
Amphetamine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD),narcolepsy,and obesity. Amphetamine was discovered as a chemical in 1887 by Lazăr Edeleanu,and then as a drug in the late 1920s. It exists as two enantiomers:levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. Amphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical,the racemic free base,which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers,or to either of them alone. Historically,it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer,and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a prescription drug in many countries,and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to the significant health risks associated with recreational use.
A psychiatric or psychotropic medication is a psychoactive drug taken to exert an effect on the chemical makeup of the brain and nervous system. Thus,these medications are used to treat mental illnesses. These medications are typically made of synthetic chemical compounds and are usually prescribed in psychiatric settings,potentially involuntarily during commitment. Since the mid-20th century,such medications have been leading treatments for a broad range of mental disorders and have decreased the need for long-term hospitalization,thereby lowering the cost of mental health care. The recidivism or rehospitalization of the mentally ill is at a high rate in many countries,and the reasons for the relapses are under research.

Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by executive dysfunction occasioning symptoms of inattention,hyperactivity,impulsivity and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive,impairing in multiple contexts,and otherwise age-inappropriate.

Stimulants are a class of drugs that increase the activity of the brain. They are used for various purposes,such as enhancing alertness,attention,motivation,cognition,mood,and physical performance. Some of the most common stimulants are caffeine,nicotine,amphetamines,cocaine,methylphenidate,modafinil.

Methylphenidate,sold under the brand names Ritalin and Concerta among others,is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used medically to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and,to a lesser extent,narcolepsy. It is a primary medication for ADHD;it may be taken by mouth or applied to the skin,and different formulations have varying durations of effect. For ADHD,the effectiveness of methylphenidate is comparable to atomoxetine but modestly lower than amphetamines,alleviating the executive functioning deficits of sustained attention,inhibition,working memory,reaction time and emotional self-regulation.

Bupropion,formerly called amfebutamone,and sold under the brand name Wellbutrin among others,is an atypical antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder and to support smoking cessation. It is also popular as an add-on medication in the cases of "incomplete response" to the first-line selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant. Bupropion has several features that distinguish it from other antidepressants:it does not usually cause sexual dysfunction,it is not associated with weight gain and sleepiness,and it is more effective than SSRIs at improving symptoms of hypersomnia and fatigue. Bupropion,particularly the immediate release formulation,carries a higher risk of seizure than many other antidepressants,hence caution is recommended in patients with a history of seizure disorder.
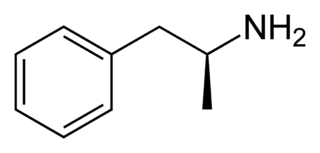
Dextroamphetamine (INN:dexamfetamine) is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and enantiomer of amphetamine that is prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used as an athletic performance and cognitive enhancer,and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. Dextroamphetamine is generally regarded as the prototypical stimulant.
Developmental disorders comprise a group of psychiatric conditions originating in childhood that involve serious impairment in different areas. There are several ways of using this term. The most narrow concept is used in the category "Specific Disorders of Psychological Development" in the ICD-10. These disorders comprise developmental language disorder,learning disorders,developmental coordination disorders,and autism spectrum disorders (ASD). In broader definitions,attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is included,and the term used is neurodevelopmental disorders. Yet others include antisocial behavior and schizophrenia that begins in childhood and continues through life. However,these two latter conditions are not as stable as the other developmental disorders,and there is not the same evidence of a shared genetic liability.
A paradoxical reaction is an effect of a chemical substance,such as a medical drug,that is opposite to what would usually be expected. An example of a paradoxical reaction is pain caused by a pain relief medication.

