A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name Palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which housed the Imperial residences. Most European languages have a version of the term, and many use it for a wider range of buildings than English. In many parts of Europe, the equivalent term is also applied to large private houses in cities, especially of the aristocracy; often the term for a large country house is different. Many historic palaces are now put to other uses such as parliaments, museums, hotels, or office buildings. The word is also sometimes used to describe a lavishly ornate building used for public entertainment or exhibitions, such as a movie palace.
Trinidad and Tobago, a country that relies heavily on industrialisation and tourism, has various transport systems.

Port of Spain, officially the City of Port of Spain, is the capital city of Trinidad and Tobago and the country's second-largest city after San Fernando and the third largest municipality after Chaguanas and San Fernando. The city has a municipal population of 37,074, an urban population of 81,142 and a transient daily population of 250,000. It is located on the Gulf of Paria, on the northwest coast of the island of Trinidad and is part of a larger conurbation stretching from Chaguaramas in the west to Arima in the east with an estimated population of 600,000.

Lismore Castle is the Irish home of the Duke of Devonshire. Located in the town of Lismore in County Waterford in the Republic of Ireland, it belonged to the Earls of Desmond, and subsequently to the Cavendish family from 1753. It was largely re-built in the Gothic style during the mid-nineteenth century for The 6th Duke of Devonshire.

The Augustusburg and Falkenlust Palaces form a historical building complex in Brühl, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, which has been listed as a UNESCO cultural World Heritage Site since 1984. The buildings are connected by the spacious gardens and trees of the Schlosspark. Augustusburg Palace and its parks also serve as a venue for the Brühl Palace Concerts. The Max Ernst Museum is located nearby.

An English country house is a large house or mansion in the English countryside. Such houses were often owned by individuals who also owned a town house. This allowed them to spend time in the country and in the city—hence, for these people, the term distinguished between town and country. However, the term also encompasses houses that were, and often still are, the full-time residence for the landed gentry that ruled rural Britain until the Reform Act 1832. Frequently, the formal business of the counties was transacted in these country houses.

The Panyols are a Pardo (tri-racial) ethnic group in Trinidad and Tobago of mixed Spanish, South American Amerindian, Trinidadian and Tobagonian Amerindian, Afro-Latin American, and Afro-Trinidadian and Tobagonian descent. They comprise the Cocoa Estate Plantations owners community along with peasant workers from Venezuela and Colombia, also referred to as Pagnols, local Spanish, Cocoa panyols. They were born of the shared Island nation, on both sides of the Gulf of Paria, Peninsulas that settling within the Northern Range Rain Forest Mountains Valleys of Trinidad and Tobago Caura River, down the mountains into the Tacarigua River into the Caroni River, and the Orinoco, and Caura River Venezuela. They played an important role in the development of the cocoa industry in Trinidad and Tobago, running the Cocoa Estate and not to be confused with the freed community of former slaves.

Hardwick Hall, in Derbyshire, is an architecturally significant Elizabethan country house in England, a leading example of the Elizabethan prodigy house. Built between 1590 and 1597 for the formidable Bess of Hardwick, it was designed by the architect Robert Smythson, an exponent of the Renaissance style of architecture. Hardwick Hall is one of the earliest examples of the English interpretation of this style, which came into fashion having slowly spread from Florence. Its arrival in Britain coincided with the period when it was no longer necessary or legal to fortify a domestic dwelling. Ownership of the house was transferred to the National Trust in 1959. It is fully open to the public and received 285,379 visitors in 2018.

Diego Martin is a town and is the urban commercial center and capital of the Diego Martin region in Trinidad and Tobago. Its location in the region is just on the south eastern border, west of the capital city of Port of Spain and east of the town of Carenage. Diego Martin town in the Northern Range was once filled with a number of small valleys but is now a densely populated area. It was named after a Spanish explorer Don Diego Martín. The area was settled by French planters and their slaves in the 1780s. It consists of a cluster of communities including Congo Village, Diamond Vale, Green Hill, Patna Village, Petit Valley, Blue Range, La Puerta Avenue, Four Roads, Rich Plain, River Estate, Blue Basin, Water Wheel, West Moorings, Bagatelle and Sierra Leone.

