
Whale watching is the practice of observing whales and dolphins (cetaceans) in their natural habitat. Whale watching is mostly a recreational activity, but it can also serve scientific and/or educational purposes. A study prepared for International Fund for Animal Welfare in 2009 estimated that 13 million people went whale watching globally in 2008. Whale watching generates $2.1 billion per annum in tourism revenue worldwide, employing around 13,000 workers. The size and rapid growth of the industry has led to complex and continuing debates with the whaling industry about the best use of whales as a natural resource.

Pamlico Sound is a lagoon in North Carolina which is the largest lagoon along the North American East Coast, extending 80 mi (130 km) long and 15 to 20 miles wide. It is part of a large, interconnected network of lagoon estuaries that includes Albemarle Sound, Currituck Sound, Croatan Sound, Roanoke Sound, Pamlico Sound, Bogue Sound, Back Sound, and Core Sound. Together, these sounds, known as the Albemarle-Pamlico sound system, comprise the second largest estuary in the United States, covering over 3,000 sq. mi. of open water. The Pamlico Sound is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Outer Banks, a row of low, sandy barrier islands that include Cape Hatteras National Seashore, Cape Lookout National Seashore, and Pea Island National Wildlife Refuge. The Albemarle-Pamlico Sound is one of nineteen great waters recognized by the America's Great Waters Coalition.

The Atlantic white-sided dolphin is a distinctively coloured dolphin found in the cool to temperate waters of the North Atlantic Ocean.

The New York–New Jersey Harbor Estuary has a variety of flora and fauna. Much of the harbor originally consisted of tidal marshes that have been dramatically transformed by the development of port facilities. The estuary itself supports a great variety of thriving estuarine aquatic species; contrary to popular stereotypes, New York Harbor and its adjacent, interdependent waters are very much alive, and steadily recovering from pollution; ecologically it is true that these waters were once dead or extremely toxic but after 45 years of cleaning the estuary is in a much better state than it has been in a hundred years. Tidal flow occurs as far north as Troy, over 150 miles away. The salt front can reach Poughkeepsie in drought conditions and is present in the lower reaches of the Raritan River for most of the year.

The Gulf of Maine is a large gulf of the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of North America. It is bounded by Cape Cod at the eastern tip of Massachusetts in the southwest and by Cape Sable Island at the southern tip of Nova Scotia in the northeast. The gulf includes the entire coastlines of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine, as well as Massachusetts north of Cape Cod, and the southern and western coastlines of the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, respectively.

A U.S. National Marine Sanctuary is a zone within United States waters where the marine environment enjoys special protection. The program began in 1972 in response to public concern about the plight of marine ecosystems.

The Farallon Islands, or Farallones, are a group of islands and sea stacks in the Gulf of the Farallones, off the coast of San Francisco, California, United States. The islands are also sometimes referred to by mariners as the Devil's Teeth Islands, in reference to the many treacherous underwater shoals in their vicinity. The islands lie 30 miles (48 km) outside the Golden Gate and 20 miles (32 km) south of Point Reyes, and are visible from the mainland on clear days. The islands are part of the City and County of San Francisco. The only inhabited portion of the islands is on Southeast Farallon Island (SEFI), where researchers from Point Blue Conservation Science and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service stay. The islands are closed to the public.

The Greater Farallones National Marine Sanctuary protects the wildlife, habitats, and cultural resources of one of the most diverse and bountiful marine environments in the world, an area of 3,295 square miles off the northern and central California coast. The waters within Greater Farallones National Marine Sanctuary are part of a nationally significant marine ecosystem, and support an abundance of life, including many threatened or endangered species.
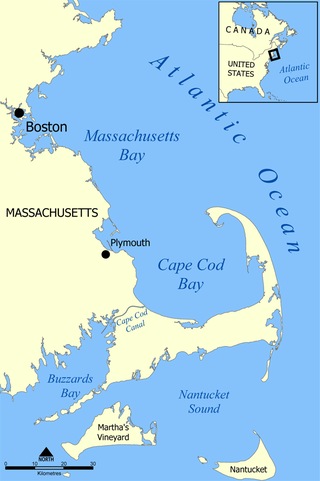
Cape Cod Bay is a large bay of the Atlantic Ocean adjacent to the U.S. state of Massachusetts. Measuring 604 square miles (1,560 km2) below a line drawn from Brant Rock in Marshfield to Race Point in Provincetown, Massachusetts, it is enclosed by Cape Cod to the south and east, and Plymouth County, Massachusetts, to the west. To the north of Cape Cod Bay lie Massachusetts Bay and the Atlantic Ocean. Cape Cod Bay is the southernmost extremity of the Gulf of Maine. Cape Cod Bay is one of the bays adjacent to Massachusetts that give it the name Bay State. The others are Narragansett Bay, Buzzards Bay, and Massachusetts Bay.

