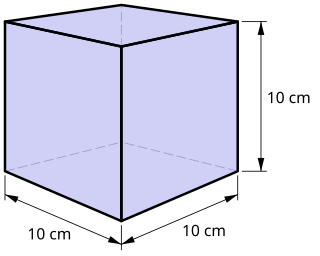
The litre or liter is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metres (m3). A cubic decimetre occupies a volume of 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre.

Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units or by various imperial or US customary units. The definition of length and height (cubed) is interrelated with volume. The volume of a container is generally understood to be the capacity of the container; i.e., the amount of fluid that the container could hold, rather than the amount of space the container itself displaces. By metonymy, the term "volume" sometimes is used to refer to the corresponding region.
A viscometer is an instrument used to measure the viscosity of a fluid. For liquids with viscosities which vary with flow conditions, an instrument called a rheometer is used. Thus, a rheometer can be considered as a special type of viscometer. Viscometers can measure only constant viscosity, that is, viscosity that does not change with flow conditions.
Flow measurement is the quantification of bulk fluid movement. Flow can be measured using devices called flowmeters in various ways. The common types of flowmeters with industrial applications are listed below:

A gas meter is a specialized flow meter, used to measure the volume of fuel gases such as natural gas and liquefied petroleum gas. Gas meters are used at residential, commercial, and industrial buildings that consume fuel gas supplied by a gas utility. Gases are more difficult to measure than liquids, because measured volumes are highly affected by temperature and pressure. Gas meters measure a defined volume, regardless of the pressurized quantity or quality of the gas flowing through the meter. Temperature, pressure, and heating value compensation must be made to measure actual amount and value of gas moving through a meter.

A rheometer is a laboratory device used to measure the way in which a viscous fluid flows in response to applied forces. It is used for those fluids which cannot be defined by a single value of viscosity and therefore require more parameters to be set and measured than is the case for a viscometer. It measures the rheology of the fluid.
The Atterberg limits are a basic measure of the critical water contents of a fine-grained soil: its shrinkage limit, plastic limit, and liquid limit.

Torricelli's law, also known as Torricelli's theorem, is a theorem in fluid dynamics relating the speed of fluid flowing from an orifice to the height of fluid above the opening. The law states that the speed of efflux of a fluid through a sharp-edged hole at the bottom of the tank filled to a depth is the same as the speed that a body would acquire in falling freely from a height , i.e. , where is the acceleration due to gravity. This expression comes from equating the kinetic energy gained, , with the potential energy lost, , and solving for . The law was discovered by the Italian scientist Evangelista Torricelli, in 1643. It was later shown to be a particular case of Bernoulli's principle.
Saybolt universal viscosity (SUV), and the related Saybolt FUROL viscosity (SFV), are specific standardised tests producing measures of kinematic viscosity. FUROL is an acronym for fuel and road oil. Saybolt universal viscosity is specified by the ASTM D2161. Both tests are considered obsolete to other measures of kinematic viscosity, but their results are quoted widely in technical literature.

Geotechnical investigations are performed by geotechnical engineers or engineering geologists to obtain information on the physical properties of soil earthworks and foundations for proposed structures and for repair of distress to earthworks and structures caused by subsurface conditions; this type of investigation is called a site investigation. Geotechnical investigations are also used to measure the thermal resistance of soils or backfill materials required for underground transmission lines, oil and gas pipelines, radioactive waste disposal, and solar thermal storage facilities. A geotechnical investigation will include surface exploration and subsurface exploration of a site. Sometimes, geophysical methods are used to obtain data about sites. Subsurface exploration usually involves soil sampling and laboratory tests of the soil samples retrieved.

A Zahn cup is a viscosity measurement device used in the paint industry. It is commonly a stainless steel cup with a tiny hole drilled in the centre of the bottom of the cup. There is also a long handle attached to the sides. There are five cup specifications, labelled Zahn cup #x, where x is the number from one through five. Large number cup sizes are used when viscosity is high, while low number cup sizes are used when viscosity is low. They are manufactured in accordance to ASTM D 4212, ASTM D1084 and ASTM D816

A positive displacement meter is a type of flow meter that requires fluid to mechanically displace components in the meter in order for flow measurement. Positive displacement (PD) flow meters measure the volumetric flow rate of a moving fluid or gas by dividing the media into fixed, metered volumes. A basic analogy would be holding a bucket below a tap, filling it to a set level, then quickly replacing it with another bucket and timing the rate at which the buckets are filled. With appropriate pressure and temperature compensation, the mass flow rate can be accurately determined.
Airwatt or air watt is a measurement unit of the effective power of vacuum cleaners. It is the airflow multiplied by suction pressure . It can also be referred to as a measurement of the energy per unit time of the air flowing through an opening, which is related to the energy that electricity carries through the power cable (wattage).
The concrete slump test measures the consistency of fresh concrete before it sets. It is performed to check the workability of freshly made concrete, and therefore the ease with which concrete flows. It can also be used as an indicator of an improperly mixed batch. The test is popular due to the simplicity of apparatus used and simple procedure. The slump test is used to ensure uniformity for different loads of concrete under field conditions.
Annular velocity is the speed of the drilling fluid's movement in a column called an annulus in oil wells. It is commonly measured in feet per minute (ft/min) or meters per minute (m/min). Annular velocity is often abbreviated as AV, though this is not exclusively so, as AV also refers to apparent viscosity which is calculated from rheometer readings from tests that the mud engineer performs.

The Ford viscosity cup is a simple gravity device that permits the timed flow of a known volume of liquid passing through an orifice located at the bottom. Under ideal conditions, this rate of flow would be proportional to the kinematic viscosity that is dependent upon the specific gravity of the draining liquid. However, the conditions in a simple flow cup are seldom ideal for making true measurements of viscosity. It is important when using a Ford Cup and when retesting liquids that the temperature of the cup and the liquid is maintained, as ambient temperature makes a significant difference to viscosity and thus flow rate.

The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Thus its SI units are newton-seconds per square meter, or pascal-seconds.
Flow conditioning ensures that the "real world" environment closely resembles the "laboratory" environment for proper performance of inferential flowmeters like orifice, turbine, coriolis, ultrasonic etc.

A spray is a dynamic collection of drops dispersed in a gas. The process of forming a spray is known as atomization. A spray nozzle is the device used to generate a spray. The two main uses of sprays are to distribute material over a cross-section and to generate liquid surface area. There are thousands of applications in which sprays allow material to be used most efficiently. The spray characteristics required must be understood in order to select the most appropriate technology, optimal device and size.

A graduated pipette is a pipette with its volume, in increments, marked along the tube. It is used to accurately measure and transfer a volume of liquid from one container to another. It is made from plastic or glass tubes and has a tapered tip. Along the body of the tube are graduation markings indicating volume from the tip to that point. A small pipette allows for more precise measurement of fluids; a larger pipette can be used to measure volumes when the accuracy of the measurement is less critical. Accordingly, pipettes vary in volume, with most measuring between 0 and 25.0 millilitres.