Atomoxetine,sold under the brand name Strattera,is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and,to a lesser extent,cognitive disengagement syndrome. It may be used alone or along with psychostimulants. It enhances the executive functions of self-motivation,sustained attention,inhibition,working memory,reaction time and emotional self-regulation. Use of atomoxetine is only recommended for those who are at least six years old. It is taken orally. The effectiveness of atomoxetine is comparable to the commonly prescribed stimulant medication methylphenidate.
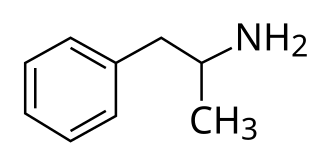
Adderall and Mydayis are trade names for a combination drug called mixed amphetamine salts containing four salts of amphetamine. The mixture is composed of equal parts racemic amphetamine and dextroamphetamine,which produces a (3:1) ratio between dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine,the two enantiomers of amphetamine. In terms of base,rather than salts,the ratio is 3.15:1 for dextro- to levoamphetamine. Both enantiomers are stimulants,but differ enough to give Adderall an effects profile distinct from those of racemic amphetamine or dextroamphetamine,which are marketed as Evekeo and Dexedrine/Zenzedi,respectively. MAS is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It is also used illicitly as an athletic performance enhancer,cognitive enhancer,appetite suppressant,and recreationally as a euphoriant. It is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the phenethylamine class.
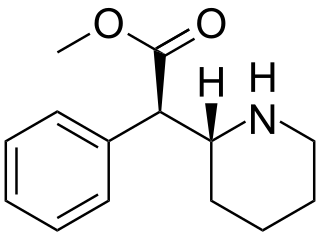
Dexmethylphenidate,sold under the brand name Focalin among others,is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in those over the age of five years. It is taken by mouth. The immediate release formulation lasts up to five hours while the extended release formulation lasts up to twelve hours. It is the more active enantiomer of methylphenidate.
Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder is the persistence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) into adulthood. It is a neurodevelopmental disorder,meaning impairing symptoms must have been present in childhood,except for when ADHD occurs after traumatic brain injury. Specifically,multiple symptoms must be present before the age of 12,according to DSM-5 diagnostic criteria. The cutoff age of 12 is a change from the previous requirement of symptom onset,which was before the age of 7 in the DSM-IV. This was done to add flexibility in the diagnosis of adults. ADHD was previously thought to be a childhood disorder that improved with age,but recent research has disproved this. Approximately two-thirds of childhood cases of ADHD continue into adulthood,with varying degrees of symptom severity that change over time and continue to affect individuals with symptoms ranging from minor inconveniences to impairments in daily functioning.
Child psychopathology refers to the scientific study of mental disorders in children and adolescents. Oppositional defiant disorder,attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder,and autism spectrum disorder are examples of psychopathology that are typically first diagnosed during childhood. Mental health providers who work with children and adolescents are informed by research in developmental psychology,clinical child psychology,and family systems. Lists of child and adult mental disorders can be found in the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems,10th Edition (ICD-10),published by the World Health Organization (WHO) and in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,Fifth Edition (DSM-5),published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). In addition,the Diagnostic Classification of Mental Health and Developmental Disorders of Infancy and Early Childhood is used in assessing mental health and developmental disorders in children up to age five.

The Standard for the Uniform Scheduling of Medicines and Poisons (SUSMP),also known as the Poisons Standard for short,is an Australian legislative instrument produced by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). Before 2010,it was known as the Standard for the Uniform Scheduling of Drugs and Poisons (SUSDP). The SUSMP classifies drugs and poisons into different Schedules signifying the degree of control recommended to be exercised over their availability to the public. As of 2024,the most recent version is the Therapeutic Goods Instrument 2024.
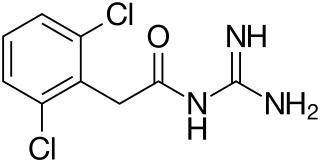
Guanfacine,sold under the brand name Tenex (immediate-release) and Intuniv (extended-release) among others,is an oral alpha-2a agonist medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and high blood pressure. Guanfacine is FDA-approved for monotherapy treatment of ADHD,as well as being used for augmentation of other treatments,such as stimulants. Guanfacine is also used off-label to treat tic disorders,anxiety disorders,and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).

Despite the scientifically well-established nature of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD),its diagnosis,and its treatment,each of these has been controversial since the 1970s. The controversies involve clinicians,teachers,policymakers,parents,and the media. Positions range from the view that ADHD is within the normal range of behavior to the hypothesis that ADHD is a genetic condition. Other areas of controversy include the use of stimulant medications in children,the method of diagnosis,and the possibility of overdiagnosis. In 2009,the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence,while acknowledging the controversy,stated that the current treatments and methods of diagnosis are based on the dominant view of the academic literature.

Lisdexamfetamine,sold under the brand names Vyvanse and Elvanse among others,is a stimulant medication that is used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adults and for moderate-to-severe binge eating disorder in adults. Lisdexamfetamine is taken by mouth. Its effects generally begin within two hours and last for up to 14 hours. In the United Kingdom,it is usually less preferred to methylphenidate for the treatment of children.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder management options are evidence-based practices with established treatment efficacy for ADHD. Approaches that have been evaluated in the management of ADHD symptoms include FDA-approved pharmacologic treatment and other pharmaceutical agents,psychological or behavioral approaches,combined pharmacological and behavioral approaches,cognitive training,neurofeedback,neurostimulation,physical exercise,nutrition and supplements,integrative medicine,parent support,and school interventions. Based on a systematic literature review and meta analysis conducted in 2024,only FDA-approved medications and psychosocial interventions have been shown to improve core ADHD symptoms compared to control groups.
Amphetamine type stimulants (ATS) are a group of synthetic drugs that are chemical derivatives of the parent compound alpha-methylphenethylamine,also known as amphetamine. Common ATS includes amphetamine,methamphetamine,ephedrine,pseudoephedrine,3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA),3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA) and 3,4-methylenedioxyethylamphetamine (MDEA). ATS when used illicitly has street names including ice,meth,crystal,crank,bennies,and speed. Within the group of amphetamine-type stimulants,there are also prescription drugs including mixed amphetamine salts,dextroamphetamine,and lisdexamfetamine.














