Related Research Articles

Labour economics, or labor economics, seeks to understand the functioning and dynamics of the markets for wage labour. Labour is a commodity that is supplied by labourers, usually in exchange for a wage paid by demanding firms. Because these labourers exist as parts of a social, institutional, or political system, labour economics is often regarded as a sociology or political science.

Microeconomics is a branch of mainstream economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. Microeconomics focuses on the study of individual markets, sectors, or industries as opposed to the national economy as whole, which is studied in macroeconomics.
In economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. In theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been demonstrated that a market will reach an equilibrium in which the quantity supplied for every product or service, including labor, equals the quantity demanded at the current price. This equilibrium would be a Pareto optimum.

In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded will equal the quantity supplied, resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted. It forms the theoretical basis of modern economics.

In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that lead to the highest profit. Neoclassical economics, currently the mainstream approach to microeconomics, usually models the firm as maximizing profit.
Marginalism is a theory of economics that attempts to explain the discrepancy in the value of goods and services by reference to their secondary, or marginal, utility. It states that the reason why the price of diamonds is higher than that of water, for example, owes to the greater additional satisfaction of the diamonds over the water. Thus, while the water has greater total utility, the diamond has greater marginal utility.
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. But the concept of equilibrium in economics also applies to imperfectly competitive markets, where it takes the form of a Nash equilibrium.
The theory of consumer choice is the branch of microeconomics that relates preferences to consumption expenditures and to consumer demand curves. It analyzes how consumers maximize the desirability of their consumption as measured by their preferences subject to limitations on their expenditures, by maximizing utility subject to a consumer budget constraint.

In economics, the marginal cost is the change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is incremented, the cost of producing additional quantity. In some contexts, it refers to an increment of one unit of output, and in others it refers to the rate of change of total cost as output is increased by an infinitesimal amount. As Figure 1 shows, the marginal cost is measured in dollars per unit, whereas total cost is in dollars, and the marginal cost is the slope of the total cost, the rate at which it increases with output. Marginal cost is different from average cost, which is the total cost divided by the number of units produced.

A production–possibility frontier (PPF), production possibility curve (PPC), or production possibility boundary (PPB), or transformation curve/boundary/frontier is a curve which shows various combinations of the amounts of two goods which can be produced within the given resources and technology/a graphical representation showing all the possible options of output for two products that can be produced using all factors of production, where the given resources are fully and efficiently utilized per unit time. A PPF illustrates several economic concepts, such as allocative efficiency, economies of scale, opportunity cost, productive efficiency, and scarcity of resources.

In economics, a production function gives the technological relation between quantities of physical inputs and quantities of output of goods. The production function is one of the key concepts of mainstream neoclassical theories, used to define marginal product and to distinguish allocative efficiency, a key focus of economics. One important purpose of the production function is to address allocative efficiency in the use of factor inputs in production and the resulting distribution of income to those factors, while abstracting away from the technological problems of achieving technical efficiency, as an engineer or professional manager might understand it.

In economics and in particular neoclassical economics, the marginal product or marginal physical productivity of an input is the change in output resulting from employing one more unit of a particular input, assuming that the quantities of other inputs are kept constant.

In economics, diminishing returns is the decrease in marginal (incremental) output of a production process as the amount of a single factor of production is incrementally increased, holding all other factors of production equal. The law of diminishing returns states that in productive processes, increasing a factor of production by one unit, while holding all other production factors constant, will at some point return a lower unit of output per incremental unit of input. The law of diminishing returns does not cause a decrease in overall production capabilities, rather it defines a point on a production curve whereby producing an additional unit of output will result in a loss and is known as negative returns. Under diminishing returns, output remains positive, however productivity and efficiency decrease.
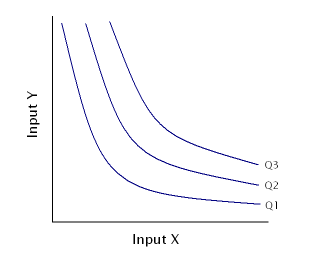
An isoquant, in microeconomics, is a contour line drawn through the set of points at which the same quantity of output is produced while changing the quantities of two or more inputs. The x and y axis on an isoquant represent two relevant inputs, which are usually a factor of production such as labour, capital, land, or organisation. An isoquant may also be known as an “Iso-Product Curve”, or an “Equal Product Curve”.
In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. In a free market economy, productively efficient firms optimize their production process by minimizing cost consistent with each possible level of production, and the result is a cost curve. Profit-maximizing firms use cost curves to decide output quantities. There are various types of cost curves, all related to each other, including total and average cost curves; marginal cost curves, which are equal to the differential of the total cost curves; and variable cost curves. Some are applicable to the short run, others to the long run.

In economics, total cost (TC) is the minimum dollar cost of producing some quantity of output. This is the total economic cost of production and is made up of variable cost, which varies according to the quantity of a good produced and includes inputs such as labor and raw materials, plus fixed cost, which is independent of the quantity of a good produced and includes inputs that cannot be varied in the short term such as buildings and machinery, including possibly sunk costs.
In economics, the long-run is a theoretical concept in which all markets are in equilibrium, and all prices and quantities have fully adjusted and are in equilibrium. The long-run contrasts with the short-run, in which there are some constraints and markets are not fully in equilibrium. More specifically, in microeconomics there are no fixed factors of production in the long-run, and there is enough time for adjustment so that there are no constraints preventing changing the output level by changing the capital stock or by entering or leaving an industry. This contrasts with the short-run, where some factors are variable and others are fixed, constraining entry or exit from an industry. In macroeconomics, the long-run is the period when the general price level, contractual wage rates, and expectations adjust fully to the state of the economy, in contrast to the short-run when these variables may not fully adjust.
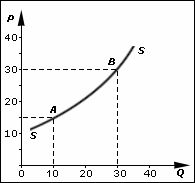
In economics, supply is the amount of a resource that firms, producers, labourers, providers of financial assets, or other economic agents are willing and able to provide to the marketplace or to an individual. Supply can be in produced goods, labour time, raw materials, or any other scarce or valuable object. Supply is often plotted graphically as a supply curve, with the price per unit on the vertical axis and quantity supplied as a function of price on the horizontal axis. This reversal of the usual position of the dependent variable and the independent variable is an unfortunate but standard convention.
In any technical subject, words commonly used in everyday life acquire very specific technical meanings, and confusion can arise when someone is uncertain of the intended meaning of a word. This article explains the differences in meaning between some technical terms used in economics and the corresponding terms in everyday usage.
This glossary of economics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in economics, its sub-disciplines, and related fields.
References
- ↑ Wicksteed, Philip Henry; The Common Sense of Political Economy (1910), Bk I Ch 2 and elsewhere.
- 1 2 von Wieser, Friedrich; Über den Ursprung und die Hauptgesetze des wirtschaftlichen Wertes [The Nature and Essence of Theoretical Economics] (1884), p. 128.