Related Research Articles

Amory Bloch Lovins is an American writer, physicist, and Chairman/Chief Scientist of the Rocky Mountain Institute. He has written on energy policy and related areas for four decades, and served on the National Petroleum Council, an oil industry lobbying group, from 2011–2018. In 1983, Lovins was awarded the Right Livelihood Award for "pioneering soft energy paths for global security." He was named by TIME magazine one of the World's 100 most influential people in 2009.
The Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS) is a nonprofit science advocacy organization based in the United States. The UCS membership includes many private citizens in addition to professional scientists. Anne Kapuscinski, Sherman Fairchild professor of sustainability science in the Environmental Studies Program at Dartmouth College, currently chairs the UCS Board of Directors, having replaced James J. McCarthy, Professor of Biological Oceanography at Harvard University and past president of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in 2015.

Energy development is the field of activities focused on obtaining sources of energy from natural resources. These activities include production of conventional, alternative and renewable sources of energy, and for the recovery and reuse of energy that would otherwise be wasted. Energy conservation and efficiency measures reduce the demand for energy development, and can have benefits to society with improvements to environmental issues.
A green economy is an economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological economics, but has a more politically applied focus. The 2011 UNEP Green Economy Report argues "that to be green, an economy must not only be efficient, but also fair. Fairness implies recognizing global and country level equity dimensions, particularly in assuring a Just Transition to an economy that is low-carbon, resource efficient, and socially inclusive."
A nuclear power phase-out is the discontinuation of usage of nuclear power for energy production. Often initiated because of concerns about nuclear power, phase-outs usually include shutting down nuclear power plants and looking towards fossil fuels and renewable energy. Three nuclear accidents have influenced the discontinuation of nuclear power: the 1979 Three Mile Island partial nuclear meltdown in the United States, the 1986 Chernobyl disaster in the USSR, and the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan.

The energy policy of the United States is determined by federal, state, and local entities in the United States, which address issues of energy production, distribution, and consumption, such as building codes and gas mileage standards. Energy policy may include legislation, international treaties, subsidies and incentives to investment, guidelines for energy conservation, taxation and other public policy techniques.

Taiwan relies on imports for almost 98% of its energy in 2016, which leaves the island's energy supply vulnerable to external disruption. In order to reduce this dependence, the Ministry of Economic Affairs' Bureau of Energy has been actively promoting energy research at several universities since the 1990s.
The Institute for Energy and Environmental Research (IEER) is an anti-nuclear organization which focuses on the environmental safety of nuclear weapons production, ozone layer depletion, and other issues relating to energy. IEER publishes a variety of books on energy-related issues, conducts workshops for activists on nuclear issues, and sponsors international symposia and educational outreach projects. IEER was established in 1987 and is based in Takoma Park, Maryland.

Greenhouse Solutions with Sustainable Energy is a 2007 book by Australian academic Mark Diesendorf. The book puts forward a set of policies and strategies for implementing the most promising clean energy technologies by all spheres of government, business and community organisations. Greenhouse Solutions with Sustainable Energy suggests that a mix of efficient energy use, renewable energy sources and natural gas offers a clean and feasible energy future for Australia.
A green-collar worker is a worker who is employed in the environmental sectors of the economy. Environmental green-collar workers satisfy the demand for green development. Generally, they implement environmentally conscious design, policy, and technology to improve conservation and sustainability. Formal environmental regulations as well as informal social expectations are pushing many firms to seek professionals with expertise with environmental, energy efficiency, and clean renewable energy issues. They often seek to make their output more sustainable, and thus more favorable to public opinion, governmental regulation, and the Earth's ecology.

The anti-nuclear movement in the United States consists of more than 80 anti-nuclear groups that oppose nuclear power, nuclear weapons, and/or uranium mining. These have included the Abalone Alliance, Clamshell Alliance, Committee for Nuclear Responsibility, Nevada Desert Experience, Nuclear Information and Resource Service, Physicians for Social Responsibility, Plowshares Movement, Women Strike for Peace, and Women's International League for Peace and Freedom. The anti-nuclear movement has delayed construction or halted commitments to build some new nuclear plants, and has pressured the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to enforce and strengthen the safety regulations for nuclear power plants.
Canada has an active anti-nuclear movement, which includes major campaigning organisations like Greenpeace and the Sierra Club. Over 300 public interest groups across Canada have endorsed the mandate of the Campaign for Nuclear Phaseout (CNP). Some environmental organisations such as Energy Probe, the Pembina Institute and the Canadian Coalition for Nuclear Responsibility (CCNR) are reported to have developed considerable expertise on nuclear power and energy issues. There is also a long-standing tradition of indigenous opposition to uranium mining.

