
The Canadian Shield, also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks that forms the ancient geologic core of the North American continent. Glaciation has left the area with only a thin layer of soil, through which the composition of igneous rock resulting from long volcanic history is frequently visible. As a deep, common, joined bedrock region in eastern and central Canada, the Shield stretches north from the Great Lakes to the Arctic Ocean, covering over half of Canada and most of Greenland; it also extends south into the northern reaches of the United States. Human population is sparse and industrial development is minimal, but mining is prevalent.

Columbia, also known as Nuna or Hudsonland, was one of Earth's ancient supercontinents. It was first proposed by Rogers & Santosh 2002 and is thought to have existed approximately 2,500 to 1,500 million years ago in the Paleoproterozoic Era. Zhao et al. 2002 proposed that the assembly of the supercontinent Columbia was completed by global-scale collisional events during 2.1–1.8 Ga.

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive and extrusive, arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems.

The Northwest Territories is a territory in Northern Canada, specifically in Northwestern Canada between Yukon Territory and Nunavut including part of Victoria Island, Melville Island, and other islands on the western Arctic Archipelago. Originally a much wider territory enclosing most of central and northern Canada, the Northwest Territories was created in 1870 from the Hudson's Bay Company's holdings that were sold to Canada from 1869-1870. In addition, Alberta and Saskatchewan were formed from the territory in 1905. In 1999, it was divided again: the eastern portion became the new territory of Nunavut. Yellowknife stands as its largest city and capital. It has a population of 42,800 and has an area of 532,643 sq mi (1,379,540 km2). The current territory lies west of Nunavut, north of latitude 60° north, and east of Yukon.
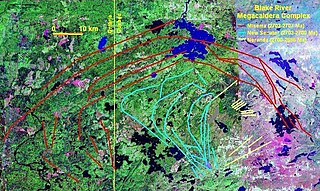
The Blake River Megacaldera Complex is a giant subaqueous caldera cluster or a nested caldera system that spans across the Ontario-Quebec border in Canada.
The High Arctic Large Igneous Province (HALIP) is a Cretaceous large igneous province in the Arctic. The region is divided into several smaller magmatic provinces. Svalbard, Franz Josef Land, Sverdrup Basin, Amerasian Basin, and northern Greenland are some of the larger divisions. Today, HALIP covers an area greater than 1,000,000 km2 (390,000 sq mi), making it one of the largest and most intense magmatic complexes on the planet. However, eroded volcanic sediments in sedimentary strata in Svalbard and Franz Josef Land suggest that an extremely large portion of HALIP volcanics have already been eroded away.

A dike swarm or dyke swarm is a large geological structure consisting of a major group of parallel, linear, or radially oriented magmatic dikes intruded within continental crust or central volcanoes in rift zones. Examples exist in Iceland and near other large volcanoes, around the world. They consist of several to hundreds of dikes emplaced more or less contemporaneously during a single intrusive event, are magmatic and stratigraphic, and may form a large igneous province.
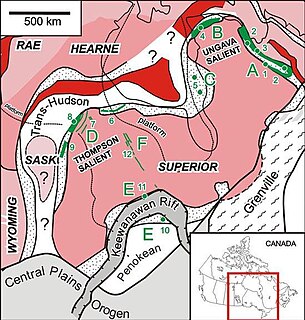
The Circum-Superior Belt is a widespread Paleoproterozoic large igneous province in the Canadian Shield of Northern, Western and Eastern Canada. It extends more than 3,400 km (2,100 mi) from northeastern Manitoba through northwestern Ontario, southern Nunavut to northern Quebec. Igneous rocks of the Circum-Superior Belt are mafic-ultramafic in composition, deposited in the Labrador Trough near Ungava Bay, the Cape Smith Belt near the southern shore of Hudson Strait and along the eastern shore of Hudson Bay in its northern portion; the Thompson and Fox River belts in the northwest and the Marquette Range Supergroup in its southern portion. The Circum Superior Belt also hosts a rare example of Proterozoic Komatiite, in the Winnipegosis komatiite belt.
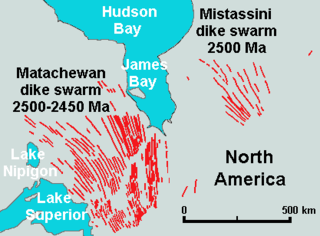
The Matachewan dike swarm is a large 2,500 to 2,450 million year old Paleoproterozoic dike swarm of Northern Ontario, Canada. It consists of basaltic dikes that were intruded in greenschist, granite-greenstone, and metamorphosed sedimentary terrains of the Superior craton of the Canadian Shield. With an area of 360,000 km2 (140,000 sq mi), the Matachewan dike swarm stands as a large igneous province.
The volcanology of Eastern Canada includes the hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations in Eastern Canada. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic settings and types of volcanic eruptions, ranging from passive lava eruptions to violent explosive eruptions. Eastern Canada has very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous provinces. They are represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarms, sill provinces and layered intrusions. The most capable large igneous provinces in Eastern Canada are Archean age greenstone belts containing a rare volcanic rock called komatiite.

