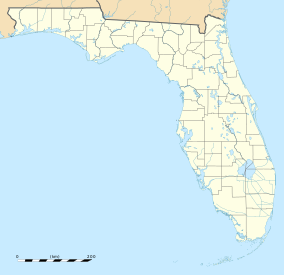
Alachua County is a county in the north central portion of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 278,468. The county seat is Gainesville, the home of the University of Florida since 1906, when the campus opened with 106 students.

Alachua is the second-largest city in Alachua County, Florida and the third-largest in North Central Florida. According to the 2020 census, the city's population was 10,574. The city is part of the Gainesville metropolitan area, which had a population of 339,247 in 2020.

Micanopy is a town in Alachua County, Florida, United States, located south of Gainesville. The population as of the 2010 census was 600. The oldest community in the interior of Florida that has been continually inhabited, it has a downtown that is designated as the Micanopy Historic District and listed on the National Register of Historic Places. It contains a number of antique stores, as well as several restaurants, a library, firehouse, and post office. The town's unofficial slogan is "The Town that Time Forgot."

The Florida Museum of Natural History (FLMNH) is Florida's official state-sponsored and chartered natural-history museum. Its main facilities are located at 3215 Hull Road on the campus of the University of Florida in Gainesville.

Paynes Prairie Preserve State Park is a Florida State Park, encompassing a 21,000-acre (85 km2) savanna in Alachua County, Florida lying between Micanopy and Gainesville. It is also a U.S. National Natural Landmark. It is crossed by both I-75 and U.S. 441. It is in the center of the Paynes Prairie Basin. The basin's primary source of drainage is Alachua Sink. During occasional wet periods, the basin will become full. A notable period occurred from 1871 to 1891 when the Alachua Sink was temporarily blocked. During this period, shallow draft steamboats were a frequent sight on Alachua Lake in the center of the prairie. The region was also historically known as the Alachua Savannah. Its drainage has been modified by several canals. Since 1927, Camps Canal has linked the basin to the River Styx which leads to Orange Lake and eventually the Atlantic Ocean through the St. Johns River. That reduced the basins water intake by half. Additional changes to the prairie's environment have been detrimental to its hydrology. In 1970, the state of Florida acquired the land and has been in the process of restoring the environment to a more natural condition ever since.

Devil's Millhopper Geological State Park is a Florida state park located in the north-westernmost part of Gainesville, Florida, off County Road 232, also known as NW 53rd Avenue and Millhopper Road, northwest of the University of Florida.

Gainesville-Hawthorne State Trail is a paved rail trail in Florida.
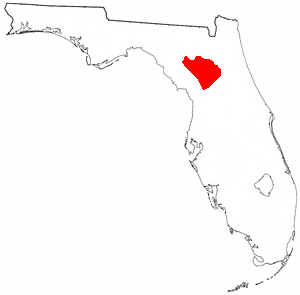
The Alachua culture is a Late Woodland Southeast period archaeological culture in north-central Florida, dating from around 600 to 1700. It is found in an area roughly corresponding to present-day Alachua County, the northern half of Marion County and the western part of Putnam County. It was preceded by the Cades Pond culture, which inhabited approximately the same area.

The Potano tribe lived in north-central Florida at the time of first European contact. Their territory included what is now Alachua County, the northern half of Marion County and the western part of Putnam County. This territory corresponds to that of the Alachua culture, which lasted from about 700 until 1700. The Potano were among the many tribes of the Timucua people, and spoke a dialect of the Timucua language.

