
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.

Biscayne National Park is a national park of the United States located south of Miami, Florida, in Miami-Dade County. The park preserves Biscayne Bay and its offshore barrier reefs. Ninety-five percent of the park is water, and the shore of the bay is the location of an extensive mangrove forest. The park covers 172,971 acres and includes Elliott Key, the park's largest island and northernmost of the true Florida Keys, formed from fossilized coral reef. The islands farther north in the park are transitional islands of coral and sand. The offshore portion of the park includes the northernmost region of the Florida Reef, one of the largest coral reefs in the world.

Lord Howe Island Marine Park is the site of Australia's and the world's most southern coral reef ecosystem. The island is 10 km in length, 2 km wide and consists of a large lagoonal reef system along its leeward side, with 28 small islets along its coast. In 1999, the waters within three nautical miles of Lord Howe Island (465.45 km2) were declared a marine park under the NSW Marine Park Act 1997 to protect its unique marine biodiversity, with the park currently being managed by the New South Wales Marine Parks Authority. Both Lord Howe Island and Balls Pyramid are incorporated within the three nautical miles protected by the state marine park. Both marine parks complement the island's status as a World Heritage Site.

Marine conservation, also known as ocean conservation, is the protection and preservation of ecosystems in oceans and seas through planned management in order to prevent the over-exploitation of these marine resources. Marine conservation is informed by the study of marine plants and animal resources and ecosystem functions and is driven by response to the manifested negative effects seen in the environment such as species loss, habitat degradation and changes in ecosystem functions and focuses on limiting human-caused damage to marine ecosystems, restoring damaged marine ecosystems, and preserving vulnerable species and ecosystems of the marine life. Marine conservation is a relatively new discipline which has developed as a response to biological issues such as extinction and marine habitats change.

Pulley Ridge is a mesophotic coral reef system off the shores of the continental United States. The reef rests on sunken barrier islands and lies 100 miles west of the Tortugas Ecological Reserve and stretches north about 60 miles at depths ranging from 60 to 80 meters. Pulley Ridge was originally discovered in 1950 during a dredging operation conducted by an academic group from Texas. While well known to fishermen, this remarkable habitat remained undiscovered by scientists until 1999 when the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) and graduate students from the University of South Florida happened upon it. This reef system, like other mesophotic ecosystems, is inhabited by photosynthesizing corals and algae that are adapted to low-light environments. It is habitat for numerous species of bottom fish including Epinephelus morio spawning area.

The staghorn coral is a branching, stony coral, within the Order Scleractinia. It is characterized by thick, upright branches which can grow in excess of 2 meters in height and resemble the antlers of a stag, hence the name, Staghorn. It grows within various areas of a reef but is most commonly found within shallow fore and back reefs, as well as patch reefs, where water depths rarely exceed 20 meters. Staghorn corals can exhibit very fast growth, adding up to 5 cm in new skeleton for every 1 cm of existing skeleton each year, making them one of the fastest growing fringe coral species in the Western Atlantic. Due to this fast growth, Acropora cervicornis, serve as one of the most important reef building corals, functioning as marine nurseries for juvenile fish, buffer zones for erosion and storms, and center points of biodiversity in the Western Atlantic.

Marine ecosystems are the largest of Earth's aquatic ecosystems and exist in waters that have a high salt content. These systems contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have a lower salt content. Marine waters cover more than 70% of the surface of the Earth and account for more than 97% of Earth's water supply and 90% of habitable space on Earth. Seawater has an average salinity of 35 parts per thousand of water. Actual salinity varies among different marine ecosystems. Marine ecosystems can be divided into many zones depending upon water depth and shoreline features. The oceanic zone is the vast open part of the ocean where animals such as whales, sharks, and tuna live. The benthic zone consists of substrates below water where many invertebrates live. The intertidal zone is the area between high and low tides. Other near-shore (neritic) zones can include mudflats, seagrass meadows, mangroves, rocky intertidal systems, salt marshes, coral reefs, lagoons. In the deep water, hydrothermal vents may occur where chemosynthetic sulfur bacteria form the base of the food web.
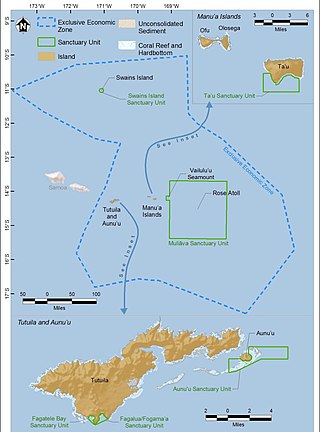
The National Marine Sanctuary of American Samoa is a federally-designated underwater area protected by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Office of National Marine Sanctuaries. This sanctuary is the largest and most remote in the National Marine Sanctuary system. Spanning 13,581 sq mi, it is thought to be home to the greatest biodiversity of aquatic species of all the marine sanctuaries. Among them are expansive coral reefs, including some of the oldest Porites coral heads on earth, deep-water reefs, hydrothermal vent communities, and rare archeological resources. It was established as Fagatele Bay National Marine Sanctuary on April 29, 1986, it is thought to be home to the greatest biodiversity of aquatic species of all the marine sanctuaries. and then expanded and renamed in 2012.

