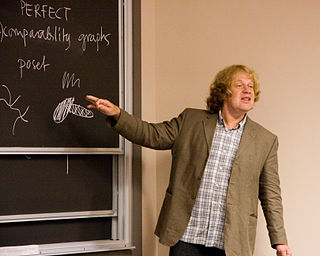Mark Norman Ellingham is a professor of mathematics at Vanderbilt University whose research concerns graph theory. [1] With Joseph D. Horton, he is the discoverer and namesake of the Ellingham–Horton graphs, two cubic 3-vertex-connected bipartite graphs that have no Hamiltonian cycle. [2]

Vanderbilt University is a private research university in Nashville, Tennessee. Founded in 1873, it was named in honor of New York shipping and rail magnate Cornelius Vanderbilt, who provided the school its initial $1-million endowment despite having never been to the South. Vanderbilt hoped that his gift and the greater work of the university would help to heal the sectional wounds inflicted by the Civil War.
In mathematics, graph theory is the study of graphs, which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of vertices which are connected by edges. A distinction is made between undirected graphs, where edges link two vertices symmetrically, and directed graphs, where edges link two vertices asymmetrically; see Graph for more detailed definitions and for other variations in the types of graph that are commonly considered. Graphs are one of the prime objects of study in discrete mathematics.

In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Ellingham–Horton graphs are two 3-regular graphs on 54 and 78 vertices: the Ellingham–Horton 54-graph and the Ellingham–Horton 78-graph. They are named after Joseph D. Horton and Mark N. Ellingham, their discoverers. These two graphs provide counterexamples to the conjecture of W. T. Tutte that every cubic 3-connected bipartite graph is Hamiltonian. The book thickness of the Ellingham-Horton 54-graph and the Ellingham-Horton 78-graph is 3 and the queue numbers 2.
Ellingham earned his Ph.D. in 1986 from the University of Waterloo under the supervision of Lawrence Bruce Richmond. [3] In 2012, he became one of the inaugural fellows of the American Mathematical Society. [4] [5]

The University of Waterloo is a public research university with a main campus in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is on 404 hectares of land adjacent to "Uptown" Waterloo and Waterloo Park. The university offers academic programs administered by six faculties and ten faculty-based schools. The university also operates three satellite campuses and four affiliated university colleges. Waterloo is a member of the U15, a group of research-intensive universities in Canada. The University of Waterloo is most famous for its cooperative education (co-op) programs, which allow the students to integrate their education with applicable work experiences. The university operates the largest post-secondary co-operative education program in the world, with over 20, 000 undergraduate students in over 140 co-operative education programs.
A fellow is a member of a group of learned people which works together in pursuing mutual knowledge or practice. There are many different kinds of fellowships which are awarded for different reasons in academia and industry. These often indicate a different level of scholarship.

The American Mathematical Society (AMS) is an association of professional mathematicians dedicated to the interests of mathematical research and scholarship, and serves the national and international community through its publications, meetings, advocacy and other programs.