/S1359-835X(00)00181-0.
- 1 2 Korusiewicz, L; Ding, J; Kumosa, M (September 1993). "High temperature crack growth behavior in a precipitate-hardened nickel base superalloy under constant KI conditions". Scripta Metallurgica et Materialia. 29 (5): 573–578. doi:10.1016/0956-716X(93)90398-C.[ non-primary source needed ]
- 1 2 "Maciej Kumosa: Pioneering High-Voltage Research". T&D World. October 4, 2012.
- ↑ Kumosa, M.; Kumosa, L.; Armentrout, D. (December 2004). "Causes and potential remedies of brittle fracture failure of composite (nonceramic) insulators". IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation. 11 (6): 1037–1048. doi:10.1109/TDEI.2004.1387827. S2CID 6636352.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Carpenter, S. H.; Kumosa, M. (September 2000). "An investigation of brittle fracture of composite insulator rods in an acid environment with either static or cyclic loading". Journal of Materials Science. 35 (17): 4465–4476. doi:10.1023/A:1004885813659. S2CID 46087234.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Kumosa, M.; Kumosa, L.; Armentrout, D. (May 2005). "Failure analyses of nonceramic insulators. Part 1: Brittle fracture characteristics". IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine. 21 (3): 14–27. doi:10.1109/MEI.2005.1437604. S2CID 6258621.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Kumosa, M; Armentrout, D; Kumosa, L; Han, Y; Carpenter, S.H (July 2002). "Analyses of composite insulators with crimped end-fittings: part II—Suitable crimping conditions". Composites Science and Technology. 62 (9): 1209–1221. doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(02)00067-2.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Kumosa, Maciej S.; Sutter, J. K. (12 February 2007). Graphite/Polyimide Composites Subjected to Biaxial Loads at Elevated Temperatures (Report).[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Kumosa, M. S. (1 October 2004). Fundamental Issues Regarding the High Temperature Failure Properties of Graphite/Polyimide Fabric Composites (Report). doi:10.21236/ADA430088. DTIC ADA430088.
- ↑ Benedikt, B.; Kumosa, M.; Predecki, P.K.; Kumosa, L.; Castelli, M.G.; Sutter, J.K. (November 2001). "An analysis of residual thermal stresses in a unidirectional graphite/PMR-15 composite based on X-ray diffraction measurements". Composites Science and Technology. 61 (14): 1977–1994. doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(01)00060-4.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Odegard, G; Kumosa, M (December 2000). "Elastic-plastic and failure properties of a unidirectional carbon/PMR-15 composite at room and elevated temperatures". Composites Science and Technology. 60 (16): 2979–2988. doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(00)00163-9.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Kumosa, M. (2001). "Shear dominated failure mechanisms in high temperature graphite/polymer matrix composites". Zeszyty Naukowe. Mechanika / Politechnika Opolska. 269 (67): 147–162.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Rupnowski, P.; Gentz, M.; Kumosa, M. (June 2006). "Mechanical response of a unidirectional graphite fiber/polyimide composite as a function of temperature". Composites Science and Technology. 66 (7–8): 1045–1055. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.07.026.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Gentz, M.; Benedikt, B.; Sutter, J.K.; Kumosa, M. (August 2004). "Residual stresses in unidirectional graphite fiber/polyimide composites as a function of aging". Composites Science and Technology. 64 (10–11): 1671–1677. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2003.12.006.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Gentz, M.; Armentrout, D.; Rupnowski, P.; Kumosa, L.; Shin, E.; Sutter, J.K.; Kumosa, M. (February 2004). "In-plane shear testing of medium and high modulus woven graphite fiber reinforced/polyimide composites". Composites Science and Technology. 64 (2): 203–220. doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(03)00260-4. hdl: 2060/20040111223 .[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Stowe, J.Q.; Predecki, P.K.; Laz, P.J.; Burks, B.M.; Kumosa, M. (July 2009). "Probabilistic molecular dynamics evaluation of the stress–strain behavior of polyethylene". Acta Materialia. 57 (12): 3615–3622. Bibcode:2009AcMat..57.3615S. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2009.04.023.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Burks, B.; Middleton, J.; Armentrout, D.; Kumosa, M. (30 September 2010). "Effect of excessive bending on residual tensile strength of hybrid composite rods". Composites Science and Technology. 70 (10): 1490–1496. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.04.029.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Burks, Brian; Kumosa, Maciej (October 2012). "The effects of atmospheric aging on a hybrid polymer matrix composite". Composites Science and Technology. 72 (15): 1803–1811. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2012.07.018.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Middleton, James; Burks, Brian; Wells, Todd; Setters, Alexander M.; Jasiuk, Iwona; Kumosa, Maciej (November 2013). "The effect of ozone and high temperature on polymer degradation in polymer core composite conductors". Polymer Degradation and Stability. 98 (11): 2282–2290. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.08.013.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Hoffman, J.; Middleton, J.; Kumosa, M. (January 2015). "Effect of a surface coating on flexural performance of thermally aged hybrid glass/carbon epoxy composite rods". Composites Science and Technology. 106: 141–148. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2014.11.010.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Håkansson, Eva; Hoffman, Joseph; Predecki, Paul; Kumosa, Maciej (January 2017). "The role of corrosion product deposition in galvanic corrosion of aluminum/carbon systems". Corrosion Science. 114: 10–16. Bibcode:2017Corro.114...10H. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2016.10.011.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Proctor, Cathy (24 May 2013). "University of Denver professor: New transmission line product would save lives". Denver Business Journal.