Mediterranean Revival is a design style introduced in the United States in the waning nineteenth century variously incorporating references from Spanish Renaissance, Spanish Colonial, Beaux-Arts, Italian Renaissance, Arabic Andalusian architecture, and Venetian Gothic architecture.

Cawood Castle is a grade I listed building in Cawood, a village in North Yorkshire, England. The surviving fifteenth-century structures formed part of a fortified medieval palace belonging to the Archbishops of York, which was dismantled in the aftermath of the English Civil War.
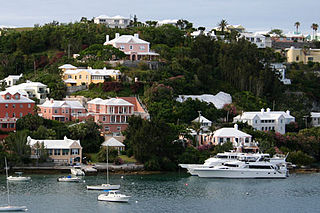
The architecture of Bermuda has developed over the past four centuries. The archipelago's isolation, environment, climate, and scarce resources have been key driving points, though inspiration from Europe, the Caribbean and the Americas is evident. Distinctive elements appeared with initial settlement in the early 17th century, and by the second half of that century features that remain common today began to appear.

Queen's Park Savannah is a park in Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago. Known locally as simply "the Savannah," it is Port of Spain's largest open space. It occupies about 260 acres (110 ha) of level land, and the distance around the perimeter is about 2.2 mi (3.5 km).

Maraval is one of the northern suburbs of Trinidad's capital, Port of Spain, a valley in northern Trinidad in Trinidad and Tobago. It is situated at the bottom of the hills of Paramin and located east of the Diego Martin valley to which it is connected directly by Morne Coco Road, and west of Santa Cruz valley, to which it is connected by Saddle Road.

The Red House is the seat of Parliament in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. The architectural design of the Red House is of Beaux-Arts style. The original building was destroyed in the 1903 water riots and was rebuilt in the year 1907. The Red House is located centrally within the capital city Port of Spain. It is currently used as a meeting place for parliament and elections and for political uses.

President's House is the official residence of the President of Trinidad and Tobago, located in the capital city Port of Spain, on Trinidad island, Trinidad and Tobago. It is next to the Royal Botanic Gardens.
The National Trust of Trinidad and Tobago is managed by an eleven-member Council of different expertise and backgrounds. Five members are elected to the position, and six are ministerial appointments. Its offices are located in Port of Spain in Trinidad.

In north-east Port of Spain, Belmont, at the foot of the Laventille Hills, was the city's first suburb. In the 1840s–'50s, parts of the area were settled by Africans rescued by the Royal Navy from illegal slaving ships. In the 1880s–'90s, the population swelled rapidly, and the characteristic Belmont street pattern of narrow, winding lanes developed. The black professional class built large homes in Belmont, as they were excluded from the more expensive neighbourhoods such as St. Clair and Maraval; Belmont became known as "the Black St. Clair". Many of these large homes have been renovated and converted to business use, but some remain in family hands. Belmont currently is a lower-middle to middle-class residential neighbourhood. It was the birthplace and early home of many important Carnival designers and bandleaders. Belmont has 9,035 inhabitants.

St Clair is a quiet, spacious, and upscale business and residential district between the Queen's Park Savannah and the Maraval River in Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago. It is home to most of the city's grandest and largest mansions and also home to the Magnificent Seven Houses. Federation Park and Ellerslie Park. St Clair is one of Port of Spain's five police districts.

Demerara windows were built primarily into 18th- and 19th-century Colonial architecture-styled buildings to cool homes in hot climates, such as Guyana, before the invention of air conditioning. The window design includes perforated sides and louvres to block direct sunlight. They are shuttered sash windows with the shutter hinged at the top so it could be propped open, sloping outward. They were generally propped open with a stick. At the window sill, a container of ice, water, or a potted plant helps cool warm air as it passes through the window into the building. The windows are generally fitted in the upper floors. Initially, this type of window was just used in the homes of the wealthy, but spread over time to the homes of other classes of people.