
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage. The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), nondestructive inspection (NDI), and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) are also commonly used to describe this technology. Because NDT does not permanently alter the article being inspected, it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation, troubleshooting, and research. The six most frequently used NDT methods are eddy-current, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant, radiographic, ultrasonic, and visual testing. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering, mechanical engineering, petroleum engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, systems engineering, aeronautical engineering, medicine, and art. Innovations in the field of nondestructive testing have had a profound impact on medical imaging, including on echocardiography, medical ultrasonography, and digital radiography.

Plastic welding is welding for semi-finished plastic materials, and is described in ISO 472 as a process of uniting softened surfaces of materials, generally with the aid of heat. Welding of thermoplastics is accomplished in three sequential stages, namely surface preparation, application of heat and pressure, and cooling. Numerous welding methods have been developed for the joining of semi-finished plastic materials. Based on the mechanism of heat generation at the welding interface, welding methods for thermoplastics can be classified as external and internal heating methods, as shown in Fig 1.
System testing is testing conducted on a complete integrated system to evaluate the system's compliance with its specified requirements.

Yoseph Bar-Cohen is a physicist at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory who specializes in electroactive materials and ultrasonic nondestructive evaluation (NDE), and is responsible for the Nondestructive Evaluation and Advance Actuators (NDEAA) lab at JPL. Bar-Cohen is a fellow of the International Society for Optical Engineering (SPIE) and the American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT).
Acoustic emission (AE) is the phenomenon of radiation of acoustic (elastic) waves in solids that occurs when a material undergoes irreversible changes in its internal structure, for example as a result of crack formation or plastic deformation due to aging, temperature gradients, or external mechanical forces.
Eddy-current testing is one of many electromagnetic testing methods used in nondestructive testing (NDT) making use of electromagnetic induction to detect and characterize surface and sub-surface flaws in conductive materials.
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a family of non-destructive testing techniques based on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. In most common UT applications, very short ultrasonic pulse-waves with center frequencies ranging from 0.1-15 MHz, and occasionally up to 50 MHz, are transmitted into materials to detect internal flaws or to characterize materials. A common example is ultrasonic thickness measurement, which tests the thickness of the test object, for example, to monitor pipework corrosion.

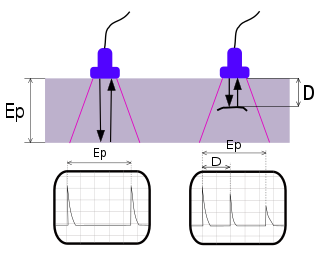
Phased array ultrasonics (PA) is an advanced method of ultrasonic testing that has applications in medical imaging and industrial nondestructive testing. Common applications are to noninvasively examine the heart or to find flaws in manufactured materials such as welds. Single-element probes, known technically as monolithic probes, emit a beam in a fixed direction. To test or interrogate a large volume of material, a conventional probe must be physically scanned to sweep the beam through the area of interest. In contrast, the beam from a phased array probe can be focused and swept electronically without moving the probe. The beam is controllable because a phased array probe is made up of multiple small elements, each of which can be pulsed individually at a computer-calculated timing. The term phased refers to the timing, and the term array refers to the multiple elements. Phased array ultrasonic testing is based on principles of wave physics, which also have applications in fields such as optics and electromagnetic antennae.

Time-of-flight diffraction (TOFD) method of ultrasonic testing is a sensitive and accurate method for the nondestructive testing of welds for defects. TOFD originated from tip diffraction techniques which were first published by Silk and Liddington in 1975 which paved the way for TOFD. Later works on this technique are given in a number of sources which include Harumi et al. (1989), Avioli et al. (1991), and Bray and Stanley (1997).
Electromagnetic testing (ET), as a form of nondestructive testing, is the process of inducing electric currents or magnetic fields or both inside a test object and observing the electromagnetic response. If the test is set up properly, a defect inside the test object creates a measurable response.

Electromagnetic acoustic transducer (EMAT) is a transducer for non-contact acoustic wave generation and reception in conducting materials. Its effect is based on electromagnetic mechanisms, which do not need direct coupling with the surface of the material. Due to this couplant-free feature, EMATs are particularly useful in harsh, i.e., hot, cold, clean, or dry environments. EMATs are suitable to generate all kinds of waves in metallic and/or magnetostrictive materials. Depending on the design and orientation of coils and magnets, shear horizontal (SH) bulk wave mode, surface wave, plate waves such as SH and Lamb waves, and all sorts of other bulk and guided-wave modes can be excited. After decades of research and development, EMAT has found its applications in many industries such as primary metal manufacturing and processing, automotive, railroad, pipeline, boiler and pressure vessel industries, in which they are typically used for nondestructive testing (NDT) of metallic structures.
Thermographic inspection refers to the nondestructive testing (NDT) of parts, materials or systems through the imaging of the temperature fields, gradients and/or patterns ("thermograms") at the object's surface. It is distinguished from medical thermography by the subjects being examined: thermographic inspection generally examines inanimate objects, while medical thermography generally examines living organisms. Generally, thermographic inspection is performed using an infrared sensor.
The American Society for Nondestructive Testing, Inc. or ASNT is a technical society for nondestructive testing (NDT) professionals. ASNT evolved from The American Industrial Radium and X-ray Society which was founded in 1941. Its headquarters is located in Columbus, Ohio, and there are 70 local sections in the United States and 14 local sections in other countries.
Terahertz nondestructive evaluation pertains to devices, and techniques of analysis occurring in the terahertz domain of electromagnetic radiation. These devices and techniques evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.

James Henry Williams Jr. is a mechanical engineer, consultant, civic commentator, and teacher of engineering. He is currently Professor of Applied Mechanics in the Mechanical Engineering Department at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). He is regarded as one of the world's leading experts in the mechanics, design, fabrication, and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) of nonmetallic fiber reinforced composite materials and structures. He is also Professor of Writing and Humanistic Studies at MIT.
Microwave imaging is a science which has been evolved from older detecting/locating techniques in order to evaluate hidden or embedded objects in a structure using electromagnetic (EM) waves in microwave regime. Engineering and application oriented microwave imaging for non-destructive testing is called microwave testing, see below.
Active thermography is an advanced nondestructive testing procedure, which uses a thermography measurement of a tested material thermal response after its external excitation. This principle can be used also for non-contact infrared non-destructive testing (IRNDT) of materials.

An ultrasonic pulse velocity (UPV) test is an in-situ, nondestructive test to check the quality of concrete and natural rocks. In this test, the strength and quality of concrete or rock is assessed by measuring the velocity of an ultrasonic pulse passing through a concrete structure or natural rock formation.
Nondestructive Evaluation 4.0(NDE 4.0) has been defined by Vrana et al. as "the concept of cyber-physical non-destructive evaluation arising from Industry 4.0 digital technologies, physical inspection methods, and business models. It seeks to enhance inspection performance, integrity engineering and decision making for safety, sustainability, and quality assurance, as well as provide timely and relevant data to improve design, production, and maintenance characteristics."

Laszlo Adler is an American physicist and a Taine McDougal Professor Emeritus in the Department of Integrated Systems Engineering at the Ohio State University. He is known for his work in Ultrasonics, Acousto-optics, and Nondestructive Evaluation of Materials. He is a holocaust survivor and has been active in scientific research for over 60 years.








