
The silicoflagellates are a small group of unicellular photosynthetic protists, or algae, belonging to the supergroup of eukaryotes known as Stramenopiles. They behave as plankton and are present in oceanic waters. They are well-known from harmful algal blooms that cause high mortality of fish. Additionally, they compose a rich fossil record represented by their silica skeletons.
The synurids are a small group of heterokont algae, found mostly in freshwater environments, characterized by cells covered in silica scales.

Brown algae are a large group of multicellular algae comprising the class Phaeophyceae. They include many seaweeds located in colder waters of the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and polar regions. Many brown algae, such as members of the order Fucales, commonly grow along rocky seashores. Most brown algae live in marine environments, where they play an important role both as food and as a potential habitat. For instance, Macrocystis, a kelp of the order Laminariales, may reach 60 m (200 ft) in length and forms prominent underwater kelp forests that contain a high level of biodiversity. Another example is Sargassum, which creates unique floating mats of seaweed in the tropical waters of the Sargasso Sea that serve as the habitats for many species. Some members of the class, such as kelps, are used by humans as food.

The Chrysophyceae, usually called chrysophytes, chrysomonads, golden-brown algae or golden algae, are a large group of algae, found mostly in freshwater. Golden algae is also commonly used to refer to a single species, Prymnesium parvum, which causes fish kills.

The Chamaemyiidae are a small family of acalyptrate flies with less than 200 species described worldwide. The larvae of these small flies are active and predatory and are often used for biological control of aphids, scale insects, and similar pests. Chamaemyiid fossils are poorly represented in amber deposits, but a few examples are known from the Eocene epoch onwards.

Althenia is a genus of aquatic plants of the family Potamogetonaceae. This has long been a group of two species in the Mediterranean Europe and South Africa, but in 2016 was revised to include an Australasian relative, Lepilaena. The genus is named after the agronomist Jean Althen.

Ochrophytes, also known as heterokontophytes or stramenochromes, are a group of algae. They are the photosynthetic stramenopiles, a group of eukaryotes, organisms with a cell nucleus, characterized by the presence of two unequal flagella, one of which has tripartite hairs called mastigonemes. In particular, they are characterized by photosynthetic organelles or plastids enclosed by four membranes, with membrane-bound compartments called thylakoids organized in piles of three, chlorophyll a and c as their photosynthetic pigments, and additional pigments such as β-carotene and xanthophylls. Ochrophytes are one of the most diverse lineages of eukaryotes, containing ecologically important algae such as brown algae and diatoms. They are classified either as phylum Ochrophyta or Heterokontophyta, or as subphylum Ochrophytina within phylum Gyrista. Their plastids are of red algal origin.

Klebsormidium is a genus of filamentous charophyte green algae comprising 20 species. The name was proposed in 1972 to resolve confusion in application and status of Hormidium and was given for the German botanist Georg Albrecht Klebs.

Chaetotaxy is the arrangement of bristles (macrochaetae) on an arthropod or annelid, or taxonomy based on their position and size. For example, it is important in Diptera, in which group it was formalised by Ernst August Girschner. The term chaetotaxy was later proposed by Carl Robert Osten-Sacken.
Mary Winifred Parke, FRS, was a British marine botanist and Fellow of the Royal Society (1972) specialising in phycology, the study of algae.
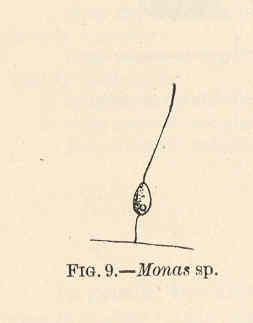
Monas is a genus of Chrysophyceae, described by Otto Friedrich Müller in 1773 as a group of Infusoria. Throughout time, it represented an aggregate genus.
Mallomonas lacuna is a species of heterokont algae. It is a tiny free-living cell, about the width of a human hair. It has ornate scales and bristles, as well as long spines. It is a relatively common part of lake or pond plankton. It differs from its cogenerates by the number, distribution, and size of its base plate pores, the secondary structures on the scale surfaces, together with characteristics of its bristles.
Mallomonas hexareticulata is a species of heterokont algae. It is a tiny free-living cell, about the width of a human hair. It has ornate scales and bristles, as well as long spines. It is a relatively common part of lake or pond plankton. It differs from its cogenerates by the number, distribution, and size of its base plate pores, the secondary structures on the scale surfaces, together with characteristics of its bristles.
Mallomonas pseudomatvienkoae is a species of heterokont algae. It is a tiny free-living cell, about the width of a human hair. It has ornate scales and bristles, as well as long spines. It is a relatively common part of lake or pond plankton. It differs from its cogenerates by the number, distribution, and size of its base plate pores, the secondary structures on the scale surfaces, together with characteristics of its bristles.
Mallomonas pleuriforamen is an extinct species of heterokont algae. It was first found in Middle Eocene lacustrine deposits from northwestern Canada. It was a tiny free-living cell, about the width of a human hair. It had ornate scales and bristles, as well as long spines. It was a relatively common part of lake or pond plankton. It differs from its cogenerates by the number, distribution, and size of its base plate pores, the secondary structures on the scale surfaces, together with characteristics of its bristles.

Mallomonas is a genus comprising unicellular algal eukaryotes and characterized by their intricate cell coverings made of silica scales and bristles. The group was first named and classified by Dr. Maximilian Perty in 1852. These organisms live in freshwater and are widely distributed around the world. Some well known species include Mallomonas caudata and Mallomonas splendens.

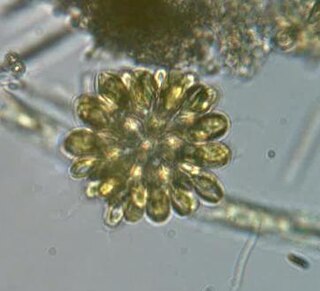
Synura is a genus of colonial chrysomonad algae covered in silica scales. It is the most conspicuous genus of the order Synurales.

Triparma is a genus of unicellular algae in the family Triparmaceae in the order Parmales. They form siliceous plates on the cell surface that aid in identification. Triparma is distinguished by its possession of three shield plates, three triradiate girdle plates, a triradiate girdle plate with notched ends, and a small ventral plate. It was first described by Booth & Marchant in 1987 and the holotype is Triparma columacea.
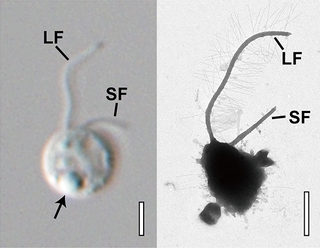
Ochromonadales is an order of single-celled algae belonging to the class Chrysophyceae, also known as golden algae. Initially it contained numerous groups of flagellates that were not closely related. During the late 20th century, advancements in molecular and ultrastructural studies allowed the transfer of many of these groups out of Ochromonadales, and the order was reduced to a single family Ochromonadaceae. They are aquatic single-celled flagellated algae, with two heterokont flagella each, some of which have secondarily lost their chloroplasts and appear colorless.












