
The Western United States is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau.
Stephen J. Pyne (1949–present) is an emeritus professor at Arizona State University, specializing in environmental history, the history of exploration, and especially the history of fire.

The Rocky Flats Plant was a United States manufacturing complex that produced nuclear weapons parts in the western United States, near Denver, Colorado. The facility's primary mission was the fabrication of plutonium pits, which were shipped to other facilities to be assembled into nuclear weapons. Operated from 1952 to 1992, the complex was under the control of the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission (AEC), succeeded by the Department of Energy (DOE) in 1977.

Environmental history is the study of human interaction with the natural world over time, emphasising the active role nature plays in influencing human affairs and vice versa.

Pondcrete is a mixture of cement and sludge. Its role is to immobilize hazardous waste and, in some cases, low-level and mixed-level radioactive waste, in the form of solid material. The material was used by the United States Department of Energy and its contractor, Rockwell International, in an attempt to handle the radioactive waste from contaminated ponds in the Rocky Flats Plant for burial in Nevada desert. Portland cement is mixed with sludge to solidify into “pondcrete” blocks and placed into large, plastic lined boxes. The sludge is taken from solar evaporation ponds which are used to remove moisture from waste materials, therefore reducing their weight. To do this, liquid waste is poured into artificial, shallow ponds. The waste is heated by solar radiation and any moisture is evaporated, leaving behind the waste. These ponds contained low level radioactive process waste as well as sanitary sewage sludge and wastes, which categorize them and the Pondcrete as a mixed waste.

The Rocky Flats National Wildlife Refuge is 5,237-acre (21.19 km2) National Wildlife Refuge in the United States, located approximately 16 miles (26 km) northwest of Denver, Colorado. The refuge is situated west of the cities of Broomfield and Westminster and situated north of the city of Arvada.
Anti-nuclear organizations may oppose uranium mining, nuclear power, and/or nuclear weapons. Anti-nuclear groups have undertaken public protests and acts of civil disobedience which have included occupations of nuclear plant sites. Some of the most influential groups in the anti-nuclear movement have had members who were elite scientists, including several Nobel Laureates and many nuclear physicists.

Kristen Iversen is an American writer of nonfiction and fiction. Her books include Full Body Burden: Growing Up in the Nuclear Shadow of Rocky Flats, Molly Brown: Unraveling the Myth and Shadow Boxing: Art and Craft in Creative Nonfiction, as well as the anthologies Don't Look Now: Things We Wish We Hadn't Seen and Doom with a View: Historical and Cultural Contexts of the Rocky Flats Nuclear Weapons Plant. She is a Professor in English and Creative Writing at the University of Cincinnati and Literary Nonfiction Editor of The Cincinnati Review. Iversen was chosen to be a Fulbright Scholar at the University of Bergen, Norway in 2020-2021.

Freedom from Fear: The American People in Depression and War, 1929–1945 is a 1999 nonfiction book by the American historian David M. Kennedy. Published as part of the Oxford History of the United States, Freedom from Fear covers the history of the United States during the Great Depression and World War II. It won the 2000 Pulitzer Prize for History.

The Bodega Bay Nuclear Power Plant was a proposed Northern California nuclear power facility that was stopped by local activism in the 1960s and never built. The foundations, located 2 miles (3.2 km) west of the active San Andreas Fault, were being dug at the time the plant was cancelled. The action has been termed "the birth of the anti-nuclear movement."

In nuclear weapon design, the pit is the core of an implosion nuclear weapon, consisting of fissile material and any neutron reflector or tamper bonded to it. Some weapons tested during the 1950s used pits made with uranium-235 alone, or as a composite with plutonium. All-plutonium pits are the smallest in diameter and have been the standard since the early 1960s. The pit is named after the hard core found in stonefruit such as peaches and apricots.
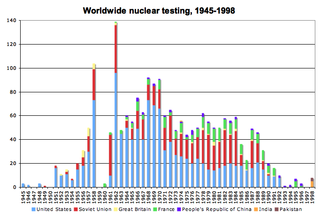
The application of nuclear technology, both as a source of energy and as an instrument of war, has been controversial.

These are lists of nuclear disasters and radioactive incidents.
Pam Solo is an arms control analyst, and Founder and President of the Civil Society Institute.
Len Earl Ackland is a journalist and retired journalism professor from the University of Colorado Boulder. He was founding director of the Center for Environmental Journalism in 1992.

The United States Government Accountability Office reported more than 150 incidents from 2001 to 2006 of nuclear plants not performing within acceptable safety guidelines. According to a 2010 survey of energy accidents, there have been at least 56 accidents at nuclear reactors in the United States. The most serious of these was the Three Mile Island accident in 1979. Davis-Besse Nuclear Power Plant has been the source of two of the top five most dangerous nuclear incidents in the United States since 1979. Relatively few accidents have involved fatalities.

The Rocky Flats Plant, a former United States nuclear weapons production facility located about 15 miles (24 km) northwest of Denver, caused radioactive contamination within and outside its boundaries. The contamination primarily resulted from two major plutonium fires in 1957 and 1969 and from wind-blown plutonium that leaked from barrels of radioactive waste. Much lower concentrations of radioactive isotopes were released throughout the operational life of the plant from 1952 to 1992, from smaller accidents and from normal operational releases of plutonium particles too small to be filtered. Prevailing winds from the plant carried airborne contamination south and east, into populated areas northwest of Denver.

Nuclear ethics is a cross-disciplinary field of academic and policy-relevant study in which the problems associated with nuclear warfare, nuclear deterrence, nuclear arms control, nuclear disarmament, or nuclear energy are examined through one or more ethical or moral theories or frameworks.














