
GNUnet is a software framework for decentralized, peer-to-peer networking and an official GNU package. The framework offers link encryption, peer discovery, resource allocation, communication over many transports and various basic peer-to-peer algorithms for routing, multicast and network size estimation.

Launchpad is a web application and website that allows users to develop and maintain software, particularly open-source software. It is developed and maintained by Canonical Ltd.

Richard Matthew Stallman, also known by his initials, rms, is an American free software movement activist and programmer. He campaigns for software to be distributed in a manner such that its users receive the freedoms to use, study, distribute, and modify that software. Software that ensures these freedoms is termed free software. Stallman launched the GNU Project, founded the Free Software Foundation, developed the GNU Compiler Collection and GNU Emacs, and wrote the GNU General Public License.

The Transport Direct Programme was a division of the UK Department for Transport (DfT) to develop standards, data and better information technology systems to support public transport. It developed and operates the Transport Direct Portal which is a public facing multi-modal journey planner. It also supports the creation and management of comprehensive databases of all public transport movements in the United Kingdom with Traveline. During 2010 two key datasets were released as Open Data and published on www.data.gov.uk.
This is a comparison of free and open-source software licences. The comparison only covers software licences with a linked article for details, approved by at least one expert group at the FSF, the OSI, the Debian project or the Fedora project. For a list of licences not specifically intended for software, see List of free content licences.

mySociety is a UK-based registered charity, previously named UK Citizens Online Democracy. It began as a UK-focused organisation with the aim of making online democracy tools for UK citizens. However, those tools were open source, so that the code could be – and soon was – redeployed in other countries.

The Affero General Public License is a free software license. The first version of the Affero General Public License (AGPLv1), was published by Affero, Inc. in March 2002, and based on the GNU General Public License, version 2 (GPLv2). The second version (AGPLv2) was published in November 2007, as a transitional license to allow an upgrade path from AGPLv1 to the GNU Affero General Public License.

A passenger information system or passenger information display system is an automated system for supplying users of public transport with information about the nature and state of a public transport service, through visual, voice or other media. They are also known as Customer Information Systems and Operational Information Systems. Among the information provided by such systems, a distinction can be drawn between:

The GNU Affero General Public License is a free, copyleft license published by the Free Software Foundation in November 2007, and based on the GNU General Public License, version 3 and the Affero General Public License.
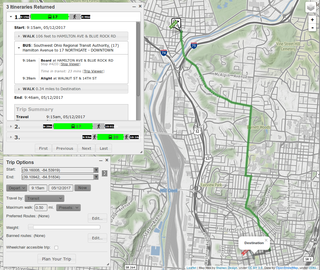
A journey planner, trip planner, or route planner is a specialized search engine used to find an optimal means of travelling between two or more given locations, sometimes using more than one transport mode. Searches may be optimized on different criteria, for example fastest, shortest, fewest changes, cheapest. They may be constrained, for example, to leave or arrive at a certain time, to avoid certain waypoints, etc. A single journey may use a sequence of several modes of transport, meaning the system may know about public transport services as well as transport networks for private transportation. Trip planning or journey planning is sometimes distinguished from route planning, where route planning is typically thought of as using private modes of transportation such as cycling, driving, or walking, normally using a single mode at a time. Trip or journey planning, in contrast, would make use of at least one public transport mode which operates according to published schedules; given that public transport services only depart at specific times, an algorithm must therefore not only find a path to a destination, but seek to optimize it so as to minimize the waiting time incurred for each leg. In European Standards such as Transmodel, trip planning is used specifically to describe the planning of a route for a passenger, to avoid confusion with the completely separate process of planning the operational journeys to be made by public transport vehicles on which such trips are made.
Zarafa was an open-source groupware application that originated in the city of Delft in the Netherlands. The company that developed Zarafa, previously known as Connectux, is also called Zarafa. The Zarafa groupware provided email storage on the server side and offered its own Ajax-based mail client called WebAccess and a HTML5-based, WebApp. Advanced features were available in commercially supported versions. Zarafa has been superseded by Kopano.
Companies whose business centers on the development of open-source software employ a variety of business models to solve the challenge of how to make money providing software that is by definition licensed free of charge. Each of these business strategies rests on the premise that users of open-source technologies are willing to purchase additional software features under proprietary licenses, or purchase other services or elements of value that complement the open-source software that is core to the business. This additional value can be, but not limited to, enterprise-grade features and up-time guarantees to satisfy business or compliance requirements, performance and efficiency gains by features not yet available in the open source version, legal protection, or professional support/training/consulting that are typical of proprietary software applications.

GNU social is a free and open source software microblogging server written in PHP that implements the OStatus standard for interoperation between installations. While offering functionality similar to Twitter, GNU social seeks to provide the potential for open, inter-service, and distributed communications between microblogging communities. Enterprises and individuals can install and control their own services and data.

The GNU General Public License is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, and modify the software. The licenses were originally written by Richard Stallman, founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project, and grant the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. This is in distinction to permissive software licenses, of which the BSD licenses and the MIT License are widely used, less restrictive examples. GPL was the first copyleft license for general use.

Traveline is a public transport route planner service provided by a partnership between local authorities and transport operators in the UK to provide impartial and comprehensive information about public transport which has operated since 2000. It prepares comprehensive public transport data for the UK and provides a number of regional public transport journey planners.

The open-core model is a business model for the monetization of commercially produced open-source software. Coined by Andrew Lampitt in 2008, the open-core model primarily involves offering a "core" or feature-limited version of a software product as free and open-source software, while offering "commercial" versions or add-ons as proprietary software.
Crown Copyright has been a long-standing copyright protection applied to official works, and at times artistic works, produced under royal or official supervision. In 2006, The Guardian newspaper's Technology section began a "Free Our Data" campaign, calling for data gathered by authorities at public expense to be made freely available for reuse by individuals. In 2010 with the creation of the Open Government Licence and the Data.gov.uk site it appeared that the campaign had been mostly successful, and since 2013 the UK has been consistently named one of the leaders in the open data space.

GNU MediaGoblin is a free, decentralized Web platform for hosting and sharing many forms of digital media. It strives to provide an extensible, federated, and freedom-respectful software replacement to major media publishing services such as Flickr, DeviantArt, and YouTube.

An isochrone map in geography and urban planning is a map that depicts the area accessible from a point within a certain time threshold. An isochrone is defined as "a line drawn on a map connecting points at which something occurs or arrives at the same time". In hydrology and transportation planning isochrone maps are commonly used to depict areas of equal travel time. The term is also used in cardiology as a tool to visually detect abnormalities using body surface distribution.