- ↑ Waters, Daniel H.; Hoffman, Joseph; Hakansson, Eva; Kumosa, Maciej (August 2017). "Low-velocity impact to transmission line conductors". International Journal of Impact Engineering. 106: 64–72. Bibcode:2017IJIE..106...64W. doi:10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.03.010.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Waters, Daniel H.; Hoffman, Joseph; Kumosa, Maciej (February 2019). "Monitoring of Overhead Transmission Conductors Subjected to Static and Impact Loads Using Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors". IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement. 68 (2): 595–605. Bibcode:2019ITIM...68..595W. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2018.2851698 .[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Grell, W.A.; Solis-Ramos, E.; Clark, E.; Lucon, E.; Garboczi, E.J.; Predecki, P.K.; Loftus, Z.; Kumosa, M. (October 2017). "Effect of powder oxidation on the impact toughness of electron beam melting Ti-6Al-4V". Additive Manufacturing. 17: 123–134. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2017.08.002 . PMC 10941301 . PMID 38496266.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Lu, T.; Solis-Ramos, E.; Yi, Y.B.; Kumosa, M. (December 2017). "Particle removal mechanisms in synergistic aging of polymers and glass reinforced polymer composites under combined UV and water". Composites Science and Technology. 153: 273–281. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.10.028 .[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Bleszynski, M.; Kumosa, M. (December 2017). "Silicone rubber aging in electrolyzed aqueous salt environments". Polymer Degradation and Stability. 146: 61–68. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.09.019 .[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Henderson, Christine N.; DeFrance, Charles S.; Predecki, Paul; Kumosa, Maciej (August 2019). "Damage prevention in transformer bushings subjected to high-velocity impact". International Journal of Impact Engineering. 130: 1–10. Bibcode:2019IJIE..130....1H. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.03.007 .[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Khadka, S.; Hoffman, J.; Kumosa, M. (September 2020). "FBG monitoring of curing in single fiber polymer composites". Composites Science and Technology. 198: 108308. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108308 .[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Khadka, S.; Predecki, P.; Kumosa, M.; Hoffman, J. (March 2022). "Monitoring solidification of tin-bismuth alloys using FBG sensors". Materialia. 21: 101320. doi: 10.1016/j.mtla.2022.101320 .[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Williams, Babajide O (2023). The Modernization of Large Power Transformer Tanks (Thesis). ProQuest 2846881952.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Williams, Jide; Hoffman, Joseph; Predecki, Paul; Kumosa, Maciej (October 2022). "Application of Polymer Matrix Composites in Large Power Transformer Tanks". IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery. 37 (5): 4190–4201. doi:10.1109/tpwrd.2022.3147410. S2CID 246539399.[ non-primary source needed ]
- ↑ Reil, Matt; Hoffman, Joseph; Predecki, Paul; Kumosa, Maciej (August 2022). "Graphene and graphene oxide energetic interactions with polymers through molecular dynamics simulations". Computational Materials Science. 211: 111548. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2022.111548 .[ non-primary source needed ]