Dudley Farm Historic State Park (Florida), also known as Dudley Farm, is a U.S. historic district and museum park located in Newberry, Florida. It was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places on October 4, 2002, and was designated a National Historic Landmark in January, 2021. The address is 18730 West Newberry Road. The farm is a particularly fine and well-preserved example of a mid-19th to mid-20th century farm.
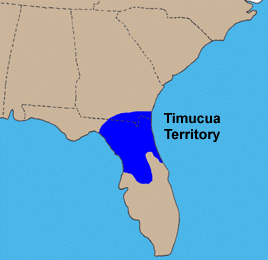
The Timucua were a Native American people who lived in Northeast and North Central Florida and southeast Georgia. They were the largest indigenous group in that area and consisted of about 35 chiefdoms, many leading thousands of people. The various groups of Timucua spoke several dialects of the Timucua language. At the time of European contact, Timucuan speakers occupied about 19,200 square miles (50,000 km2) in the present-day states of Florida and Georgia, with an estimated population of 200,000. Milanich notes that the population density calculated from those figures, 10.4 per square mile (4.0/km2) is close to the population densities calculated by other authors for the Bahamas and for Hispaniola at the time of first European contact. The territory occupied by Timucua speakers stretched from the Altamaha River and Cumberland Island in present-day Georgia as far south as Lake George in central Florida, and from the Atlantic Ocean west to the Aucilla River in the Florida Panhandle, though it reached the Gulf of Mexico at no more than a couple of points.
Ahaya was the first recorded chief of the Alachua band of the Seminole tribe. European-Americans called him Cowkeeper, as he held a very large herd of cattle. Ahaya was the chief of a town of Oconee people near the Chattahoochee River. Around 1750 he led his people into Florida where they settled around Payne's Prairie, part of what the Spanish called tierras de la chua, "Alachua Country" in English. The Spanish called Ahaya's people cimarones, which eventually became "Seminoles" in English. Ahaya fought the Spanish, and sought friendship with the British, allying with them after Spain ceded Florida to Great Britain in 1763, and staying loyal to them through the American Revolutionary War. He died shortly after Britain returned Florida to Spain in 1783.
Mission San Francisco de Potano was a Spanish mission near Gainesville, Florida, United States. The mission of San Francisco de Potano was founded in 1606 by the Franciscans Father Martín Prieto and Father Alonso Serrano. It was the first doctrina in Florida west of the St. Johns River. The mission was at the south edge of present-day San Felasco Hammock Preserve State Park.
The indigenous peoples of Florida lived in what is now known as Florida for more than 12,000 years before the time of first contact with Europeans. However, the indigenous Floridians living east of the Apalachicola River had largely died out by the early 18th century. Some Apalachees migrated to Louisiana, where their descendants now live; some were taken to Cuba and Mexico by the Spanish in the 18th century, and a few may have been absorbed into the Seminole and Miccosukee tribes.
The Battle of San Felasco Hammock was a battle of the Second Seminole War fought by Florida's Seminole Indians to prevent their removal to the Arkansas Territory in accordance with the Indian Removal Act of 1830. Euro-American settlers established the town of Newnansville, Florida, around Fort Gilleland. The site upon which both Fort Gilleland and Newnansville once stood is now encompassed by the city of Alachua, Florida. The San Felasco Hammock is currently part of San Felasco Hammock Preserve State Park.
Ocale was the name of a town in Florida visited by the Hernando de Soto expedition, and of a putative chiefdom of the Timucua people. The town was probably close to the Withlacoochee River at the time of de Soto's visit, and may have later been moved to the Oklawaha River.
San Buenaventura de Potano was a Spanish mission near Orange Lake in southern Alachua County or northern Marion County, Florida, located on the site where the town of Potano had been located when it was visited by Hernando de Soto in 1539. The Richardson/UF Village Site (8AL100), in southern Alachua County, has been proposed as the location of the town and mission.
Warren's Cave is a dry karst cave in Alachua County, Florida. It is the longest dry cave in Florida, with more than 4 miles (6.4 km) of mapped passages. The cave is located on the margin of the Cody Scarp near the San Felasco Hammock Preserve State Park, northwest of the city of Gainesville. The property on which the entrance to Warren's Cave is located, the Warren Cave Nature Preserve, is owned by the National Speleological Society. Warren's cave was probably formed by a high water table when sea levels in the Quaternary Period were elevated close to 100 feet (30 m) above current sea level, corresponding to the Wicomico terrace.
The city of Gainesville, Florida, USA, was incorporated in 1869.
Spring Grove, Florida was a settlement in Alachua County, Florida during the territorial period in Florida, serving for three years as the county seat of the county. It was about four miles west of Hogtown, probably in the San Felasco Hammock, west or northwest of present-day Gainesville. Four archaeological sites in the San Felasco Hammock Preserve State Park may have been part of Spring Grove. A post office was established in Spring Grove in 1829. In 1835, a unit of volunteer mounted riflemen called the Spring Grove Guards was organized in Alachua County under authority of the Florida territorial council. Most of the 60 or so members were from Spring Grove and Hogtown. The unit ceased operations in less than a year, after the Second Seminole War began. The territorial council designated Spring Grove as the county seat of Alachua County in February 1836. Three years later, in February 1839, the territorial council moved the county seat to Newnansville. The post office closed sometime in 1848.