Elkhorn coral is an important reef-building coral in the Caribbean. The species has a complex structure with many branches which resemble that of elk antlers; hence, the common name. The branching structure creates habitat and shelter for many other reef species. Elkhorn coral is known to grow quickly with an average growth rate of 5 to 10 cm per year. They can reproduce both sexually and asexually, though asexual reproduction is much more common and occurs through a process called fragmentation.

The Florida Reef is the only living coral barrier reef in the continental United States. It lies a few miles seaward of the Florida Keys, is about 4 miles wide and extends 270 km (170 mi) from Fowey Rocks just east of Soldier Key to just south of the Marquesas Keys. The system encompasses more than 6,000 individual reefs. Florida waters are home to over 500 marine fish and mammal species along with more than 45 species of stony corals and 35 species of octocorals.

Coral reef protection is the process of modifying human activities to avoid damage to healthy coral reefs and to help damaged reefs recover. The key strategies used in reef protection include defining measurable goals and introducing active management and community involvement to reduce stressors that damage reef health. One management technique is to create Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) that directly limit human activities such as fishing.

Tripneustes gratilla, the collector urchin, is a species of sea urchin. Collector urchins are found at depths of 2 to 30 metres in the waters of the Indo-Pacific, Hawaii, the Red Sea, and The Bahamas. They can reach 10 to 15 centimetres in size.

The Phoenix Islands Protected Area (PIPA) is located in the Republic of Kiribati, an ocean nation in the central Pacific approximately midway between Australia and Hawaii. PIPA constitutes 11.34% of Kiribati's exclusive economic zone (EEZ), and with a size of 408,250 km2 (157,630 sq mi), it is one of the largest marine protected areas (MPA) and one of the largest protected areas of any type on Earth. The PIPA was also designated as the world's largest and deepest UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2010.

Human activities have substantial impact on coral reefs, contributing to their worldwide decline. Damaging activities encompass coral mining, pollution, overfishing, blast fishing, as well as the excavation of canals and access points to islands and bays. Additional threats comprise disease, destructive fishing practices, and the warming of oceans.[2] Furthermore, the ocean's function as a carbon dioxide sink, alterations in the atmosphere, ultraviolet light, ocean acidification, viral infections, the repercussions of dust storms transporting agents to distant reefs, pollutants, and algal blooms represent some of the factors exerting influence on coral reefs. Importantly, the jeopardy faced by coral reefs extends far beyond coastal regions. The ramifications of climate change, notably global warming, induce an elevation in ocean temperatures that triggers coral bleaching—a potentially lethal phenomenon for coral ecosystems.

Looe Key is a coral reef located within the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. It lies to the south of Big Pine Key. This reef is within a Sanctuary Preservation Area (SPA). Part of Looe Key is designated as "Research Only," an area which protects some of the patch reefs landward of the main reef.

Eastern Dry Rocks is a coral reef located within the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. It lies seven miles southeast of Key West and one mile east of Sand Key light within the Key West National Wildlife Refuge. This reef is within a Sanctuary Preservation Area (SPA).

A marine habitat is a habitat that supports marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea. A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species. The marine environment supports many kinds of these habitats.

Pterois is a genus of venomous marine fish, commonly known as lionfish, native to the Indo-Pacific. It is characterized by conspicuous warning coloration with red or black bands, and ostentatious dorsal fins tipped with venomous spines. Pterois radiata, Pterois volitans, and Pterois miles are the most commonly studied species in the genus. Pterois species are popular aquarium fish. P. volitans and P. miles are recent and significant invasive species in the west Atlantic, Caribbean Sea and Mediterranean Sea.
Cape Byron Marine Park is one of four marine parks in New South Wales, Australia, and is the most recently sanctioned. The Cape Byron Marine Park is located in Northern NSW and extends 37 kilometres (23 mi) from the Brunswick River to Lennox Head. The marine park extends out to 3 nautical miles which dictates the border between state and federal jurisdiction. The marine park covers an area of 220 square kilometres (85 sq mi) and includes a variety of marine terrain including beaches, rocky shores, open ocean and the tidal waters of the Brunswick River and its tributaries, the Belongil Creek and Tallow Creek. The Cape Byron Marine Park was declared in 2002 and the zoning plan was implemented in April 2006. Of the 15 distinct marine ecosystems identified within the Tweed-Moreton bioregion, the Cape Byron Marine Park supports 10 of these.

Jamaica, an island located within the Caribbean Sea, known for being a popular tourist destination because of its pristine white sand beaches, is now faced with the issue of mass coral depletion. Both environmental and human factors contribute to the destruction of these corals, which inevitably affect Jamaica's environmental sustainability and economy. Actions have been put in place to counteract the negative consequences associated with the loss of the corals, which act as a symbol of hope for the revival of Jamaica's environment.