Mycle Schneider is a Paris-based nuclear energy consultant and anti-nuclear activist. He is the lead author of The World Nuclear Industry Status Reports. He has advised members of the European Parliament on energy issues for more than twenty years. In 1997 he received the Right Livelihood Award.

Energy laws govern the use and taxation of energy, both renewable and non-renewable. These laws are the primary authorities related to energy. In contrast, energy policy refers to the policy and politics of energy.

The nuclear power debate is a long-running controversy about the risks and benefits of using nuclear reactors to generate electricity for civilian purposes. The debate about nuclear power peaked during the 1970s and 1980s, as more and more reactors were built and came online, and "reached an intensity unprecedented in the history of technology controversies" in some countries. Thereafter, the nuclear industry created jobs, focused on safety, and public concerns mostly waned. In the last decade, however, with growing public awareness about climate change and the critical role that carbon dioxide and methane emissions plays in causing the heating of the earth's atmosphere, there has been a resurgence in the intensity of the nuclear power debate. Nuclear power advocates and those most concerned about climate change point to nuclear power's reliable, emission-free, high-density energy, alongside a generation of young physicists and engineers working to bring a new generation of nuclear technology into existence to replace fossil fuels. On the other hand, skeptics point to nuclear accidents such as the death of Louis Slotin, the Windscale fire, the Three Mile Island accident, the Chernobyl disaster, and the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, combined with escalating acts of global terrorism, to argue against continuing use of the technology.

More than 80 anti-nuclear groups are operating, or have operated, in the United States. These include Abalone Alliance, Clamshell Alliance, Greenpeace USA, Institute for Energy and Environmental Research, Musicians United for Safe Energy, Nevada Desert Experience, Nuclear Control Institute, Nuclear Information and Resource Service, Public Citizen Energy Program, Shad Alliance, and the Sierra Club. These are direct action, environmental, health, and public interest organizations who oppose nuclear weapons and/or nuclear power. In 1992, the chairman of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission said that "his agency had been pushed in the right direction on safety issues because of the pleas and protests of nuclear watchdog groups".
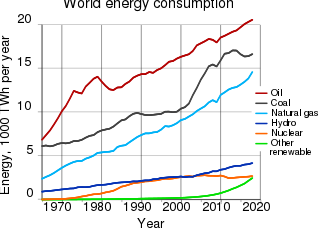
The environmental impact of the energy industry is diverse. Energy has been harnessed by human beings for millennia. Initially it was with the use of fire for light, heat, cooking and for safety, and its use can be traced back at least 1.9 million years. In recent years there has been a trend towards the increased commercialization of various renewable energy sources.

Barry William Brook is an Australian scientist. He is an ARC Australian Laureate Professor and Chair of Environmental Sustainability at the University of Tasmania in the Faculty of Science, Engineering & Technology. He was formerly an ARC Future Fellow in the School of Earth and Environmental Sciences at the University of Adelaide, Australia, where he held the Sir Hubert Wilkins Chair of Climate Change from 2007 to 2014. He was also Director of Climate Science at the Environment Institute.
M. V. Ramana is a physicist who works at the Nuclear Futures Laboratory and the Program on Science and Global Security, both at Princeton University, on the future of nuclear power in the context of climate change and nuclear disarmament. Ramana is a member of the International Panel on Fissile Materials and the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists’ Science and Security Board.

There are large variations in peoples’ understanding of the issues surrounding nuclear power, including the technology itself, climate change, and energy security. Proponents of nuclear energy contend that nuclear power is a sustainable energy source that reduces carbon emissions and increases energy security by decreasing dependence on imported energy sources. Opponents believe that nuclear power poses many threats to people and the environment. While nuclear power has historically been opposed by many environmentalist organisations, some support it, as do some scientists.
References
- ↑ Clayton, Mark (2011-03-14). "Japanese nuclear reactor update: Amid signs of progress, new problems". The Christian Science Monitor .
"There should be much more attention paid to the spent-fuel pools," says Arjun Makhijani, a nuclear engineer and president of the anti-nuclear power Institute for Energy and Environmental Research.
- ↑ Davidson, Keay (1998-07-20). "Activists: Super-laser may bring tiny nukes". San Francisco Chronicle .
...says a report by physicist Arjun Makhijani and his colleague Hisham Zerriffi. They work at a leading anti-nuclear think tank, the Institute for Energy and Environmental Research in Takoma Park, Md.
- ↑ IEER Program Staff Profiles
- ↑ "Energy and Agriculture in the Third World" Archived October 25, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "A Time to Choose" Archived October 25, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ John Bartlow Martin Award Archived 2009-04-08 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ DC Hiroshima-Nagasaki Peace Committee Archived January 29, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ 2007/2008 JBL Award Archived August 10, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