The New England Aquarium is a nonprofit organization located in Boston, Massachusetts. The species exhibited include harbor and northern fur seals, California sea lions, African and southern rockhopper penguins, giant Pacific octopuses, weedy seadragons, and thousands of saltwater and freshwater fishes. In addition to the main aquarium building, attractions at Central Wharf include the Simons Theatre and the New England Aquarium Whale Watch. More than 1.3 million guests visited the aquarium each year prior to the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic.

Cordell Bank National Marine Sanctuary is a marine sanctuary located off the coast of California. It protects an area of 1,286 sq mi (3,331 km2) of marine wildlife. The administrative center of the sanctuary is on an offshore granite outcrop 4.5 sq mi (12 km2) by 9.5 sq mi (25 km2), located on the continental shelf off of California. The outcrop is, at its closest, 6 mi (10 km) from the sanctuary itself.

The Agulhas Bank is a broad, shallow part of the southern African continental shelf which extends up to 250 km (160 mi) south of Cape Agulhas before falling steeply to the abyssal plain.

Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with demersal fish that do live on or near the bottom, and reef fish that are associated with coral reefs.
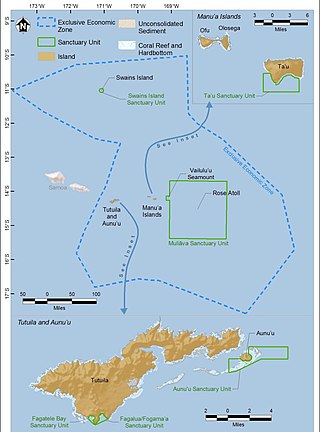
The National Marine Sanctuary of American Samoa is one of many federally-designated underwater areas protected by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Office of National Marine Sanctuaries. This sanctuary is the largest and most remote in the National Marine Sanctuary system. Spanning 13,581 sq mi, it is home to the greatest biodiversity of aquatic species of all marine sanctuaries. Among them are expansive coral reefs, including some of the oldest Porites coral heads on earth, deep-water reefs, hydrothermal vent communities, and rare archeological resources. It was established in 1986, and then expanded and renamed in 2012.

PS Portland was a large side-wheel paddle steamer, an ocean-going steamship with side-mounted paddlewheels. She was built in 1889 for passenger service between Boston, Massachusetts, and Portland, Maine. She is best known as the namesake of the infamous Portland Gale of 1898, a massive blizzard that struck coastal New England, claiming the lives of over 400 people and more than 150 vessels.

The harborseal, also known as the common seal, is a true seal found along temperate and Arctic marine coastlines of the Northern Hemisphere. The most widely distributed species of pinniped, they are found in coastal waters of the northern Atlantic, Pacific Oceans, Baltic and North Seas.

A bait ball, or baitball, occurs when small fish swarm in a tightly packed spherical formation about a common centre. It is a last-ditch defensive measure adopted by small schooling fish when they are threatened by predators. Small schooling fish are eaten by many types of predators, and for this reason they are called bait fish or forage fish.

The Marine Policy of the Barack Obama administration comprises several significant environmental policy decisions for the oceans made during his two terms in office from 2009 to 2017. By executive action, President Obama increased fourfold the amount of protected marine space in waters under United States control, setting a major precedent for global ocean conservation. Using the U.S. president's authority under the Antiquities Act of 1906, he expanded to 200 nautical miles the seaward limits of Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument in Hawaiʻi and the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument around the U.S. island possessions in the Central Pacific. In the Atlantic, President Obama created the Northeast Canyons and Seamounts Marine National Monument, the first marine monument in the U.S. exclusive economic zone (EEZ) in the Atlantic.
The Northeastern United States Continental Shelf (NEUS) is the large marine ecosystem designated by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration that occupies the portion of the continental shelf of the Atlantic Ocean. The NEUS is defined as extending roughly from the Canadian province of Nova Scotia to Cape Hatteras in the US state of North Carolina. This large marine ecosystem is notable for its proximity to the Gulf Stream current, meridional variation of climate, and commercial fisheries.
Cetaceans form an infra-order of marine mammals. In 2020, approximately 86 species of cetaceans had been identified worldwide. Among these species, at least 35 have been sighted in the wider Caribbean region with very widespread distribution and density variations between areas. Caribbean waters are a preferred breeding site for several species of mysticeti, who live further north the rest of the year. The tucuxi and the boto live at the southern periphery of the Caribbean region in the freshwaters of the Amazon river and surrounding drainage basins.



















