
Marl prairies are wet prairies that allow for a slow seepage of overland water and exist in the Everglades, usually bordering deeper sloughs, and contain low-growth vegetation. [1]

Marl prairies are wet prairies that allow for a slow seepage of overland water and exist in the Everglades, usually bordering deeper sloughs, and contain low-growth vegetation. [1]
Marl is loose earthy deposits mixed with clay and calcium carbonate and sits on limestone bedrock. Marl prairies are home to microbes, bacteria, and algae, and serve as an important food source to some fish, tadpoles, and invertebrates. [2] Marl prairies are also thought to be the preferred breeding ground of the endangered Cape Sable Seaside Sparrow. [3]

Flamingo is the southernmost headquarters of Everglades National Park, in Monroe County, Florida, United States. Flamingo is one of the two end points of the 99-mile (159-km) Wilderness Waterway, and the southern end of the only road through the park from Florida City. It began as a small coastal settlement on the eastern end of Cape Sable on the southern tip of the Florida peninsula, facing Florida Bay. The actual town of Flamingo was located approximately 4+1⁄2 miles west of the current Flamingo campground area. All that remains of the former town are a few remnants of building foundations, and it is considered a ghost town.

Everglades National Park is an American national park that protects the southern twenty percent of the original Everglades in Florida. The park is the largest tropical wilderness in the United States and the largest wilderness of any kind east of the Mississippi River. An average of one million people visit the park each year. Everglades is the third-largest national park in the contiguous United States after Death Valley and Yellowstone. UNESCO declared the Everglades & Dry Tortugas Biosphere Reserve in 1976 and listed the park as a World Heritage Site in 1979, and the Ramsar Convention included the park on its list of Wetlands of International Importance in 1987. Everglades is one of only three locations in the world to appear on all three lists.

Great Sand Dunes National Park and Preserve is an American national park that conserves an area of large sand dunes up to 750 feet (230 m) tall on the eastern edge of the San Luis Valley, and an adjacent national preserve in the Sangre de Cristo Range, in south-central Colorado, United States. The park was originally designated Great Sand Dunes National Monument on March 17, 1932, by President Herbert Hoover. The original boundaries protected an area of 35,528 acres. A boundary change and redesignation as a national park and preserve was authorized on November 22, 2000, and then established on September 24, 2004. The park encompasses 107,342 acres while the preserve protects an additional 41,686 acres for a total of 149,028 acres. The recreational visitor total was 527,546 in 2019.

Muleshoe National Wildlife Refuge is a 6,440-acre (26.1 km2) wildlife refuge located about 20 mi (32 km) south of Muleshoe, Texas, on Texas State Highway 214. It is the oldest national wildlife refuge in Texas, having been established as the Muleshoe Migratory Waterfowl Refuge by executive order of President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1935. Roosevelt issued a proclamation in 1940 to change the name to the Muleshoe National Wildlife Refuge. In 1980, Muleshoe National Wildlife Refuge was designated as a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service.

Pictured Rocks National Lakeshore is a U.S. National Lakeshore in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, United States. It extends for 42 miles (67 km) along the shore of Lake Superior and covers 73,236 acres. The park has extensive views of the hilly shoreline between Munising and Grand Marais in Alger County, Michigan, with picturesque rock formations, waterfalls, and sand dunes.

Tallgrass Prairie National Preserve is a United States National Preserve located in the Flint Hills region of Kansas, north of Strong City. The preserve protects a nationally significant example of the once vast tallgrass prairie ecosystem. Of the 400,000 square miles (1,000,000 km2) of tallgrass prairie that once covered the North American continent, less than 4% remains, primarily in the Flint Hills. Since 2009, the preserve has been home to the growing Tallgrass Prairie bison herd.

Pipestone National Monument is located in southwestern Minnesota, just north of the city of Pipestone, Minnesota. It is located along the highways of U.S. Route 75, Minnesota State Highway 23 and Minnesota State Highway 30. The quarries are sacred to many tribal nations of North America, including the Dakota, Lakota, and other tribes of Native Americans, and were considered neutral territory in the historic past where all Nations could quarry stone for ceremonial pipes. The catlinite, or "pipestone" is traditionally used to make ceremonial pipes, vitally important to traditional Plains Indian religious practices. Archeologists believe the site has been in use for over 3000 years with Minnesota pipestone having been found inside North American burial mounds dated much earlier.

