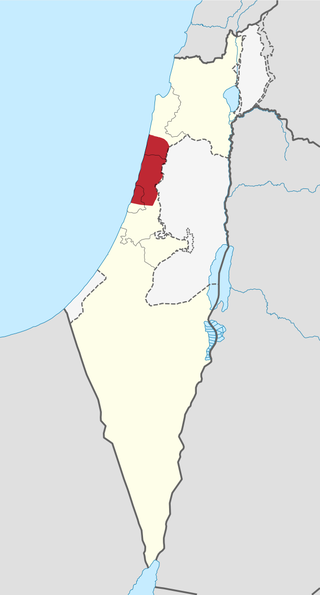
The Sharon plain is the central section of the Israeli coastal plain. The plain lies between the Mediterranean Sea to the west and the Samarian Hills, 15 km (9.3 mi) to the east. It stretches from Nahal Taninim, a stream marking the southern end of Mount Carmel in the north, to the Yarkon River in the south, at the northern limit of Tel Aviv, over a total of about 90 km (56 mi). The level of the Sharon plain is connected to the level of the Mediterranean Sea by the Sharon Escarpment.

Hod HaSharon is a city in the Central District of Israel. The city is located approximately 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) east of the Mediterranean coastline, south of Kfar Saba, southeast of Raanana, and northeast of Ramat HaSharon.

The Battle of Haifa, called by the Jewish forces Operation Bi'ur Hametz, was a Haganah operation carried out on 21–22 April 1948 and a major event in the final stages of the civil war in Palestine, leading up to the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. The objective of the operation was the capture of the Arab neighborhoods of Haifa. The operation formed part of the 1948 Palestinian expulsion and flight, with approximately 15,000 Arab residents being displaced between April 21–22, and with only 4,000 remaining in the city by mid-May from a pre-conflict population of approximately 65,000.

The Aleppo Codex is a medieval bound manuscript of the Hebrew Bible. The codex was written in the city of Tiberias in the tenth century CE under the rule of the Abbasid Caliphate, and was endorsed for its accuracy by Maimonides. Together with the Leningrad Codex, it contains the Aaron ben Moses ben Asher Masoretic Text tradition.

Beit Alfa is a kibbutz in the Northern District of Israel, founded in 1922 by immigrants from Poland. Located at the base of the Gilboa ridge, it falls under the jurisdiction of Gilboa Regional Council. As of 2022 its population was 1,386.

Neve Yaakov is an Israeli settlement in East Jerusalem, part of the Israeli-occupied territories, north of the settlement of Pisgat Ze'ev and south of the Palestinian locality of al-Ram. Established in 1924 during the period of the British Mandate, it was depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. The area was captured by Israel in the Six-Day War and a new neighborhood was built nearby, at which time international opposition to its legitimacy began. The international community considers Israeli settlements in East Jerusalem illegal under international law, but the Israeli government disputes this, defining it as a neighborhood within the jurisdiction of the Jerusalem Municipality, which provides all services. The population of Neve Yaakov is 23,300. Neve Yaakov is one of the Ring Settlements of East Jerusalem. The settlement is also the location of the IDF's Central Command for the West Bank, Jerusalem, Sharon, Gush Dan and Shephelah.

Tel Mond is a town in the Sharon region of Israel, located east of Netanya and north of Kfar Saba. In 2022 it had a population of 14,477..

Kfar Yona is a city in the Sharon subdistrict in the Central District of Israel. It is located between the cities Netanya and Tulkarm, about 8 km east of Netanya in the central junction between Highway 6 and Highway 4. The village was established in 1932 by Maurice Fischer and was declared a local council in the year 1940. Following developments in the fields of construction, industry and, education, the local council received city status in February 11th 2014. In 2024 the city has a jurisdiction of 11,550 dunams (~11.55 km2) and a population of 29,953.

Magdiel is a Youth Aliyah boarding school in Hod Hasharon, Israel.

Tiferet Yisrael Synagogue, most often spelled Tiferet Israel, also known as the Nisan Bak Shul, after its co-founder, Nisan Bak was a prominent synagogue between 1872 and 1948 in the Jewish Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem.

The Tiberias massacre took place on 2 October 1938, during the 1936–39 Arab revolt in Tiberias, then located in the British Mandate of Palestine and today is located in the State of Israel.

Givat Brenner, is a kibbutz in the Central District of Israel. Located around two kilometres south of Rehovot, it falls under the jurisdiction of Brenner Regional Council. Founded in 1928, it is named after writer Yosef Haim Brenner, who was killed in the Jaffa riots of 1921. In 2022 it had a population of 2,701. It is the largest kibbutz in Israel.

Givat HaShlosha is a kibbutz in central Israel. Located about 4 km east of Petah Tikva, near the Yarkon river, it falls under the jurisdiction of Drom Hasharon Regional Council. In 2022 it had a population of 922.

Na'an is a kibbutz near the city of Rehovot in Israel. Located within the Central District, it falls under the jurisdiction of Gezer Regional Council and borders the villages of Ganei Hadar, Ramot Meir and Sitria. Founded in 1930, it is the first kibbutz established by Jews born in Eretz Israel. Kibbutz Naan is the largest kibbutz in Israel in terms of population.
Hof HaSharon Regional Council, is a regional council in the Central and Tel Aviv districts of Israel. It is located on the coastline in the Sharon area between Netanya and Herzliya.

Beit Yitzhak-Sha'ar Hefer is a moshav in central Israel. Located in the Sharon plain near Netanya, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hefer Valley Regional Council. In 2022 Beit-Yitzhak-Sha'ar Hefer had a population of 2,138.

Matan is a community settlement in central Israel. Located near Yarhiv and Nirit, it falls under the jurisdiction of Drom HaSharon Regional Council. In 2022 it had a population of 3,570.

Kfar Hess is a moshav in central Israel. Located in the Sharon plain to the south-east of Tel Mond and covering 3,800 dunams, located 262.5 feet above sea level and it falls under the jurisdiction of Lev HaSharon Regional Council. In 2022 it had a population of 1,550.
Magdiel is a Hebrew name associated with any of the following:
Beth Alpha is a sixth-century CE synagogue located at the foot of the northern slopes of the Gilboa mountains near Beit She'an, Israel. It is now part of Bet Alfa Synagogue National Park and managed by the Israel Nature and Parks Authority.