Related Research Articles

Salford is a city in Greater Manchester, England, situated on the western bank of the River Irwell which forms its boundary with Manchester city centre. Landmarks in the city include the former town hall, Salford Cathedral, Salford Lads' Club and St Philip's Church. In 2021 it had a population of 129,794. The demonym for people from Salford is Salfordian.

A panda car, or just panda, is a small- or medium-sized marked British police car.

Thomas Worthington was a 19th-century English architect, particularly associated with public buildings in and around Manchester. Worthington's preferred style was the Gothic Revival.

Merseyside Police is the territorial police force responsible for policing Merseyside in North West England. The service area is 647 square kilometres with a population of around 1.5 million. As of September 2017 the service has 3,484 police officers, 1,619 police staff, 253 police community support officers, 155 designated officers and 208 special constables. The force is led by Chief Constable Serena Kennedy.
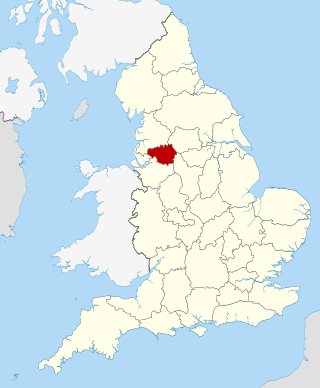
Greater Manchester Police (GMP) is the territorial police force responsible for law enforcement within the metropolitan county of Greater Manchester in North West England.

Sir Percy Joseph Sillitoe KBE DL was a chief constable of several police forces. He changed the role of radios, civilian staff, and women police officers within the police. He was later Director General of MI5, the United Kingdom's internal security service, from 1946 to 1953.

Lancashire Constabulary is the territorial police force responsible for policing the ceremonial county of Lancashire in North West England. The force's headquarters are at Hutton, near the city of Preston. As of September 2020, the force has 3,088 police officers, 190 special constables, and 280 police community support officers (PCSO), 300 police support volunteers (PSV), and 2,287 staff.
Liverpool and Bootle Constabulary was a short-lived police force in England from 1 April 1967 to 1 April 1974. It was created as a merger of the Liverpool City Police and Bootle Borough Police, and covered the adjacent county boroughs of Liverpool and Bootle. It was amalgamated under the Local Government Act 1972 with parts of the Lancashire Constabulary and Cheshire Constabulary to form Merseyside Police. Its Chief Constable for the entire duration of its existence was Sir James Haughton.

The School of Medical Sciences at the University of Manchester is one of the largest in the United Kingdom with around 6,000 undergraduates, 3,000 postgraduates and 2,000 staff. It is the third oldest medical school in England and the largest medical school in the United Kingdom. The Faculty is a member of the Manchester Academic Health Science Centre and has four affiliated teaching hospitals at Manchester Royal Infirmary, Wythenshawe Hospital, Salford Royal Hospital and the Royal Preston Hospital.

Salford was, from 1844 to 1974, a local government district in the county of Lancashire in the northwest of England, covering the city of Salford. It was granted city status in 1926.

The City of Manchester forms part of the metropolitan county of Greater Manchester, which had its county council abolished in 1986. Manchester consists of several districts, but these districts do not represent a tier of government.

The Police Act 1964 was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that updated the legislation governing police forces in England and Wales, constituted new police authorities, gave the Home Secretary new powers to supervise local constabularies, and allowed for the amalgamation of existing forces into more efficient units.

Sir Robert Mark was a senior British police officer who served as Chief Constable of Leicester City Police, and later as Commissioner of the Metropolitan Police from 1972 to 1977.

Richard Lane was an English architect of the early and mid-19th century. Born in London and based in Manchester, he was known mainly for his restrained and austere Greek-inspired classicism. He also designed a few buildings – mainly churches – in the Gothic style. He planned and designed many of the houses in the exclusive Victoria Park estate.
The 1928 New Year Honours were appointments by King George V to various orders and honours to reward and highlight good works by citizens of the United Kingdom and British Empire. They were announced on 30 December 1927.

The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Manchester in north west England.
Salford City Police was the police force responsible for policing the borough of Salford, near Manchester, England from 1844 through to 1968. Prior to Salford gaining city status in 1926 the force was called Salford Borough Police.

George Noel Hill FRIBA, MTPI (1893–1985) was a British architect. He was the City Architect of Manchester and the Lancashire County Architect.

The Manchester City Police Headquarters historic building is located in Manchester, England. It was built during 1933–37 as the headquarters of the Manchester City Police.
References
- ↑ Manchester obtained city status in the United Kingdom in 1853
- ↑ Frangopulo, N. J., ed. (1962). Rich Inheritance. Manchester: Education Committee. p. 276.
- ↑ "Sir Robert Peacock, M.V.O.: Death of the Chief Constable of Manchester". The Police Review and Parade Gossip. Flickr. 26 November 1926. p. 202. Retrieved 4 January 2025.
- ↑ "Wells [née Perry], Nesta Helen". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/58141.(Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ↑ Darlington, Neil (2024). "Central Police Headquarters Bootle Street Manchester". A Biographical Dictionary of the Architects of Greater Manchester, 1800–1940. The Victorian Society . Retrieved 4 January 2025.