Big Cypress National Preserve is a United States National Preserve located in South Florida, about 45 miles west of Miami on the Atlantic coastal plain. The 720,000-acre (2,900 km2) Big Cypress, along with Big Thicket National Preserve in Texas, became the first national preserves in the United States National Park System when they were established on October 11, 1974. In 2008, Florida film producer Elam Stoltzfus featured the preserve in a PBS documentary.

Taylor Slough, located in the southeastern corner of the Florida Everglades, along with the much larger Shark River Slough farther to the west, are the principal natural drainages for the freshwater Everglades and the essential conduit for providing overland freshwater to Florida Bay.

Cape Sable is the southernmost point of the United States mainland and mainland Florida. It is located in southwestern Florida, in Monroe County, and is part of the Everglades National Park.

The Cape Lookout Lighthouse is a 163-foot-high lighthouse located on the southern Outer Banks of North Carolina. It flashes every 15 seconds and is visible at least 12 miles out to sea and up to 19 miles. It is one of the very few lighthouses that operate during the day. It became fully automated in 1950. The Cape Lookout Lighthouse is the only such structure in the United States to bear the checkered daymark, intended not only for differentiation between similar light towers, but also to show direction. The center of the black diamonds points in a north-south direction, while the center of the white diamonds points east-west.

Shark Valley is a geological depression at the head of the Shark River Slough in far western Miami-Dade County, Florida, United States. It is currently part of Everglades National Park. Shark Valley empties into Shark River in the Ten Thousand Islands of Monroe County. Shark Valley characteristically includes sawgrass prairie that floods during the rainy season, hence the name "river of grass"—Pa-Hay-Okee, from the Mikasuki language—for such marshes in the Everglades. Shark Valley features a Visitor Center with educational displays, a park video, an underwater camera and informational brochures. The entrance to Shark Valley is located along Tamiami Trail near the Miami-Dade–Collier County line.

The seaside sparrow is an American sparrow.

The Anahuac National Wildlife Refuge (NWR) is a wildlife conservation area along the coast of Texas (USA), west of the town of High Island, Texas. It borders East Bay, part of the Galveston Bay complex, behind Bolivar Peninsula at the Gulf of Mexico.

The Cape Sable seaside sparrow is a subspecies of the seaside sparrow, a species of bird in the family Passerellidae native to the United States. This subspecies is endemic to southern Florida. It is designated endangered under the Endangered Species Act.

Before drainage, the Everglades, a region of tropical wetlands in southern Florida, were an interwoven mesh of marshes and prairies covering 4,000 square miles (10,000 km2). The Everglades is both a vast watershed that has historically extended from Lake Okeechobee 100 miles (160 km) south to Florida Bay, and many interconnected ecosystems within a geographic boundary. It is such a unique meeting of water, land, and climate that the use of either singular or plural to refer to the Everglades is appropriate. When Marjory Stoneman Douglas wrote her definitive description of the region in 1947, she used the metaphor "River of Grass" to explain the blending of water and plant life.
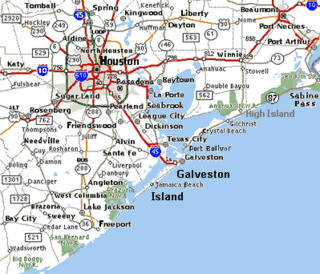
The Brazoria National Wildlife Refuge is a 44,414-acre (179.74 km2) wildlife conservation area along the coast of Texas (USA), east of the towns of Angleton and Lake Jackson, Texas. It borders Christmas Bay and the Intracoastal Waterway, separated from the Gulf of Mexico by Follet's Island.

Shark River Slough (SRS) is a low-lying area of land that channels water through the Florida Everglades, beginning in Water Conservation Area 3, flowing through Everglades National Park, and ultimately into Florida Bay. Together with Taylor Slough to the east, Shark River Slough is an essential conduit of overland freshwater to Florida Bay. Shark River Slough is also known as the "River of Grass."

Ammospiza is a genus of birds in the family Passerellidae, in the group known as American sparrows.