
Electronic mail is a method of transmitting and receiving messages using electronic devices. It was conceived in the late–20th century as the digital version of, or counterpart to, mail. Email is a ubiquitous and very widely used communication medium; in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries.
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is an Internet standard communication protocol for electronic mail transmission. Mail servers and other message transfer agents use SMTP to send and receive mail messages. User-level email clients typically use SMTP only for sending messages to a mail server for relaying, and typically submit outgoing email to the mail server on port 587 or 465 per RFC 8314. For retrieving messages, IMAP is standard, but proprietary servers also often implement proprietary protocols, e.g., Exchange ActiveSync.
An email address identifies an email box to which messages are delivered. While early messaging systems used a variety of formats for addressing, today, email addresses follow a set of specific rules originally standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in the 1980s, and updated by RFC 5322 and 6854. The term email address in this article refers to just the addr-spec in Section 3.4 of RFC 5322. The RFC defines address more broadly as either a mailbox or group. A mailbox value can be either a name-addr, which contains a display-name and addr-spec, or the more common addr-spec alone.
Various anti-spam techniques are used to prevent email spam.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email authentication method which ensures the sending mail server is authorized to originate mail from the email sender's domain. This authentication only applies to the email sender listed in the "envelope from" field during the initial SMTP connection. If the email is bounced, a message is sent to this address, and for downstream transmission it typically appears in the "Return-Path" header. To authenticate the email address which is actually visible to recipients on the "From:" line, other technologies such as DMARC must be used. Forgery of this address is known as email spoofing, and is often used in phishing and email spam.
Greylisting is a method of defending e-mail users against spam. A mail transfer agent (MTA) using greylisting will "temporarily reject" any email from a sender it does not recognize. If the mail is legitimate, the originating server will try again after a delay, and if sufficient time has elapsed, the email will be accepted.
A bounce message or just "bounce" is an automated message from an email system, informing the sender of a previous message that the message has not been delivered. The original message is said to have "bounced".
Sender ID is an historic anti-spoofing proposal from the former MARID IETF working group that tried to join Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and Caller ID. Sender ID is defined primarily in Experimental RFC 4406, but there are additional parts in RFC 4405, RFC 4407 and RFC 4408.
Email filtering is the processing of email to organize it according to specified criteria. The term can apply to the intervention of human intelligence, but most often refers to the automatic processing of messages at an SMTP server, possibly applying anti-spam techniques. Filtering can be applied to incoming emails as well as to outgoing ones.
Email authentication, or validation, is a collection of techniques aimed at providing verifiable information about the origin of email messages by validating the domain ownership of any message transfer agents (MTA) who participated in transferring and possibly modifying a message.
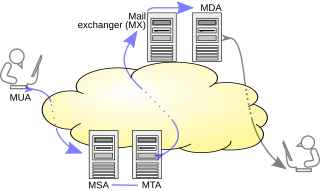
A message submission agent (MSA), or mail submission agent, is a computer program or software agent that receives electronic mail messages from a mail user agent (MUA) and cooperates with a mail transfer agent (MTA) for delivery of the mail. It uses ESMTP, a variant of the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), as specified in RFC 6409.
Forward-confirmed reverse DNS (FCrDNS), also known as full-circle reverse DNS, double-reverse DNS, or iprev, is a networking parameter configuration in which a given IP address has both forward (name-to-address) and reverse (address-to-name) Domain Name System (DNS) entries that match each other. This is the standard configuration expected by the Internet standards supporting many DNS-reliant protocols. David Barr published an opinion in RFC 1912 (Informational) recommending it as best practice for DNS administrators, but there are no formal requirements for it codified within the DNS standard itself.
The Sender Rewriting Scheme (SRS) is a scheme for bypassing the Sender Policy Framework's (SPF) methods of preventing forged sender addresses. Forging a sender address is also known as email spoofing.
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication method designed to detect forged sender addresses in email, a technique often used in phishing and email spam.
Email forwarding generically refers to the operation of re-sending a previously delivered email to an email address to one or more different email addresses.
Backscatter is incorrectly automated bounce messages sent by mail servers, typically as a side effect of incoming spam.
A bounce address is an email address to which bounce messages are delivered. There are many variants of the name, none of them used universally, including return path, reverse path, envelope from, envelope sender, MAIL FROM, 5321-FROM, return address, From_, Errors-to, etc. It is not uncommon for a single document to use several of these names.
SMTP Authentication, often abbreviated SMTP AUTH, is an extension of the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) whereby a client may log in using any authentication mechanism supported by the server. It is mainly used by submission servers, where authentication is mandatory.
Spam reporting, more properly called abuse reporting, is the action of designating electronic messages as abusive for reporting to an authority so that they can be dealt with. Reported messages can be email messages, blog comments, or any kind of spam.
A mailbox provider, mail service provider or, somewhat improperly, email service provider is a provider of email hosting. It implements email servers to send, receive, accept, and store email for other organizations or end users, on their behalf.