Volcanism of Northern Canada has produced hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations across Northern Canada. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic settings and types of volcanic eruptions, ranging from passive lava eruptions to violent explosive eruptions. Northern Canada has a record of very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous provinces. They are represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarms, sill provinces and layered intrusions.

The Franklin dike swarm, also called the Franklin dikes, is a Proterozoic dike swarm of the Franklin Large Igneous Province in Northern Canada. It is one of the several major magmatic events in the Canadian Shield and it was formed 723 million years ago. Areas in the Franklin have been prospected for nickel, copper, and platinum group metals.
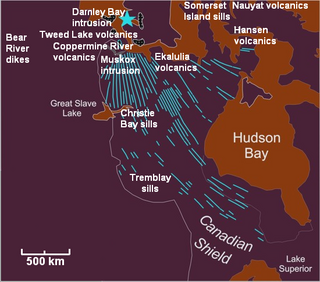
The Coppermine River Group is a sequence of Mesoproterozoic continental flood basalts forming part of the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province in the Northwest Territories and Nunavut, Canada. It is among the largest flood basalt provinces on Earth, covering the area with a volume of approximately 650,000 km3 (155,943 cu mi).

The Franklin Large Igneous Province is a Neoproterozoic large igneous province in the Canadian Arctic of Northern Canada. It represents one of the largest large igneous provinces in Canada, consisting of the Natkusiak flood basalts on Victoria Island, the Coronation sills on the southern shore of the Coronation Gulf and the large Franklin dike swarm, which extends for more than 1,200 km (750 mi) across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago and northwestern Greenland. The Franklin Large Igneous Province covers an area of more than 1,100,000 km2 (420,000 sq mi).

The Mackenzie Large Igneous Province (MLIP) is a major Mesoproterozoic large igneous province of the southwestern, western and northwestern Canadian Shield in Canada. It consists of a group of related igneous rocks that were formed during a massive igneous event starting about 1,270 million years ago. The large igneous province extends from the Arctic in Nunavut to near the Great Lakes in Northwestern Ontario where it meets with the smaller Matachewan dike swarm. Included in the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province are the large Muskox layered intrusion, the Coppermine River flood basalt sequence and the massive northwesterly trending Mackenzie dike swarm.

The Mistassini dike swarm is a 2.5 billion year old Paleoproterozoic dike swarm of western Quebec, Canada. It consists of mafic dikes that were intruded in the Superior craton of the Canadian Shield. With an area of 100,000 km2 (39,000 sq mi), the Mistassini dike swarm stands as a large igneous province.

The Nipissing sills, also called the Nipissing diabase, is a large 2217– to 2210–million year old group of sills in the Superior craton of the Canadian Shield in Ontario, Canada, which intrude the Huronian Supergroup. Nipissing sills intrude all the Huronian sediments and older basement rocks in the northern margin of the Sudbury Basin; they were emplaced after the faulting and folding of Huronian rocks, and are hornblende gabbro of tholeiitic basalt composition. In the Sudbury–Elliot Lake area the Nipissing diabase is deformed; outcrops are parallel to the fold axes of the Huronian sedimentary rocks. Nipissing diabase intrusions are east-northeast trending and are no wider than 460 m (1,510 ft).

The Okavango Dyke Swarm is a giant dyke swarm of the Karoo Large Igneous Province in northeast Botswana, southern Africa. It consists of a group of Proterozoic and Jurassic dykes, trending east-southeast across Botswana, spanning a region nearly 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) long and 110 kilometres (68 mi) wide. The Jurassic dykes were formed approximately 179 million years ago, composed of mainly tholeiitic mafic rocks. The formation is related to the magmatism at the Karoo triple junction, induced by the plate tectonic break up of the Gondwana supercontinent in the early Jurassic.

The geology of Ontario consists of the study of the rock formations in the most populated province of Canada. Ontario has some of the oldest rocks on Earth. It is made up of ancient Precambrian igneous and metamorphic rock and overlain by younger sedimentary rocks and soils.
The geology of the Northwest Territories has been mapped in different quadrangles by the Canadian government. The region has some of the oldest rocks in the world and among the oldest in North America, formed from several sections of stable craton continental crust, including the Slave Craton, Rae Craton and Hearne Craton. These rocks form the Archean and Proterozoic Precambrian basement rock of the region and are the subject of extensive research to understand continental crust and tectonic conditions on the early Earth.
















